Content:
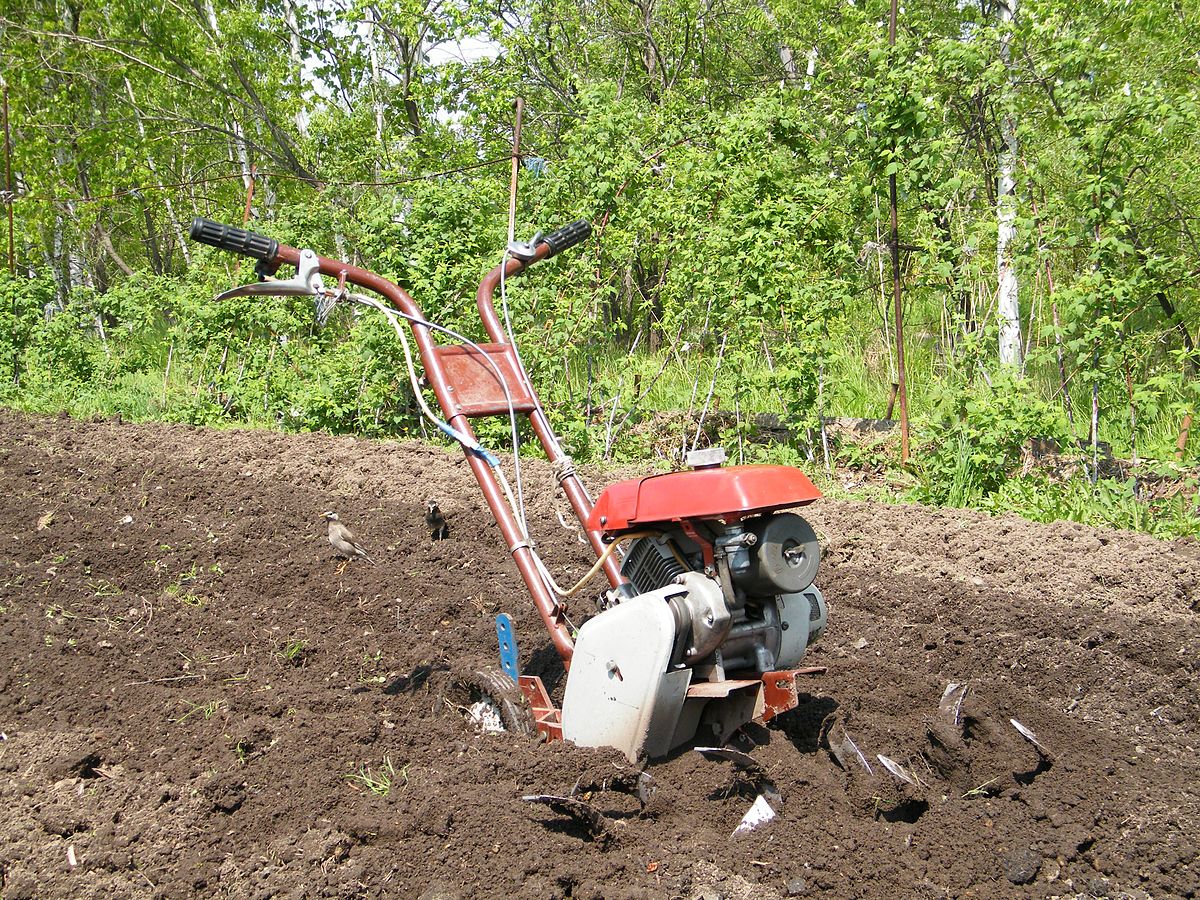
Motor-cultivator Krot is a legendary walk-behind tractor produced by JSC “MMP im. V.V. Chernyshev ”since 1978 and managed to become a truly national brand. During this time, the unit has undergone several upgrades and turned into a reliable technique that performs a wide range of works. To date, the model range of Moles consists of 6 most common units, which allow the summer resident and gardener to choose the model that best suits their needs and financial capabilities.
Applications
Modern models of a motor-cultivator are used for such works as:
- Loosening the soil;
- Milling the soil to the depth of the arable horizon without turning the layer;
- Hilling of row crops (potatoes, corn);
- Weeding of row spacings;
- Harrowing;
- Planting and harvesting potatoes;
- Leveling (alignment);
- Mowing grass on lawns, decorative lawns, pastures and hayfields;
- Pumping water from open sources (lakes, ponds, planters) using a mobile hinged pumping station;
- Transportation of goods.
