Content:
Ferns are the oldest inhabitants of our planet. They grew up during the life of dinosaurs. At that time, wild ferns were arboreal forms and were ubiquitous. On the territory of Russia, ferns can be found in the Leningrad region, in the Urals and the Moscow region. In the modern world, herbaceous forms are used as decorations in landscape design, planting in shaded flower beds.
More than 300 genera are known with more than 10,000 species. There are plants that live on trees (epiphytes) and terrestrial species (lithophytes). In addition, there are a number of plants similar to ferns, but which are of different classes (Blehnum, Devallia).
Description of culture
What is a fern? The fern is a deciduous perennial species, of the Fern-like division, with a developed root system. Depending on the species, sizes vary from dwarf forms not exceeding 3 cm to tall, arboreal forms.
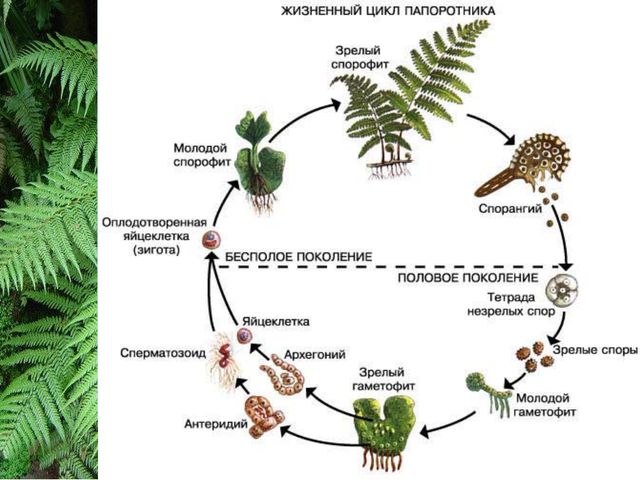
It is mistakenly believed that the terrestrial structure of the fern is represented by leaves. What is usually meant by a fern leaf is actually a leaf blade on which the shoot system is located. Such a fern leaf has the name given by science "frond". Faya grows directly from the root. On the inner side of the frond are the reproductive organs of the fern - a sporophyte with a haploid chromosome set. It is currently known how many chromosomes a fern has. On average, the value varies around 1200 units.
The decorative appearance is due to the cultivation of various forms of frond: openwork, feathery, cut, capable of growing into a lush and spreading bush.
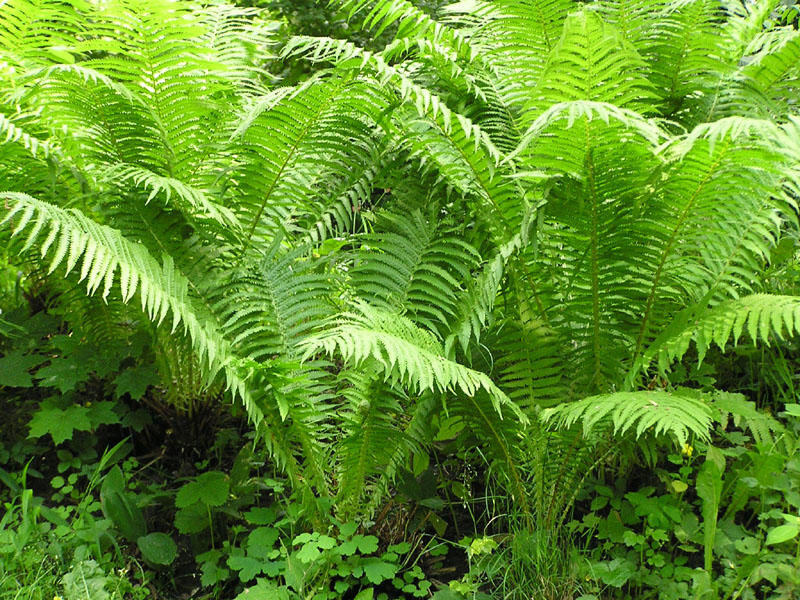
Ferns are found in nature in coniferous forests and subtropics, they are common in almost all climatic zones. Fern grows where there is shelter from direct sunlight.
