Content:
Raspberry is a popular fruit and berry crop in Russian garden plots. It is grown quite actively in most regions. Given the above, it is not surprising that many gardeners are wondering how raspberries reproduce.
How raspberries reproduce
Before choosing a specific method of how to propagate raspberries, you should take into account some general recommendations that will allow you to get not only excellent seedlings, but also an extensive berry harvest in the foreseeable future.
Usually, planting material is taken from healthy and strong shoots, on which there are no signs of disease and damage by harmful insects. Only seedlings obtained from plants with strong stems and clean foliage can guarantee a 100% copy of the mother material.
It should not be forgotten that raspberries are a light-loving plant that prefers diffused sunlight. Given this fact, it is highly recommended for landing to choose areas located on the south side, on which partial shade will remain on a sultry noon.
The shrub is less demanding on moisture, but it is very susceptible to mulching. The berry grows well on slightly acidic fertile soils. But the soil must necessarily remain loose so that the formation and growth of the root system in cuttings and cuttings does not slow down.
There are several ways how you can propagate raspberries:
- lignified offspring;
- green root suckers;
- root cuttings;
- green cuttings;
- dividing the bush.
Before breeding raspberries in your garden or suburban area, it is strongly recommended to learn more about how shrubs are propagated in more detail.
Reproduction by lignified offspring
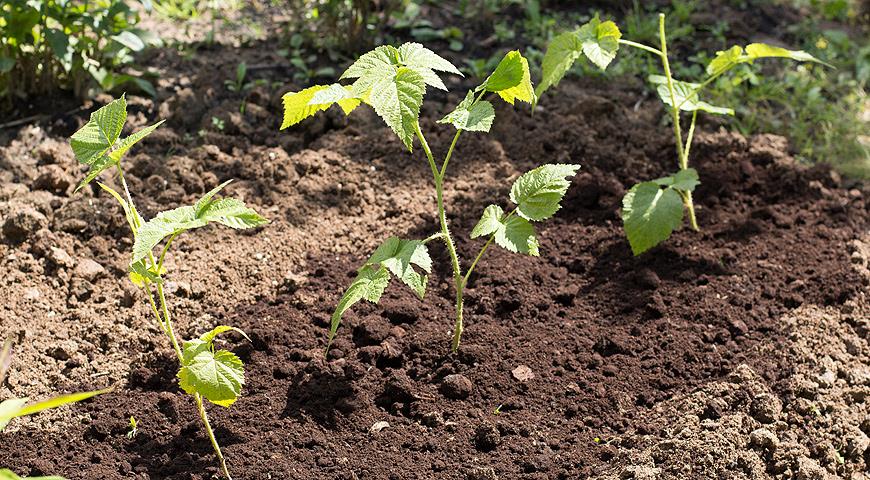
Reproduction of raspberries by lignified offspring is usually carried out in the autumn period. To get a high-quality offspring, you should choose a healthy bush and carefully dig out root suckers from it, which have already become woody.
The offspring should be dug out, which are not too close to the bush - at a distance of about 35 cm. The sprout should be removed from the ground in such a way that most of the root system remains intact, and the length of the roots should be no less than the length of a simple pencil (longer is allowed).
It is not recommended to use offspring for breeding raspberries, on the roots of which irregularly shaped bulges or bluish specks are visually visible. The described symptoms signal the presence of a disease in a plant. Healthy offspring can be used for transplanting without fear. The most important condition is that you must first remove all existing sheet plates.
Reproduction by green root suckers
Autumn is not suitable for the propagation of such fruit and berry crops as raspberries with green root suckers. This is usually done when the next growing season is just beginning, that is, in the spring season.
Usually, for reproduction of remontant raspberries, green offspring are used, which have managed to grow to a height of 15 to 25 cm.To obtain them, specimens should be dug that are located no closer than 35 cm to the bush. Moreover, digging should be carried out together with an earthen clod.
In the process of choosing an offspring for such a procedure as reproduction, be sure to carefully examine its top. If it looks a little wilted, do not dig out the root offspring. The plant is most likely affected by a raspberry fly.
Healthy cuttings should be planted immediately after digging. Otherwise, the offspring will wither. Planting should be carried out in pre-moistened pits with the addition of wood ash.
Propagation by root cuttings
Reproduction of raspberries by root cuttings is most often carried out if the shrub is already old enough, but the variety is very high quality and it does not come out to buy a similar one.
Cuttings of fruit and berry crops most often begin in the spring. But as practice shows, the reproduction of raspberries through cuttings in the fall also has a right to exist.
The answer to the question of how to propagate raspberries by cuttings in spring lies on the surface. You just need to perform the following sequence of actions:
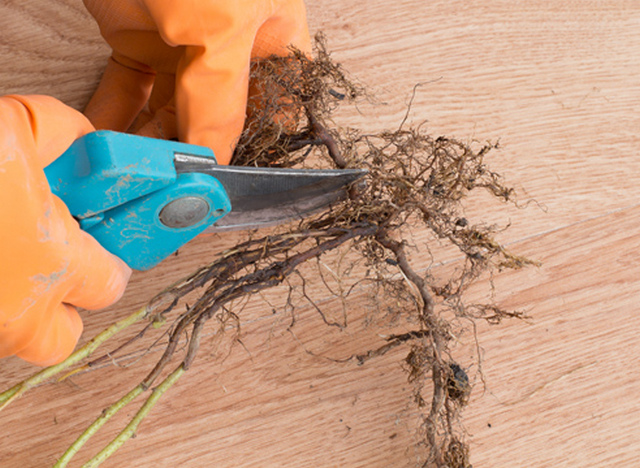
- Dig up the soil at a distance of at least 35 cm from the bush;
- Dig up the adventitious root with all the branches;
- Examine the stalk carefully;
- Choose healthy roots with a diameter of more than 0.3 cm;
- Cut the root into cutting planting material in such a way that at least one bud is present on each segment. Each stalk should be between 9 and 11 cm long;
- Keep growing roots intact.