Also, such a cultivator can be used when marking rows for planting commercial and uterine berry plantations (currants, gooseberries, raspberries).
Description of construction
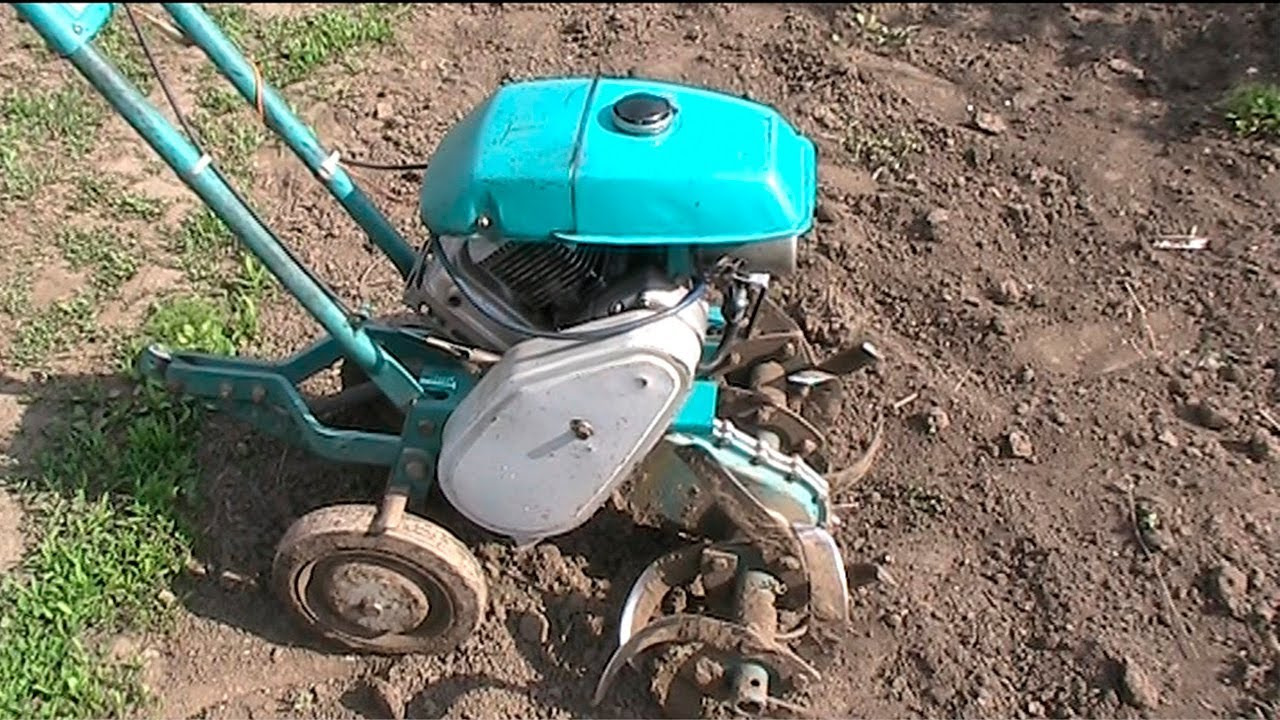
The standard cultivator Krot of the most common model MK-1A consists of the following elements:
- Frame - a supporting structure that takes the weight of the engine with a gearbox;
- The gasoline engine is a single-cylinder power unit that ensures rotation of active working bodies (cutters, weeding machines) through a gearbox, movement of the cultivator when using a hiller and other passive tillage tools;
- Fuel tank - a container located above the engine and designed to store the fuel mixture;
- Reducer - a mechanism connected to the engine crankshaft and converting the forward movement of its piston into rotation of the shaft with cutters, lugs.
- Rear support (transport) wheels - designed for transporting the unit from the garage or car to the place of work, milling and loosening the soil with the help of active working bodies (front soil milling cutters);
- Opener - a ripper located on the frame between the support wheels, with the help of which the depth of soil cultivation is set by the working bodies installed in the front part (cutters, weeder);
- Steering column - two-horned handle with rubberized grips and clutch control levers, carburetor throttle, gear selector (forward / reverse);
- Protective guards - are installed in front of the cutters and serve to protect the employee from dirt, stones, debris flying out from under the working bodies.
