Content:
The wasps are related to the common well-known black-and-yellow stinging insects by belonging to the suborder of stalk-bellied wasps. In nature, these insects are very common, are parasites and occupy a prominent place in the biocenosis of their native habitats.
Long-tailed wasp wasps lifestyle and habitat
The predominant habitat of most of the 100 thousand species of wasp wasps, which are present today, is the tropics. In temperate latitudes (on the territory of Russia), you can find only a few varieties. Common to all of them is the laying of eggs or larvae on or directly into the body of caterpillars and other insects. Not everyone can sting.
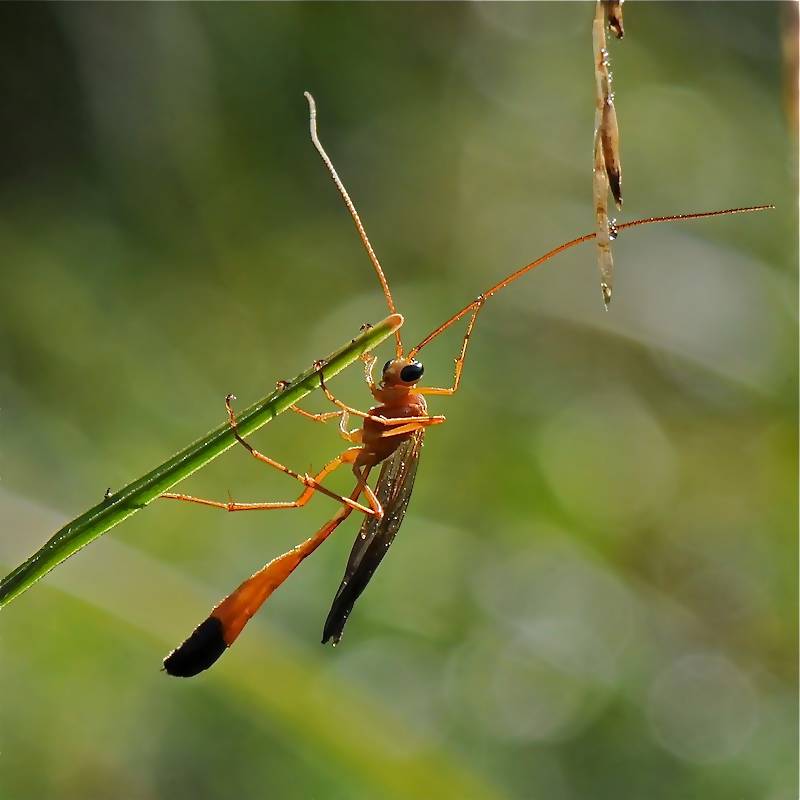
Wasp riders do not look too threatening, especially those that are found in Russia. Their size is from 3 mm to 3 cm in length, and the chance of meeting the largest representatives is extremely low due to their extreme rarity. All species have different colors: from translucent to deep black.
The riders have no sting. Instead, there is a long ovipositor. However, the insect is quite capable of causing harm, since a special poisonous secret is released from the ovipositor. Puncturing the opponent's skin with a sharp end, the wasp injects poison, which has a paralyzing effect, although it does not pose a danger to the insect's life. All riders are parasites, which are divided into 3 groups:
- ectoparasites, which attach eggs and larvae to the surface of the body of other arthropods;
- endoparasites that introduce eggs into the body of other insects, while using paralyzing poison;
- superparasites that can infect their own kind.
What wasp riders are found in Russia
Compared to the tropics, the Russian climate is poorly suited for most riders. And yet, in Russian latitudes, they are also found, although less often. The most common types:
- Mimarommatids. A tenacious detachment, representatives of which live even in the subantarctic. They lay their eggs on those of other arthropods.
- Mutillids (German wasps) are distinguished by their attractive appearance and bright color. More than 4 thousand species of mutilid are found in nature, and all males are larger than females. The size does not exceed 3 cm, and the body is covered with hard hairs. They lay eggs on wasps, bees and flies.
- Nutcrackers. Like relatives, they lay offspring on insects. Adults feed on plant sap.
- Proctotrupoid riders. An adult has a microscopic body length of maximum 5 mm. In agriculture, they have found application as a means of biological protection against pests.
- Chalcids. One of the most numerous orders, which includes up to 200 species. Its representatives are highly valued in agriculture, as they destroy those insects that are a threat to pollinators.
- Evanioid wasps. They differ in a special body structure. Their abdomen is raised from the chest. They leave offspring on other types of wasps, cockroaches and sawflies, for which they gained fame as defenders of the forest.
- Typhia. About 20 species are found in Europe, and another 30 in Russia and on the territory of the CIS countries.The body length of an adult does not exceed 1 cm. Usually they have a black body color and brown wings. They prefer to lay their eggs on beetles: dung beetles, May beetles and others. A rare case of symbiosis, since the victim does not die immediately, but continues to coexist with the wasp larva.
In Europe, crabronids (sand wasps) are widespread, there are over 600 species in total, but in total there are about 8 thousand varieties of them that are found throughout the planet. Usually they make holes in the sand, where larvae are raised in the nests. Food (bees, other wasps, other hymenoptera) is delivered to them by adults, paralyzing the victims with their poison.