Description of fern varieties
It is not possible to list all types of fern. Their number exceeds 300. Ferns prefer areas in the shade with constant soil moisture.
The following types are most popular:
- The common ostrich, or ostrich feather, got its name from the characteristic shape of the leaves. The feathery structure of frond bears a resemblance to the openwork lattice of ostrich feathers. In springtime, the leaf blades are rolled up in the form of a cocoon. When a warm time comes, they unfold, with the possibility of a fluffy funnel forming. The root system is the central root. In this regard, it is necessary to regularly loosen the soil layer and carry out mulching;
- Common bracken looks like a low bush, reaching 70 cm in height. It is well adapted to impoverished and arid lands. The horizontally elongated leaves are similar to eagle feathers, which served as the starting point for giving the name to the species. The rhizome is highly branched and horizontal;
- The female cochidian forms buds from often dissected leaf blades.Sizes range from 30-70 cm, depending on the variety. The rhizome of the kochedyzhnik is shortened and thick. The reproductive organs are covered with a velvety layer. This species is distinguished by a long growing period. In the absence of a transplant, it can live for over 10 years;
- Nippon kochedzhnik has a characteristic feature. The frond is silvery-gray with reddish veins. The plant prefers shaded areas, however, to enhance the color of the veins, a small amount of sunlight is a prerequisite, preferably morning. Reproduction occurs by the offspring of the root system, since when spores are planted, varietal color is not preserved.
Fern breeding
How does fern breed? Ferns can reproduce in several ways.
Asexual plant, ferns are flowerless and seedless. In nature, the life cycle of a fern begins with a spore. On the inner side of the frond of an adult plant, there are brownish protuberances, which are "vessels" for the spores necessary for the fern development cycle. In order to propagate a plant with spores, you must:
- In the fall, cut off parts of the leaves with containers for spores;
- Dry them in paper bags at room temperature;
- Fern spores are fine powder. At the end of January, sow the spores into a soil mixture of peat, turf and sand in a ratio (2: 1: 1);
- Moisten fern seeds from a spray bottle and cover with glass, placing in a warm room;
- The first shoots appear a couple of months after planting; from this moment, there is no need to cover the seedlings;
- As they grow, it is necessary to transplant young plants into separate pots, 7-8 cm high and 10-12 cm in diameter.
In this way, by the beginning of spring, you can get seedlings that can be transplanted into open ground.
How else can a fern be propagated? For long-rhizome species, the best option is reproduction by dividing the bush. It is better to carry out the procedure in early spring, after the end of the frost.
Some species have the ability to reproduce with rhizome whiskers, giving rise to young shoots. Having dug in the mustache to a depth of 8-12 cm and provided watering, after a short time, you can transplant the resulting new copy.
Some species form brood buds on the leaves, from which the development of young plants occurs. To do this, it is required to separate the new primordium from the adult plant and place it on moist peat moss. Covering the planting with glassware, you need to leave the seedlings to form in a warm, shaded place. After 2-3 weeks, the rooted seedlings can be planted in open ground.
Culture properties
The chemical composition of the plant is saturated with trace elements. Most often, parts of the plant are used in cosmetic procedures, in medicine and cooking. Being in fact a low-calorie product, the fern is valued for its high assimilation of its constituent proteins.
In eastern peoples, fern is included in the diet. Young shoots rich in vitamins A, B, E and PP are most useful.
The use of young bracken shoots is popular. As the plant grows, it becomes poisonous and unusable. Its beneficial qualities are manifested in strengthening the immune system, maintaining the cardiovascular system, optimizing blood glucose levels, and stimulating metabolic processes. In addition, toxins and toxins are removed from the body.
In cosmetic procedures, bracken is valued for slowing down the aging process and maintaining a fresh appearance. Useful of bracken salad.Having previously boiled a fresh plant, you need to marinate and stew the product. After adding onion fried with meat, you can serve it chilled.
There are a number of contraindications for the use of fern: pregnancy and the presence of diseases of the internal organs. Before using such a product, it is necessary to undergo consultation with a specialist.