How to work with Mole
Working with a motor cultivator consists in such operations as:
- Fastening the steering column to the frame - this operation is performed if the unit was transported in the trunk of a car;
- Preparation of an oil-gasoline mixture in a ratio of 1:40 (oil of the MG-8A brand) or 1:20 (brand M-12P, AZMOL Start2T);
- Moving the walk-behind tractor on the rear support wheels to the place of work with the engine not turned on;
- Installation of working bodies;
- Working depth adjustment;
- Opening the supply valve on the fuel line from the gas tank to the carburetor;
- Pressing 2-3 times the suction on the carburetor;
- Setting the throttle control lever at 30-400 relative to the initial closed position;
- Starting the engine - jerking the starter rope and holding the clutch lever depressed will start the engine. After starting the throttle lever, the required engine speed is set.
Specifications
The model range of the Mole cultivator has the following characteristics:
- Engine type - two, - less often four-stroke, carburetor;
- Number of cylinders - 1;
- Fuel used - gasoline A-80;
- The capacity of the fuel tank is 1.8 liters.
- Power - 2.6-5.5 hp;
- Engine cooling type - air;
- Reducer drive - chain;
- Number of gears - 2 (forward / reverse); in the MK-1A model - 1 (front);
- The presence of reverse gear (reverse) is available in all models, except for the very first MK-1A;
- Capture width - from 35 to 90 cm;
- The depth of tillage with the unit is 25 cm;
- Dimensions:
- Width - 81 cm;
- Length - 130 cm;
- Height - 106 cm.
- Weight - 48-55 kg;
- Productivity - 1.5-2 ares / hour;
- Cost - 18,000-20,000 rubles.
Attachments for the Mole
To perform various types of work, the following attachments are installed on the cultivator:
- Composite soil milling cutter, consisting of 4-8 individual working elements and extensions;
- Mounted mower;
- Hinged single-body hiller;
- Fan potato digger (ripper with a lancet paw and a fan of wire feathers located on it);
- Transporter potato digger;
- Pololnik (pololnik);
- Single-axle bogie with lifting capacity up to 0.2 t (up to 200 kg);
- Pumping station for pumping water;
- Wheels with grousers (a feature of such wheels is that they consist of metal rims, with plates located along the contour for better contact with the soil);
- Wheels for plant protection during hilling and weeding of row spacings.
However, only the soil tiller is included in the scope of delivery of the machine. All other equipment is purchased separately.
Therefore, when purchasing, you should study the manual and the delivery set of the unit and make sure that everything specified in it comes with the cultivator.
Technical features at different jobs
Each of the types of work performed by the motor-cultivator has its own technical features in the preparation and mounting of the corresponding attachments, the execution technology:
- Milling, loosening, weeding - in this type of work, the milling cutter is installed on the gearbox shaft, using the opener, the loosening depth is set.After starting the engine, the unit deepens and begins to move along the treated area with smooth forward jerks.
- Planting potatoes, hilling - the cutter is removed from the gearbox shaft, and metal wheels with lugs are installed. The rear support wheels are removed and a single-body hiller is installed on the cultivator. When planting, a furrow is cut, the potato achenes are manually placed in it, after which the row planted in this way is poured with the help of the same hiller. When hilling, instead of wheels with lugs, protective wheels are installed on the gearbox shaft. The formation of the ridge occurs when the hiller moves between two rows of the crop.
- Harvesting potatoes - remove the cutter and support wheels from the cultivator, install metal wheels with lugs and a fan potato digger. Dig up potatoes, using such attachments, directing it exactly in the center of the row. At the same time, the body of the potato digger lifts the tubers, which, falling on the fan from the twigs, are freed from the ground and, falling from them, remain lying on the soil.
- Grass mowing - for mowing, the front milling cutter is removed, and rubberized iron wheels are installed in its place. The segment mower is connected to the front of the tiller frame; it is driven by a belt installed on the pulleys of the unit and the motor of the cultivator.
- Pumping water - the pumping station is installed in front of the cultivator. The pump drive, like the mowers, is carried out using a V-belt drive. To pump out water, an intake hose with a filter and an injection hose are put on the corresponding branch pipes of the pumping station (they are lowered into the container).
