Content:
A bacterial burn is very dangerous for fruit trees, as it is an infectious disease and causes irreparable harm. One or two seasons are enough for him to destroy all garden trees. The disease is picked up by stone and pome crops. Therefore, it is important for gardeners not to lose vigilance, and to take action from the first moment of detecting an ailment.
The causative agent of the disease is the bacterium Erwinia (Erwinia amylovora). The bacteria originate from America, and the spread in Europe began in the middle of the 20th century. Its presence was officially recognized in Russia in 2009. At the moment, the bacterium has the status of "limited distribution in the territory of the Russian Federation" (it was found only in Belgorod, Saratov, Samara, Tambov, Voronezh, Kaliningrad regions, as well as in Karachay-Cherkessia).
What are the symptoms of bacterial burn
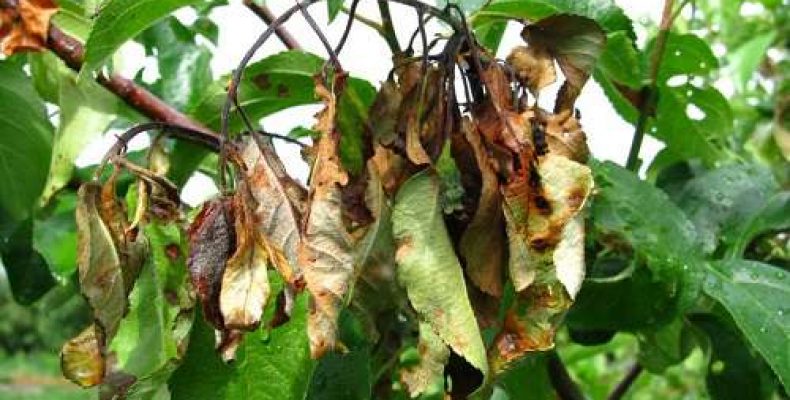
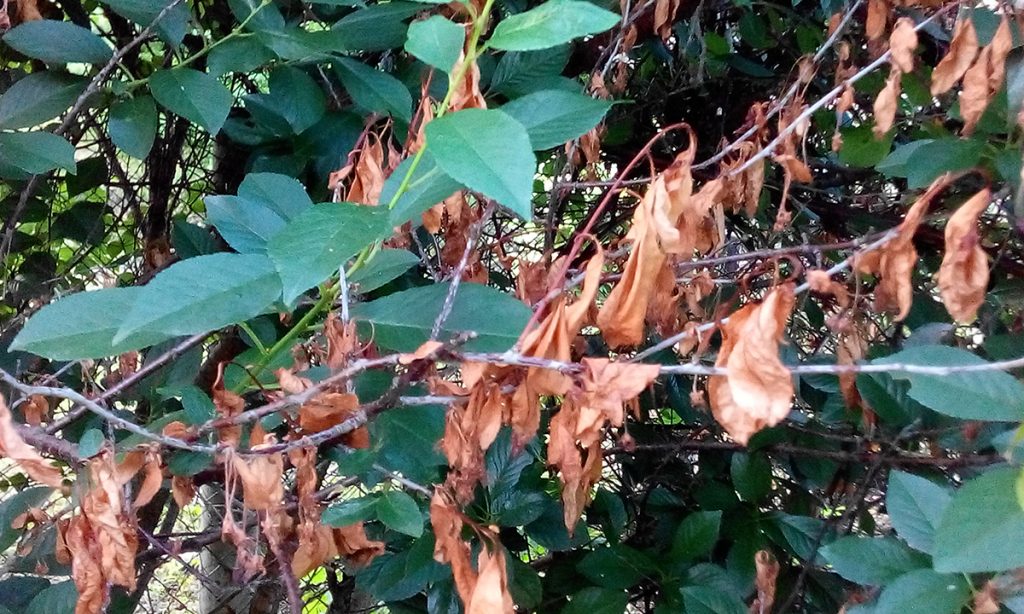
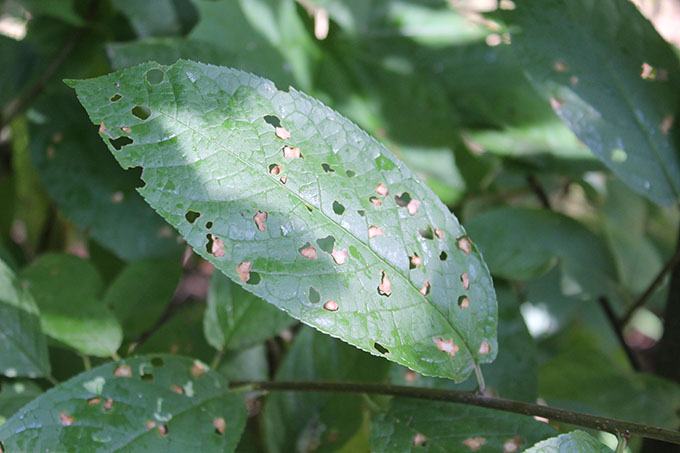
With a fire blight, changes occur throughout the tree. The main symptom is a change in the state of the bark, in which it looks sticky and becomes covered with a white exudate. Over time, the exudate turns brown. With this disease, red areas appear on the leaves, which are located between the veins of the leaf plate.
In addition, shoots, flowers and fruits change. Shoots twist and wither. Blackening of their tips is observed, very similar to a burn. Flowers and buds turn brown and gradually die off. The ovaries darken and stop growing.
The infection develops and is transmitted as follows:
