Content:
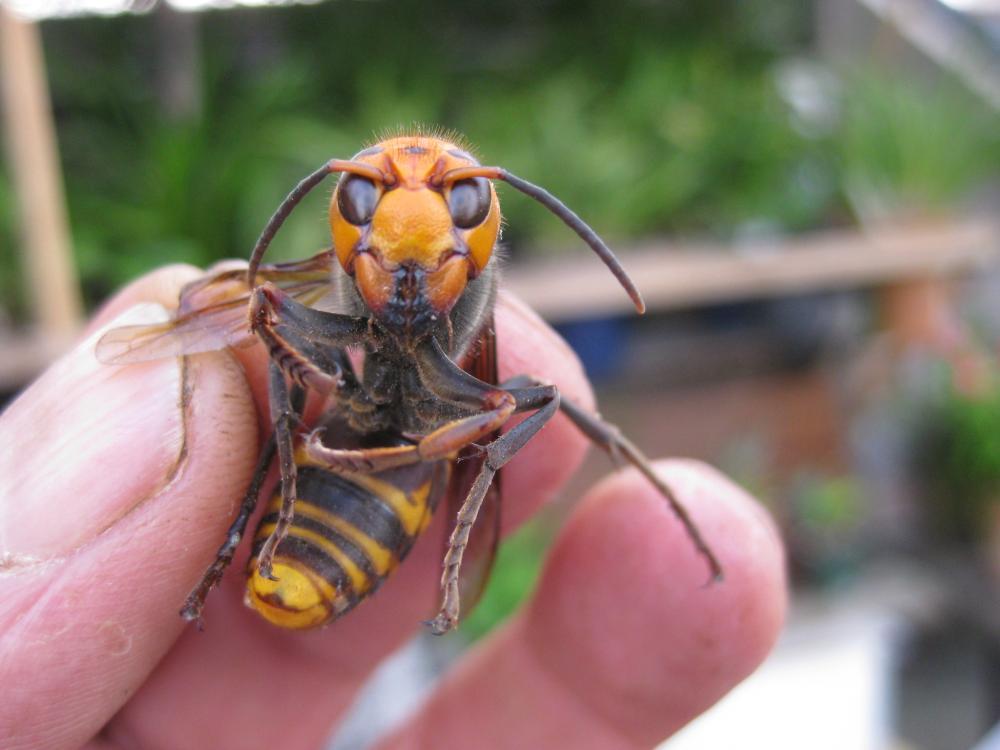
Hornets occupy a special place among the stinging Hymenoptera. This type of wasp has a characteristic yellow-black color, but differs from its counterparts in its larger size. Like other wasps, the hornet defends itself with a sting, inflicting numerous painful wounds on its opponent.
What to do with a hornet bite
In the summer, people are often stung by hornets, wasps and other insects. Most often, this occurs at a time when Hymenoptera, attracted by sweet fruity aromas, fly too close to a table covered with sweets or a person fragrant with perfume. Sharp movements, waving hands and other attempts of people to get rid of the intruder are perceived by the hornet as a threat of attack and cause a desire to bite the "attacking" people. Defending himself, he uses the weapon he has - a sting.