- Transportation of goods - rubberized metal or pneumatic wheels are installed on the gearbox shaft, the support wheels and the opener are removed, a coupling device is installed in the place of the latter, to which the trolley with the body is hooked with a finger. Bulk and other cargoes weighing no more than 200 kg are transported in the cart.
Common breakdowns of motor cultivator units
Ignition system
Fault description:
· The engine will not start;
· The engine, having worked for some time, stalls, runs intermittently;
Causes:
· Defective spark plug;
· The tip of the high voltage wire is not installed all the way to the candle;
· The high voltage electrical wire is broken;
· Failure of magneto;
· Plug dirty.
Elimination:
· Unscrew the plug and clean the electrodes, if necessary replace the spare part with a new one;
· Check the connection of the high-voltage wire;
· Adjust ignition.
Engine
Fault description:
· The engine does not start;
· The engine does not pick up working speed;
· The engine speed "floats" at the same position of the throttle control lever.
Causes:
· Fuel does not flow into the carburetor;
· The fuel supply hose is clogged;
· Carbon deposits have formed in the channels and the cylinder head;
· Strong tension of the V-belt;
· Clogged air filter;
· There is no compression.
Elimination:
· Blow out with air, disassemble and clean the fuel supply system;
· Replace pistons, rings, cylinder;
· Check the cylinder head cover gasket for integrity, replace if necessary.
Carburetor
Fault description:
- The engine starts and stops almost immediately;
- The engine runs unevenly, with dips or interruptions, often stalls;
- The engine will not start.
Causes:
- Incorrectly adjusted carburetor;
- The fuel filter or gas supply hose is clogged;
- Clogged spray ("needle");
- Due to the loss of tightness, the float does not block the access of fuel;
- The hole in the idle channel is clogged.
Elimination:
- Adjust the carburetor;
- Disassemble the carburetor and clean or blow through all channels (jets), clean the sprayer (“needle”);
- Replace float and fuel valve.
Reducer
Fault description:
- The gearbox shaft rotates unevenly;
- The gearbox shaft does not rotate.
Causes:
- Low oil level in the gearbox;
- Loss of tightness of oil seals, ingress of dirt and earth into the gearbox;
- Wear of gear sprocket teeth;
- Wear of bearing assemblies;
- Open circuit of the reducer.
Elimination:
- Dismantling and cleaning the gearbox;
- Oil change, control of its level during the use of the unit;
- Replacing the chain, sprockets and bearings when they are worn out.
Reverse
Fault description - ne reverse gear is engaged.
The reason is that the reverse gear was not adjusted during break-in.
Remedy - adjust the reverse.
Drive belt (for attachments)
Fault description:
- The belt slips;
- The belt slips off the pulley.
Causes:
- Application of a belt of non-standard, long length;
- The belt has increased in length (stretched out);
- The belt is loose;
- The belt is on the wrong pulley.
Elimination:
- Tighten the belt with a tension roller;
- Replace the stretched belt;
- Check the correct position of the belt in relation to the engine pulleys and the attached or trailed equipment.
Maintenance and repair
In order for the cultivator to serve as long as possible, the owner must take care of it, check its technical condition, identify a specific malfunction and make timely repairs.
Upon completion of the work, the outer surfaces, open parts of the cultivator are thoroughly cleaned of dirt and sand, residues of vegetation, washed, wiped, and dried well.
Maintenance of the unit includes the following work:
- Checking the integrity of the fuel and oil supply system. In order to avoid leakage of the fuel mixture, the supply hoses and gaskets must be intact, without damage, tightening of the threaded connections must ensure complete tightness of the entire system.
- Adjustment of idle speed, as well as maximum engine speed.
- Checking the tension of the V-belt.
- Air filter cleaning involves removing dust, soil, and vegetation residues from the housing and filter element. If the filter itself is very dirty, it should be replaced.
- The engine ignition system is monitored by an external examination of its elements, the gap between the spark plug electrodes is measured with a probe, and the set magneto sparking moment is checked.
The Mole motor-cultivator is a good and reliable "helper" for the summer resident and gardener, allowing you to do a lot of work in your garden or summer cottage. At the same time, maintenance, repairs and improvements of the unit will not be a big deal for a person with minimal knowledge and skills in working with motor vehicles.