Potatoes are one of the most popular crops grown in Russia. Unfortunately, most of the territory is not in the most favorable climatic conditions. Low temperatures, short summers, high humidity very often provoke the development of various diseases.
Disease and its types
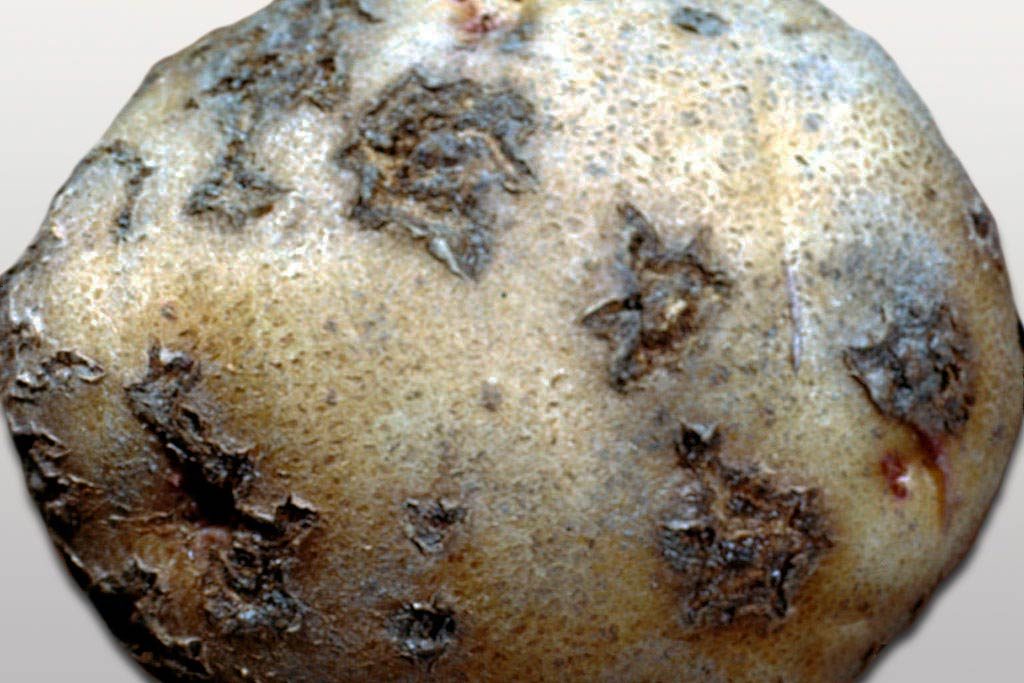
Potato scab is a disease caused by the proliferation of fungal spores. An infected crop is not dangerous to humans. Potato scab makes tubers visually unattractive and reduces nutritional value, in particular, the starch level is halved. In addition, the safety of the crop falls several times. Rotting tubers is very active, from which sometimes you have to dispose of almost all the potatoes.
The main prerequisites for the development of the disease:
- Disregard for the rules of crop rotation;
- Growing potatoes on one site for more than 3 years in a row;
- Excess nitrogen in the soil;
- Prolonged high temperatures, from which the soil is very hot;
- Uncontrolled application of organic fertilizers;
- Weak soil acidity;
- Planting initially contaminated planting material into the ground;
- Activation of the spores that were in the soil.
There are several types of this disease.
Black scab
Potato rhizoctonia is the most dangerous form that affects not only the fruits, but all other parts of the plant, including the ground ones. The causative agent of the infection is Rhizoctonia solani. Infection of sprouts leads to growth inhibition and complete atrophy. If the leaves and stems are affected by rhizoctonia, then it is useless to take treatment measures, the plant must be urgently eliminated.
Visually, the disease manifests itself in the form of black spots, similar to adhered earth. The optimal breeding environment for spores is high humidity and temperatures above + 18˚C, as well as cold and rainy springs. The soils on which this infection most often develops are loamy. If tubers infected with black scab are allowed to plant, the sprouts will hatch very weak and, most likely, die before flowering. You should not expect a harvest from such bushes.