Diseases and pests
If weakened by excessive watering or lack of air humidity, the possibility of fern infection increases.
Fern bacterial, fungal and viral diseases are the most common. They appear in the form of blooms, deformation of leaves, the beginning of decay of roots and stems. As a fight, it is necessary to remove and destroy the affected parts. Process with specialized means, according to the instructions. During the initial stages of infestation, decoctions based on onions, garlic or white mustard can be used.
The appearance of brown rust spots on the tips of the leaves signals an anthracnose infestation. It is necessary to remove and burn damaged parts, treat with a fungicide and reduce the frequency and abundance of watering.
The formation of moist brown spots that grow in size is a sign of mottling. The treatment regimen is identical to that of anthracnose.
The development of downy mold is a sign of the development of fungal gray mold. In the initial stages, it is necessary to reduce the amount of nitrogen-containing fertilizers, to place neighboring plants at a distance from each other. Remove damaged leaves and treat with a special fungicide against gray rot.
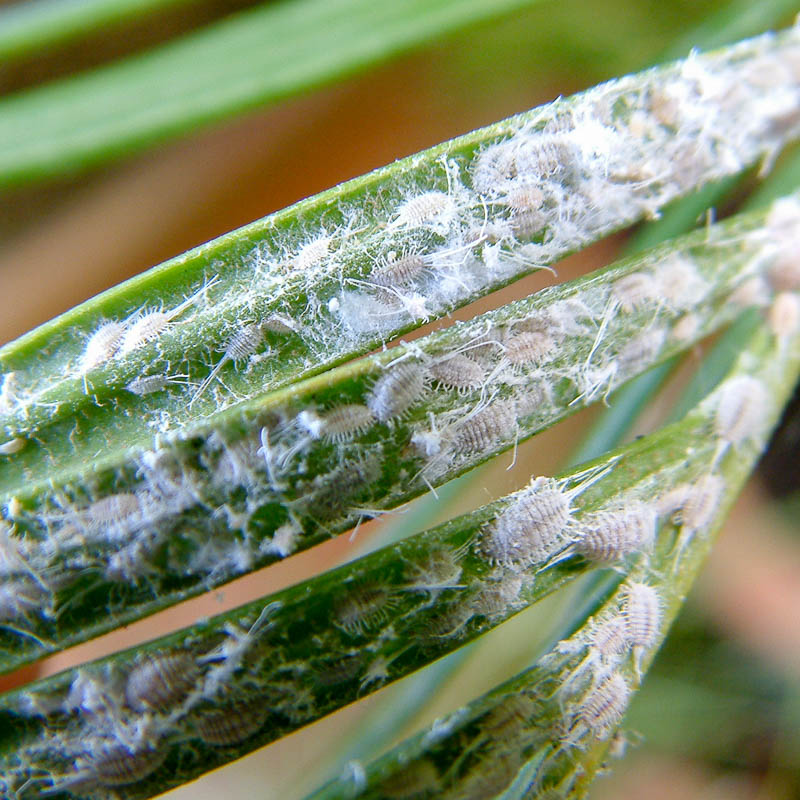
A mealybug root lesion looks like a white bloom. It is necessary to change the soil in the pot, rinse the root system with water. Clean the pot and scald with boiling water. Do not place an infected plant next to healthy ones - the parasite easily moves from pot to pot.
The formation of vitreous secretions on the leaves is caused by small worms that injure the roots of the plant. As a treatment, the root system should be cut off and rooting should be carried out again, completely changing the soil.
Useful information about the plant
Considering a fern as a home plant, you can create an original floral arrangement. Fern looks good in landscape design. It is imperative to install ferns in single pots - in contact with other species, leaf blades can be traumatized.
The interesting ability of ferns to purify the air by absorbing formaldehyde, toluene and xylene, acting as an air filter, is invaluable. In addition, the concentration of bacteria in the air is reduced.
It is better to choose places for planting ferns that are not exposed to direct sunlight. The temperature regime in the warm season should be 18-21 ℃, in the cold season - 18 ℃.
By regularly inspecting the plant for the initial symptoms of various diseases and pest infestation, the disease can be prevented and the plant preserved.