The poison in the hornet makes the stung place painful and causes serious harm to human health. Once in the blood, it causes intoxication, accompanied by unpleasant symptoms:
- high blood pressure;
- rapid heart rate;
- nausea and vomiting reflexes;
- an increase in body temperature;
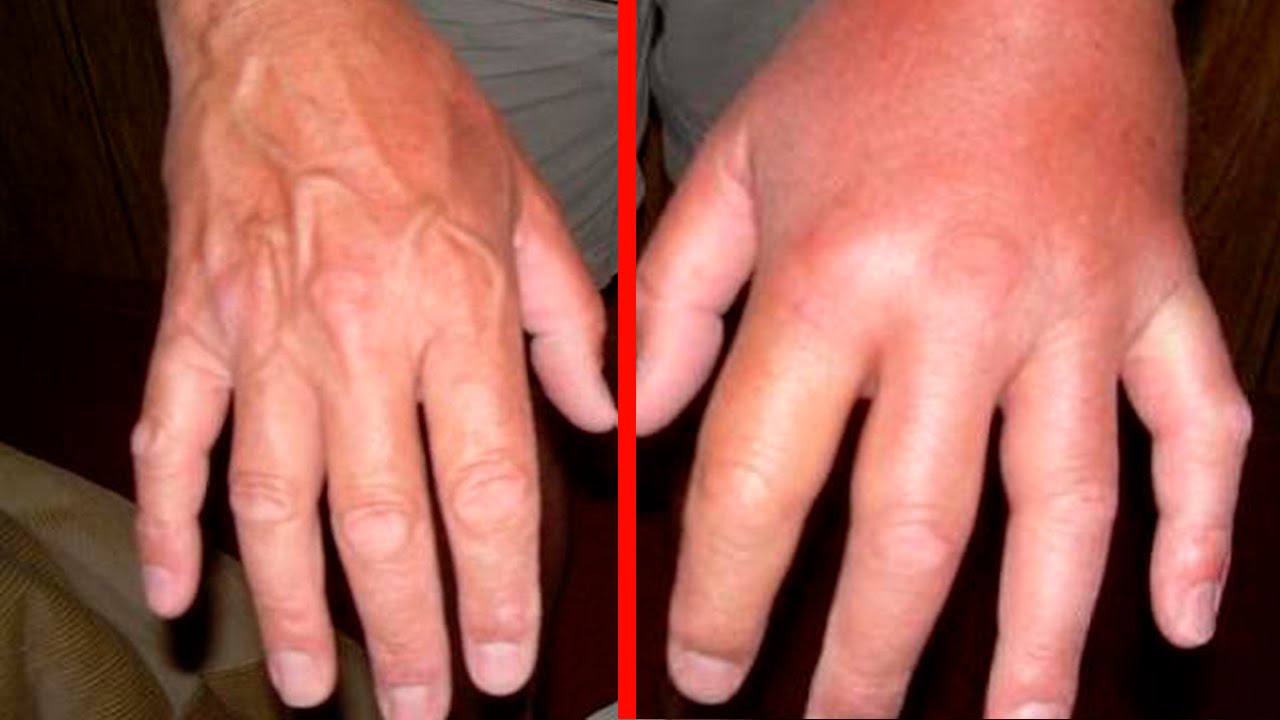
- skin irritation and redness in the damaged areas.
In addition, the release of histamine into the bloodstream contributes to the occurrence of allergic reactions that can lead to anaphylactic shock.
A particular danger is a meeting of a person with a swarm of hornets.
The wasp hive is always guarded by insects flying around it, ready to raise the alarm if necessary. The approach of a person or pet can provoke an attack by a whole swarm of wasps. Do not touch the nest with your hands, poke it with sticks or other objects.
Having decided on the elimination of a hive found near a person's dwelling, you need to have reliable means of protection and special devices to implement your plan.
Hornet bite: first aid
To avoid unpleasant consequences, after the sting, the victim needs to be helped quickly and competently.
- You need to start helping by examining the affected area of the skin to make sure that the wasp sting is not left in the wound. Pull it out with tweezers if necessary.
- To avoid infection from a hornet feeding on carrion, it is recommended to treat the sting site with a solution of hydrogen peroxide or chlorhexidine.
- To slow down the process of getting the toxins contained in the hornet venom, cold can be imposed on the affected area. In this case, ice and food stored in the freezer will do. If necessary, cold compresses soaked in ice water are also suitable.
- Drinking plenty of fluids will help remove toxic substances from the patient's body naturally.
What to do if a hornet has bitten in a limb
When stinging in the arm or leg, in addition to the measures listed above, you should try to apply a fixing bandage or tourniquet to the area above the bite site. It will also help slow the entry of toxic substances into the body.
Pain, redness and swelling with a normal reaction of a healthy body pass quickly enough. The recovery process can take from 10-15 minutes. up to 4-6 hours. To speed up, you can use numerous pharmacy ointments that help stop itching and burning.