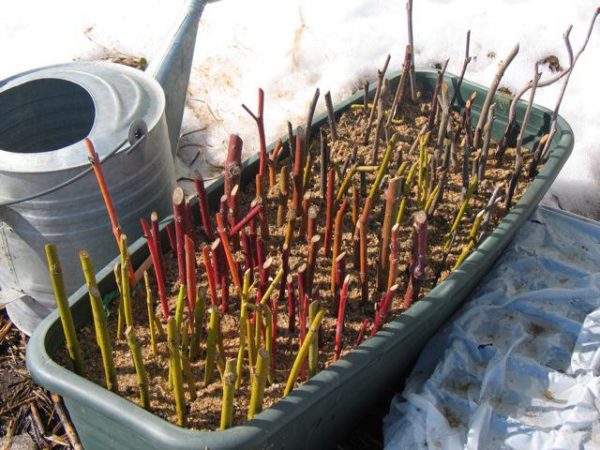
To successfully plant prepared cuttings, you will also need to act according to certain rules:
- soak root cuttings immediately after cutting for several hours in an aqueous solution of a growth stimulant; this procedure will promote the development of the root system and allow the cuttings to take root sooner;
- plant cuttings in a bed with previously loosened and moistened soil; the cuttings themselves do not need to be rinsed beforehand;
- make sure that the bed prepared for planting cuttings of Tarusa raspberry or any other variety is thoroughly dug up and cleared of weeds;
- dig a groove with a depth of 5 to 7 cm;
- lay the cuttings in the groove - one after the other without gaps between them;
- sprinkle with earth;
- compact the earth so that no air voids remain;
- pour soft water over fresh plantings.
Growing root cuttings into a complete plant requires some care. First of all, we are talking about the following points:
- top dressing (done immediately after planting, it is usually enough to dilute 1 tbsp. l of nitroammofoska at the rate of 1 tbsp. l per square meter so that the remontant shrub actively grows);
- periodic removal of weeds (carried out all summer);
- watering;
- loosening the soil (in order to avoid the formation of a crust from the soil).
Propagation by green cuttings
Answering the question of how to propagate raspberries in the spring, one cannot but recall the propagation by green cuttings. This method is used quite often, regardless of what kind of raspberry we are talking about: Tarusa, Krasa Rossii, Cumberlenge or some other. Often, green cuttings are successfully combined with shrub thinning. The removed shoots are used for rooting. This is done as follows: cuttings are selected from cut shoots. Each green stalk should be between 9 and 14 cm long and have a couple of leaves at the top. An oblique cut is made at the bottom of the shoot. At night, cuttings prepared for planting should be kept in a growth stimulant solution without fail.As the latter, indolylbutyric acid will be very effective. It only needs 50 mg per liter of water. There is one nuance in the preparation of the solution. Initially, indolylbutyric acid should be diluted in 50 grams of medical grade alcohol and only then add water at room temperature.
After the procedure for cutting raspberries in the spring is completed, it is important to plant properly selected and properly prepared cuttings.
Landing is carried out in accordance with the following algorithm:
- the initial planting of the material is carried out in a greenhouse or greenhouse covered with a film;
- a soil is being prepared, consisting at the base of expanded clay (a two-centimeter layer is enough) and soil pride, humus and river fine sand in equal proportions; on top, you can additionally pour a layer of sand - 2 cm;
- the lower end of the cuttings deepen into the soil by about 3 cm;
- throughout the entire period of the cuttings being in the greenhouse, the average humidity is about 90%;
- before winter comes (about October), when the root system of the future shrub is already formed, the grown seedling is dug up;
- rooted cuttings are transplanted to a nutritious bed with loose and moist soil for another year;
- in the spring, raspberries are planted in a permanent place of growth.
Reproduction by dividing the bush
Reproduction by dividing the bush is the fastest and "laziest" way of breeding raspberries from all of the above. Extending a raspberry patch using division is very simple:
- in the fall, a raspberry bush is dug up along with the root system (it is very important to try to preserve all the roots);
- depending on the size and number of shoots, the bush is divided into parts - from 2 to 5;
- bushes are transplanted to a permanent place of growth in pre-prepared pits.
After planting is complete, all that remains is to cut off all branches shortly, leaving only a small part of the growth with a couple of live buds. Water the seedling throughout the season until it begins to grow. In addition, each separated part needs to be fed.
Each gardener independently chooses the most suitable breeding method for raspberries. They all require a certain amount of effort. But since everyone loves homemade preparations made from such a delicious berry as raspberries, it is not surprising that few people neglect cuttings, dividing bushes and other methods that make it possible to expand the size of the raspberry and increase the yield.