Content:
African swine fever is increasingly affecting livestock in Russia. Cattle farms in the Leningrad, Nizhny Novgorod, Saratov, Tver, Omsk regions, Sosnovsky district and other large settlements are concerned about how to preserve their livestock population. Every farmer should know the symptoms of swine ASF and how it is transmitted. Many are concerned about the question of whether this infection is transmitted and what danger it poses to people. And also, is it allowed to eat the meat of infected pigs.
African swine fever - what is this disease
Swine ASF is a viral disease that is quite resistant to treatment. Experts believe that the infectious agent remains viable for 18 months. Individuals of all ages can get sick. Scientists distinguish several subspecies of infection: A, B and C. This disease was first discovered on the African continent, hence its name. In the wild, the virus is carried by a wild African pig and insects of the genus ornithodoros.
How African swine fever is transmitted
Livestock can become infected with African plague after contact with infected individuals. Also, the causative agent of the disease can be found in feed, water, inventory, transport for transporting pigs. Damage to the mucous membranes and skin, blood and insect bites help the virus penetrate.
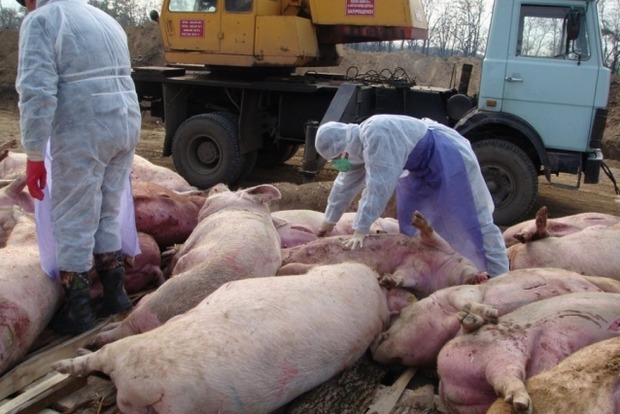
Sick animals often die. Individuals that were able to survive become carriers of the infection. Once it enters the bloodstream, the virus multiplies rapidly. After the first symptoms appear, the disease affects more than 37% of the herd.
Is African swine fever dangerous to humans?
Scientists are sure that ASF is not dangerous for humans - the human body is not susceptible to the pathogen. No harm will be done to health even when a person eats the meat of an infected animal. To date, not a single case of transmission of this disease to people has been recorded.
Despite the fact that ASF, according to scientific data, is not dangerous to humans, experts believe that there are still some risks.
Reasons why you should stop eating such meat:
- Infection can weaken a person's immune system.
- The disease develops unexpectedly. The virus belongs to the class of asfaviruses, it has the ability to mutate. There is a high probability of its modification and the appearance of new variations.
- ASF can exacerbate the development of serious diseases.
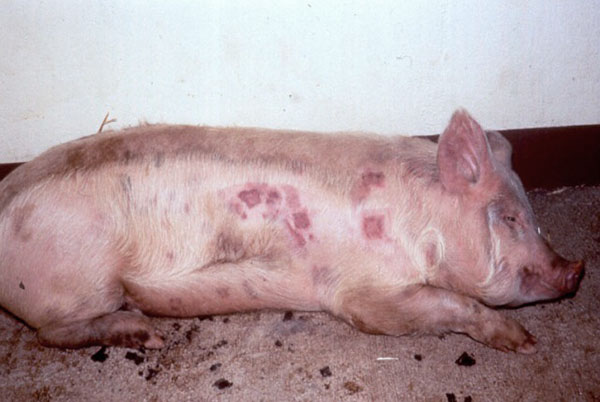
Symptoms of African swine fever
The incubation period lasts from 2 to 14 days. The duration of the period is influenced by: how much virus has entered the body, the individuality of immunity and the form of the course of the disease.Timely diagnosis in the initial period plays an important role in treatment. The disease has several degrees, differing in the first manifestations:
- fever (temperature above 40 ° C);
- loss of appetite;
- apathy;
- difficulty breathing, cough;
- the appearance of discharge from the eyes and nose;
- impaired motility, instability;
- hind limb paralysis;
- pneumonia;
- the appearance of bruising, subcutaneous edema on the face and trunk;
- hair loss;
- failure of the gastrointestinal tract;
- vomiting.