What to do if a hornet stung in the head
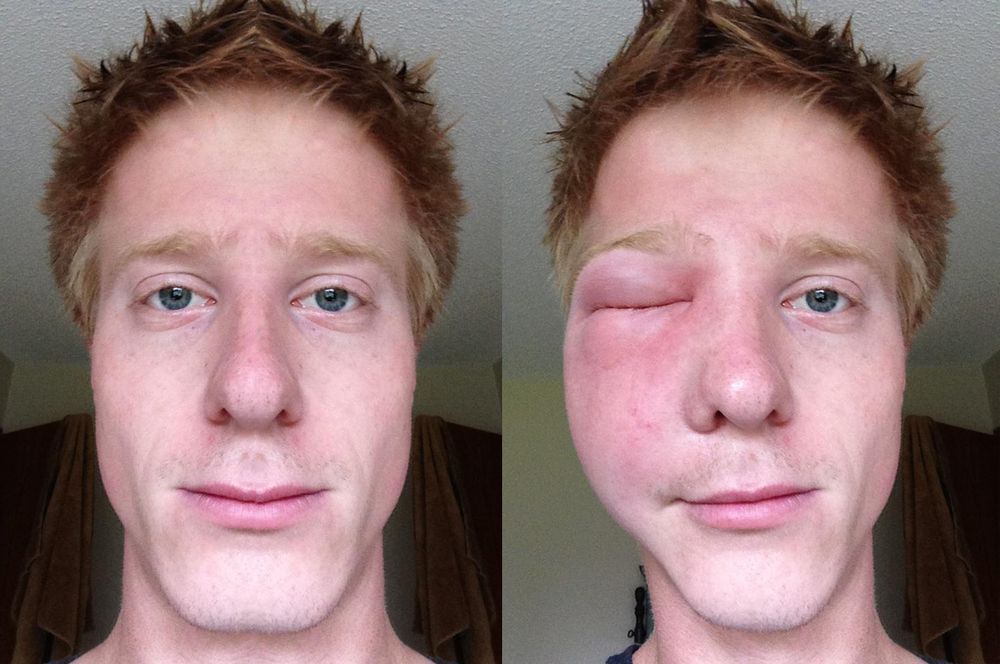
The head, face, neck are the most dangerous places when stinging a hornet, since:
- Toxins and infections in the eye can cause increased discomfort and inflammation.
- The proximity of the vessels of the brain when poison enters them can increase the speed and strength of toxic poisoning. This can cause dizziness and loss of consciousness.
- Lesions of the tongue and larynx make it impossible to eat well. If swelling occurs, the swelling can disrupt the natural breathing rhythm.
They cause anxiety and stings in the armpits and popliteal cavities, which contain large veins. Getting directly into a blood vessel, the poison very quickly begins to affect the well-being of the person attacked by the hornet. The unpleasant sensations that continue to grow should become an alarming sign for the victim. This applies to both local and general reactions of the body.
In case of deterioration in general well-being, increased redness of the skin, persistent pain symptoms and an excess of body temperature, you should contact the nearest medical institution for advice and treatment.
If, with a bite of a finger, the edema that has begun rises above the hand and continues to increase and spread further, this indicates the occurrence of an allergy, which is not a joke.
Bitten by a hornet: what to do with allergies
After disinfecting the lesion and placing it with cold, you should take an antihistamine. This must be done in order to avoid the occurrence of allergies, the predisposition to which the person affected by the hornet bite may simply not know about.
For allergy sufferers who are seen by a specialist and who are aware of the peculiarities of their disease, it is important to have a set of anti-shock medicines with them, allowing them to provide the victim with quick and timely assistance.
In addition to preparations in the form of tablets, there are solutions for injections. Such injections are placed, if necessary, directly through the clothing into a part of the body accessible for the procedure.
General rules of behavior after being stung
In many cases, the discomfort after being hit by a hornet disappears within a fairly short time, without causing consequences and complications. Despite this, one should not forget that this insect is poisonous, its bite imposes an additional burden on the human body. Therefore, it is important 1-2 days after the sting:
- observe a regime that is sparing for the body;
- avoid strenuous physical activity;
- avoid direct sunlight;
- try to drink plenty of fluids.
This will help the body recover from the resulting intoxication and protect against the manifestation of a delayed allergic reaction.
Few people enjoy meeting and getting to know the hornet closely. In preparation for the beginning of the new summer season, it is useful to purchase repellents that can protect against stinging Hymenoptera insects. It makes sense to go through your home medicine cabinet and make sure you have antihistamines that are up to date. You should also learn the rules above on how to provide first aid after being stung by a hornet. Perhaps this will help save someone's life.