The rest of the very numerous families of wasp wasps prefer the hot and humid climate of the tropics and subtropics. In the relict forests of the Amazon, you can find unique insects up to 8 cm long. It is noteworthy that scientists still continue to find new species, while a considerable number of unique insects are so rare that they can be classified as endangered.
The life cycle of wasp wasps
You can meet the wasp of the parasite anywhere in the world, except perhaps Antarctica and the islands of the Arctic Ocean covered with eternal ice. They prefer to settle near natural reservoirs, where high air humidity is constantly maintained. Thickets of flowering plants for them are ideal conditions for life and reproduction.
All wasp larvae feed on insects. They eat the tissues of beetles, caterpillars, flies, bees, spiders and even other wasps. Although an adult does not always lead a predatory lifestyle. Some wasps successfully feed on plant juices, flower nectar. There are even those who do not need food at all, since, after laying eggs, they die almost immediately. A special family of braconids lays their eggs on butterflies, while they themselves eat grain crops, parasitize in apiaries, eating honey, not disdaining fruit juices and flower nectar.
The optimal time of the year for the breeding of parasitic wasps is summer, especially in wet and warm weather. Under such conditions, the population can grow several times in a short time. After mating, the female is almost immediately ready to lay eggs in the body of an insect that serves as food for future larvae. How many eggs will be in each clutch directly depends on the characteristics of the given species. On average, 1 female lays up to 20 eggs in the victim's body. By the time the wasp larvae pupate, the host insect dies. For this reason, young wasps eat very moderately so that their prey does not die prematurely.
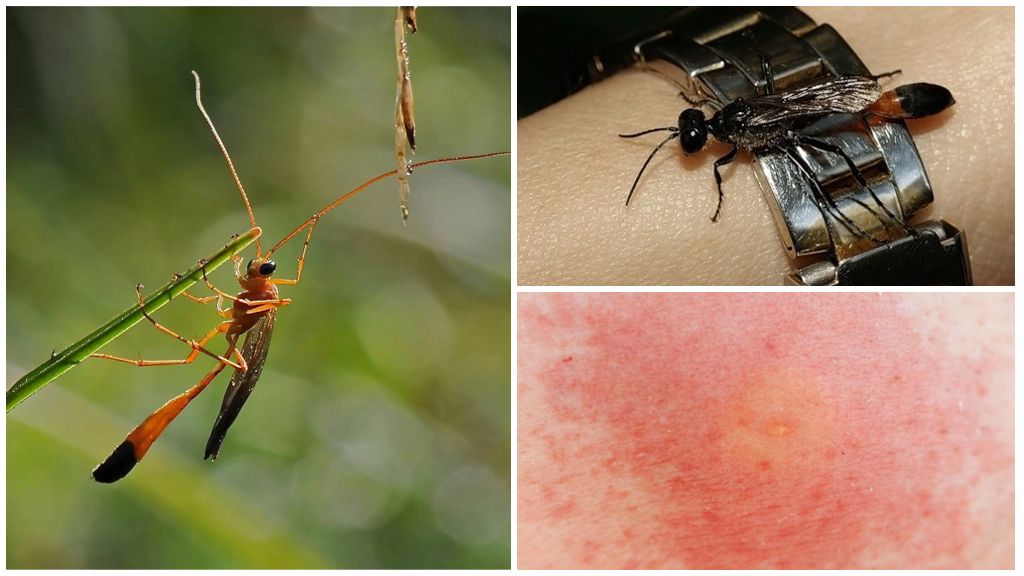
Is the wasp wasp dangerous to humans?
In many ways, fear of insects is an irrational fear. This is especially true for wasp wasps. An adult insect produces poison in order to paralyze the victim, in which eggs will be laid. With a threat to its life, an insect can also injure a person (not all species, because most are very small in size). But in Russia, there are no riders who lay eggs under human skin. A person experiences the bite of a wasp horsewoman without consequences for himself.
During the bite, the insect pierces the skin and injects a small dose of poison. Compared to the common striped wasp, it will be several times less painful. It can be compared to the attack of an ordinary ant.There will be a small redness at the puncture site, a small swelling, itching sensation is possible, but after an hour the trace disappears completely.
The main preventive measure against wasp stings by wasps is careful human behavior in nature. If striped hymenoptera are found near the reservoir, then you should not pick them up or catch them. Better to just step aside. On walks near natural bodies of water, in damp meadows and in the forest, it is worth wearing closed clothes that are tight to the body, under which it is difficult for insects to climb.
What to do when a wasp was bitten by a rider
If, with all the precautions, a wasp rider bit a person, then you should proceed as follows:
- Wipe the bite site with an antiseptic.
- If necessary, take an anti-inflammatory and pain reliever. Allergy sufferers need antihistamine medication.
- In a severe case, when there are signs of deterioration, the victim is taken to the hospital.
However, dangerous consequences are threatened by a meeting with individuals whose size is much larger than 3 cm, which is practically impossible on the territory of Russia, according to official data.
If the trace of a wasp bite does not go away for more than 5 days, you should consult a doctor. Probably, a certain infection has joined this, which is not excluded when meeting a wasp in nature. But even such a reaction is not typical, since the predominant size of insects found in Russia is much less than 3 cm, respectively, the bite mark is tiny. Therefore, there is no point in being afraid of these Hymenoptera.