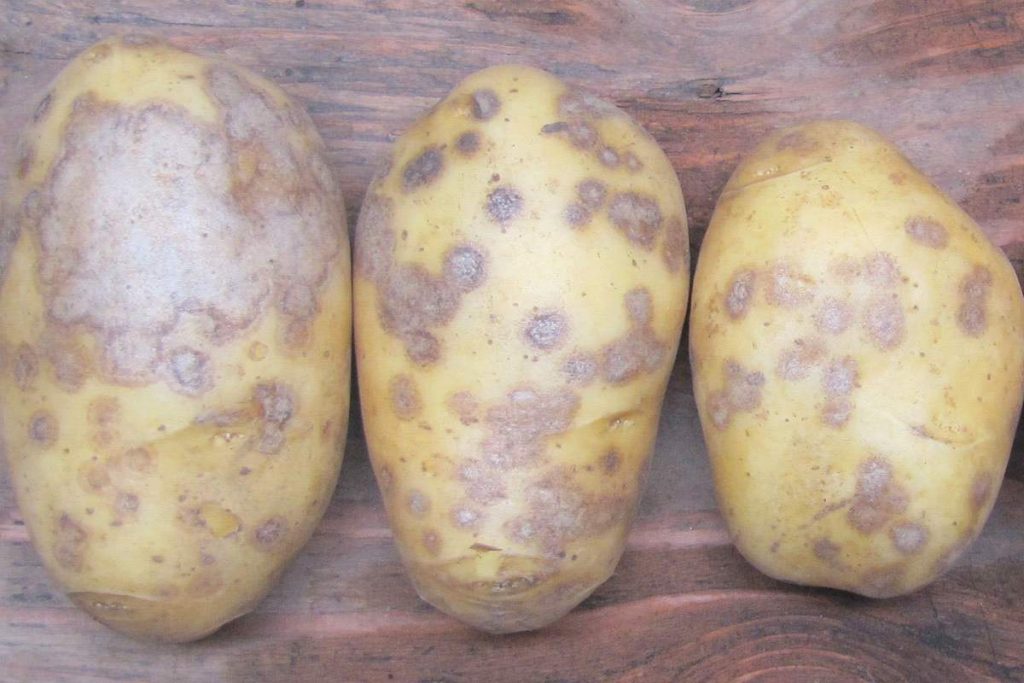
Silvery scab
The causative agent of this disease is the Helminthosporium solani mushroom. The spots can cover up to half of the tuber area. Visually, they are not very visible; dry gray areas can be observed at the site of the lesion. The spores of this fungus are very cold hardy and can tolerate temperatures up to +3 ˚C. During storage, the potatoes do not rot, but they dry out. Due to desiccation, more than a third of the total harvest is lost. Most often, the disease spreads on light soils, for example, loam or sandy loam with high humidity. The period of active distribution is the phase of flowering and tuberization.
Powdery scab
The causative agent - Spongospora subterranean, is very active, spreads quickly both in the soil and on the plant. This type of scab appears on potatoes after prolonged rains, when the soil becomes very heavy and damp. The tubers may be completely covered with reddish-brown warts. White growths appear on the stems. Favorable temperature for breeding is +12 ˚C. The fungus remains active in the soil for up to 5 years. When storing the crop, diseased tubers dry out, stick together with healthy ones and infect them.
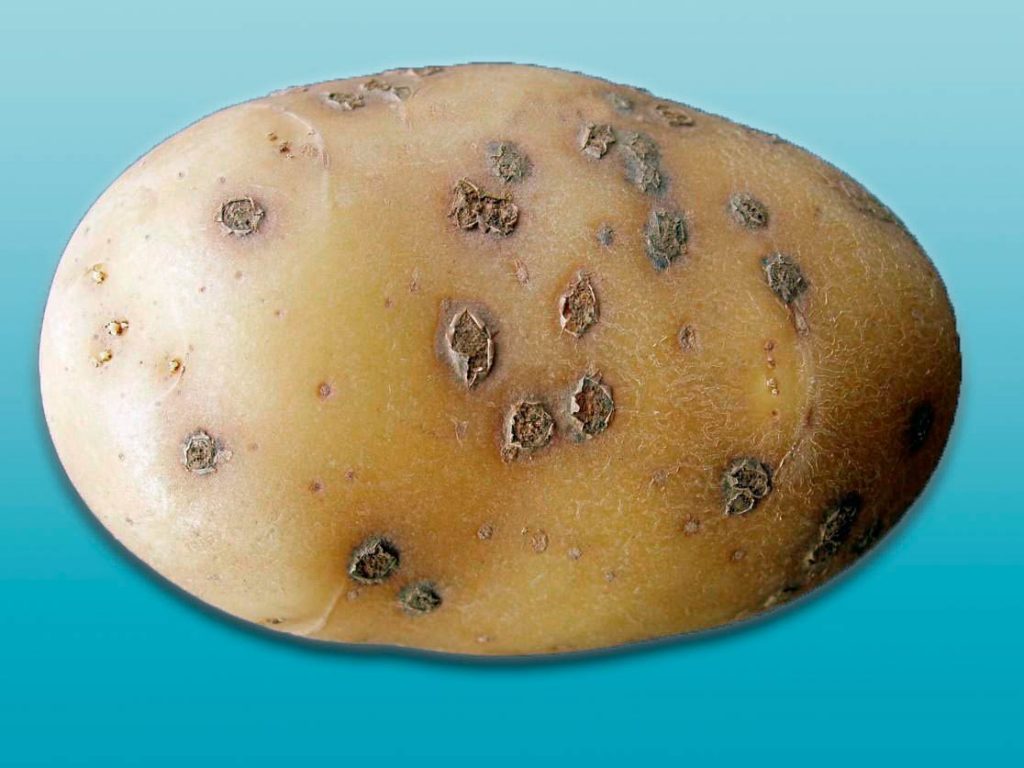
Common scab
The causative agent of the disease is the fungus Streptomyces scabies. Spores inhabit light, dry soils with an alkaline environment. They begin to actively spread in hot weather at temperatures above +25 ˚C.The most vulnerable varieties of potatoes with a thin skin. The fungus appears in the form of brown, rough spots, with strong overgrowth, the peel hardens and cracks, and the fruit begins to rot. Most often, this disease spreads to tubers, during storage it does not apply to a healthy crop, since spores hibernate from low temperatures.
