Content:
Farmers and gardeners are losing huge yields due to depleted soils. Grape bushes need additional fertilizing before flowering, during fruit set and harvest ripening. Boron is one of the most important trace elements. Thanks to boron dressing, the number of ovaries increases, larger berries ripen, and the yield increases. The taste of grapes improves, it is better stored.
Boron for grapes
This element is involved in the chemical processes of mineral and energy exchange of living organisms. Boron is not found in its pure form; its main natural compounds are boric acid and its salts, among which the most famous is borax.
Boron-containing substances are used:
- for dressing;
- stimulating seed germination;
- as an insecticide and fungicide.
Boron participates in photosynthesis, affects the assimilation of trace elements necessary for the normal development of the plant, ensures the ripening of fruits, increases the yield and resistance of the vine to the negative effects of the environment. In general, the importance of boron can hardly be overestimated. But its lack can lead to serious consequences.
Boron deficiency symptoms
The lack of an element affects the condition of the grape bush almost immediately. However, the symptoms of the problem may be slightly delayed. The grower should carefully monitor the condition of the plant, because the boron deficiency can be easily determined independently.
What factors indicate a lack of boron:
- slow development of shoots during the growing season;
- mosaic color of leaves during the growing season;
- domed bending of leaves;
- reducing the distance between adjacent shoots, their unnatural convergence;
- death of the top of the vine by mid-summer;
- weak flowering and small ovary;
- browning and shedding of inflorescences;
- pea berries and brown flesh;
- decay of rhizomes.
A young grape bush may even die due to a boron deficiency. And these are by no means "horror stories" of experienced gardeners.
Boric acid for grapes: spraying
Experienced growers know that spraying during the development of the grape bush, flowering, emergence and ripening of berries give tangible results:
- abundant flowering with an increase in the number of ovaries;
- growth of shoots and rhizomes is stimulated;
- the taste of grapes improves: the content of sugars and vitamins increases, aroma increases. The berry ripens large. From fruits collected on bushes treated with boron, drinks with a higher tasting rating are obtained;
- the berries do not crack from excessive moisture, the keeping quality of the fruits increases;
- the plant's resistance to adverse climatic phenomena is growing;
- the development of grape diseases is prevented;
- the yield increases significantly (an increase of up to 25%).
Winegrowers, in order to saturate the plant with the necessary element, spray the bush with an aqueous solution of boric acid with zinc salt.Prepare it by mixing 5 g of boron and zinc salt in 10 liters of water.
For grape bushes, use a 0.25% aqueous solution prepared from 1 liter of water and 2.5 g of boric acid powder. In this case, 1 glass of hot water is taken to dissolve the powder, and then the volume is brought to 1 liter with cold water.
To enlarge the ovaries
To increase the number of inflorescences and ovaries, the vineyard must be sprayed with a solution of boric acid three times:
- seven days before flowering;
- during the main flowering;
- during the formation of ovaries.
Spraying grapes to improve pollination
In order to "call" more pollinating insects to the site, ordinary sugar is added to the acid solution, based on the ratio of 1 kg of granulated sugar to 10 liters of water. An acidic solution with sugar can be used to replace the vineyard spray formulations during the flowering period (second dressings).
Improving protection against infections
For the prevention of diseases and when the first signs of infection appear, the bushes need to be treated with a composition prepared in this way:
- dissolve 1 tbsp in 10 liters of water. l. boric acid (for complete dissolution, you need to use hot water, and then add cold water to the required volume);
- add a little potassium permanganate to the solution (so that the liquid becomes light pink);
- add 40 drops of pharmaceutical iodine to the liquid.
Boron fertilization before and during flowering
Boron for grapes is one of the main elements and an indispensable condition for the normal development of the bush and obtaining high yields. The first boric fertilizing by spraying is carried out in the period from the time of flowering to the appearance of full-fledged ovaries. By this time, young shoots already have 3-4 leaves.
First option
The spray solution is made from:
- boric acid (20 g);
- sugar (3 tbsp. l.);
- urea (25 g);
- potassium humate (40 ml);
- Kemira Lux (20 g);
- citric acid (30 g);
- novosila (60 drops);
- iron sulfate (10 g).
The proportion is indicated for 10 liters of water.
All ingredients are dissolved or diluted one by one in a small volume of warm water and poured into a mixing container. Then pure water is added to it, bringing the volume to 10 liters.