Description of the forms of the disease
There are two forms of ASF: chronic and atypical
- Chronic form can last up to 60 days. Individuals suffer from diarrhea, fever, loss of appetite, cough and shortness of breath. The pigs lose weight, their skin wrinkles and bruises appear on the inner thighs, abdomen and muzzle.
- Atypical form most often affects piglets in which maternal immunity has already been formed. With this form, animals can recover, but there is a high likelihood of complications. According to the latest data, the mortality rate is 30-60%.
ASF diagnostics
It is impossible to diagnose African plague at home. For detection, laboratory tests are required. Diagnosis is also accompanied by the collection of samples, specimens and pathological, epizootic data. The best diagnostic methods are the method of fluorescent antibodies and the hemadsorption reaction.
African swine fever treatment
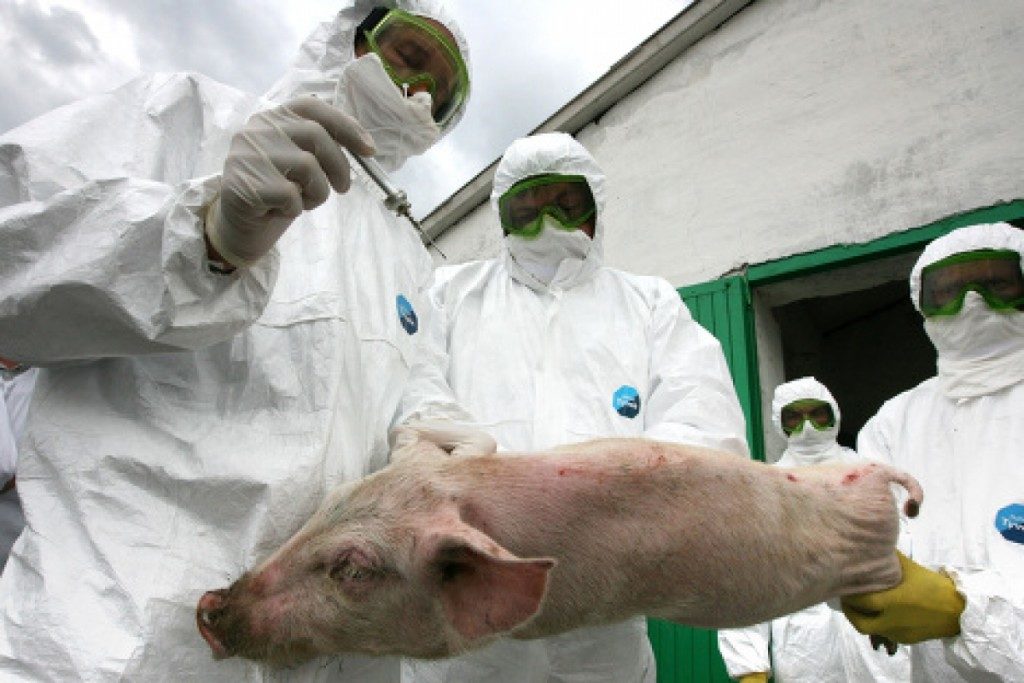
To date, a cure for the causative agent of the disease has not yet been created. You can get rid of ASF by exterminating the entire herd that is in the quarantine zone. Animals are recommended to be destroyed in a bloodless way, and the carcasses to burn. It is also worth paying special attention to the place where the herd is kept: all equipment and flooring are burned.
Prevention
The following preventive measures will help:
- buy feed from certified sellers, where there is no likelihood of contamination of products with infections;
- thermally process animal feed before serving;
- regularly treat the farm and equipment with disinfectants;
- minimize contact between pigs and birds;
- purchase animals that have received documents and have been examined by a veterinarian;
- vaccinate sows.
ASF is a viral disease transmitted through objects in contact with a sick individual. Although there is no cure for it, livestock can be protected by vaccination, disinfection, and limiting contact between pets. The virus is not yet dangerous for humans, however, the possibility of its mutation is not excluded.