Lumpy scab
The causative agent is the mushroom Oospora pustulans Owen. The spread of infection occurs through the eyes and mechanical damage (chips, cuts, cracks). In these places, brown or brown tubercles are formed. With active growth, the tubercles turn into large growths. This type of scab develops at a temperature of +11 ˚C on sod-podzolic and swampy soils.
Treatment
You should not be afraid of this disease, since it is quite possible to deal with scab on potatoes.
First of all, you need to take preventive measures that will help get rid of the pathogen. How to treat potatoes before planting from scab? Such modern fungicides as Maxim, Integral, Fenoram, Baktofit and others are highly effective. A detailed description of dosages is given in the instructions on the package.
In addition to chemical treatment, it is important to comply with agrotechnical requirements:
- Selection of healthy planting material without the slightest signs of infection;
- When buying potatoes for planting, preference should be given to varieties with high immunity, for example, Ostara, Mentor, Aspia, Lyubimets, Lady Rosetta, Krostotr and many others;
- It is recommended to plant potatoes after legumes, onions and grains. It is strictly forbidden to plant potatoes after any species of Solanaceae, since plants of the same family are carriers of infections for each other;
- Soil acidification. If it turns out that the soil has an alkaline environment, then you can prepare a solution of 2 tbsp. ammonium sulfate and 10 liters of water and water the bushes with it (half a liter each).
- Site change every 4-5 years;
- Drawing up and strict adherence to the feeding plan;
- Timely planting, don't plant potatoes too early;
- 7-10 days before harvesting, the tops are mowed and disposed of;
- Potatoes must be harvested on time in warm, dry weather.
You can increase scab resistance using folk methods:
- At the time of planting, the planting holes need to be treated with 1 liter of poultry manure solution (proportion 1:15).
- When sprouts more than 10 cm long appear, the area is again watered with a solution of droppings or mullein, reducing the dosage by 2 times.
- In the phase of bush formation, it is useful to water the area with nettle infusion. The solution is prepared at the rate of 1:10 and insisted for 7 days. Pour 1 liter of infusion on each bush.
- At the time of bud formation, the bushes can be treated with an ash solution (3 tablespoons per 10 liters of water).
- When active flowering begins, you can repeat the watering with mullein solution again.
An effective measure of scab control is the cultivation of green manure in the aisles. Suitable for sowing are vetch, mustard, lupine, radish and peas. When the culture grows to 20 cm, it is mown. Also, after harvesting potatoes, you can sow winter crops on the site: rye and oats. These crops heal the soil and kill infections, thereby protecting against the proliferation of spores.
You can get rid of scab directly by applying a complex of fertilizers. When the tubers germinate and the stems grow, a plot of 100 m2 can be treated with copper sulfate (40 g), manganese (20 g) and boric acid (25 g).
You can suppress a fungal infection with the help of drugs:
- Circus. Just one treatment during the budding period allows for a healthier and richer harvest.The application rates are indicated in the instructions on the package.
- Fito plus. One package of the product is enough for 3 liters of water. The prepared solution can be used for pre-sowing treatment and spraying during the growing season. The drug significantly reduces the incidence of scab.
- The popular chemical Maxim can be used not only for spraying tubers before planting, but also for irrigating bushes. The solution is prepared from the ratio of 20 ml of the drug to 1 liter of water. It can also be used for etching prior to storage. On 100 kg of potatoes, you need to spray 1.5 liters of the finished solution.
Getting rid of scab is a rather complicated process, since spores remain active for several years. To avoid the development of the disease, it is necessary to take preventive measures, treat already affected plants and carefully observe the cultivation techniques.