Second option
This top dressing is done 2 times 7-10 days before flowering.
The composition is prepared from:
- urea (35 g);
- ferrous sulfate (15 g);
- boric acid (10 g);
- citric acid (10 g),
All ingredients are diluted in 10 liters of water.
Third option
The recipe is designed for 10 liters of water:
- superphosphate (150 g);
- ammonium sulfate (90 g);
- ammonium nitrate (60 g);
- potassium chloride or potassium sulfate (60 g);
- borax or boric acid (10 g);
- zinc sulfate (10 g);
- manganese sulfate (15 g);
- cobalt sulfate (0.5 g);
- ammonium molybdate (7 g).
This variant is also suitable for spraying during the ripening period.
Top dressing during fruit ripening
First option
The sprayed composition includes (calculation for 10 liters of water):
- boric acid (20 g);
- pharmacy iodine (3.5 g);
- Tiovit Jet (20 g);
- Kemira Lux (20 g);
- potassium humate (60 ml);
- sugar (3 tbsp. l.);
- baking soda (75 g);
- novosil (90 drops);
- potassium permanganate (2 g)
All components are dissolved separately in warm water (or an aqueous suspension is prepared) and poured into a container to prepare the composition.Then add clean water to the container, bringing the volume to 10 liters.
Second option
Foliar dressing of the vine after fruit setting can be carried out with the following composition (calculated for 10 liters of water):
- boric acid or borax (10 g);
- zinc sulfate (15 g);
- ammonium molybdate (15 g);
- iron vitriol (5 g);
- magnesium sulfate (15 g);
- potassium permanganate (3 g).
What to do in case of overdose
There should be a measure for everything, this also applies to the saturation of plants with boron. Its excess is signaled by the following points:
- drying leaves located near the ground with peculiar burns;
- leaves drying out from the edges, yellowed and twisted inward;
- decrease in productivity indicators.
An overdose has a negative effect on the plant and the soil around it - fallen damaged leaves become a breeding ground for pathogens. The soil near the bush becomes a hotbed of infection.
Memo to winegrowers
In order for the events to bring real benefits, and not harm the plant, you should:
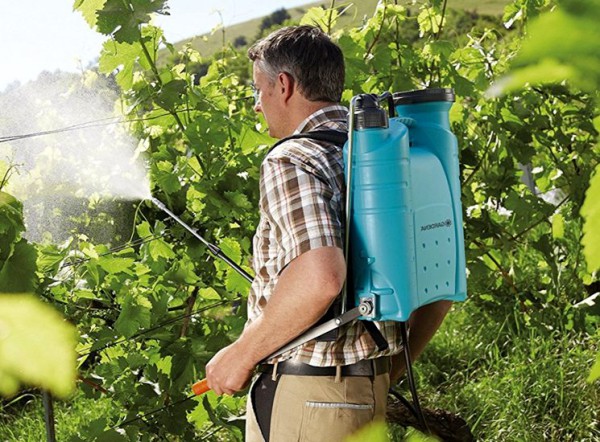
- set the device for spraying to fine-dispersed mode in order to prevent large droplets from accumulating on the leaves. In case of failure and transition to coarse-droplet spraying, use should be discontinued;
- for spraying, choose a day with cloudy weather or evening time, when the risk of burning leaves to the leaves is minimized;
- the vines should be treated evenly so that there are no missing areas, and the whole plant receives nutrition.
Boron alternatives
In addition to boric acid solution, grape bushes can be treated with an aqueous solution of borax (10 g of substance per 10 l of water), fertilizers containing boron can be applied to the soil. Fertilizers are also produced that dissolve in water - they can be used for spraying. So, for example, Mag Bor is used for spraying grapes, a drug in which you can find not only boron, but also magnesium.
Inexpensive but effective boric acid is available for almost every experienced gardener. It should be remembered that when spraying, boron is more easily absorbed by the plant. Treatments have an effect on the growth of yields, increase the health of berries, complementing their taste. Do not forget that feeding the vine on the leaf must be done before flowering, during flowering, during the ripening of the crop.
















“The first boron fertilization by spraying is carried out during the period from the time of flowering to the appearance of full-fledged ovaries. By this time, young shoots already have 3-4 leaves. " This quote is not clear about the sheets. At this time, there are already much more sheets. There are 3-4 leaves a month ago.