- Getting into wood for the first time, ervinia starts the reproduction process, however, during the first wintering, almost all bacteria die. With the arrival of spring, only 10% of survivors activate all forces for a rapid increase in numbers, which leads to the appearance of exudate.
- When the flowering period begins, insects, pests and birds, when visiting a sick tree, pick up some of the bacteria on their paws.
- Subsequently, the disease is transferred by them to healthy plants, in which Ervinias continue their growth in nectar and along the peduncle get to the vascular system, and through it to all organs and tissues of the plant.
- When the entire system is damaged, the bacteria wake up genes that produce toxins. These substances block the immunity of the fruit tree and lead to tissue death. The exudate becomes even greater. The ovaries gradually die off.
- The dead tissue continues to cling tightly to the branch. And new "visitors" to the tree, after contact, again carry the disease and start the cycle over again.
Bacterial burn of fruit trees: control measures
Control measures and ultimate success depend on the time of detection of the disease and how far Erwinia managed to infect the fruit tree. At each stage, the nature of the treatment is different:
- At the initial stage, when the signs have just appeared, stripping all diseased branches from the seedling will help, followed by their burning. They even cut off up to 15-20 cm of a healthy area in order to exclude further progression of the disease.The cut is treated with a solution of copper sulfate 1% (dosage: for 10 liters of water - 100 g of the substance).
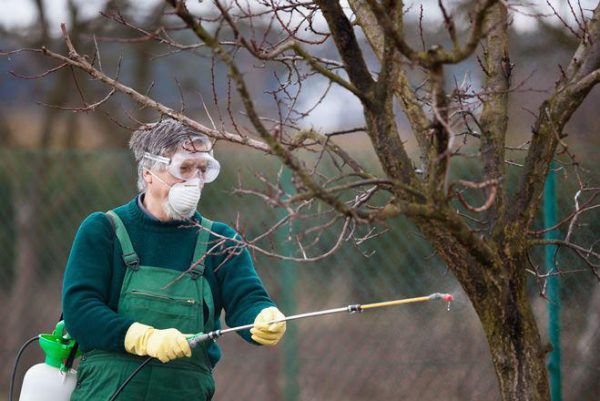
- Also, at the beginning of the disease, copper-containing drugs are often used, such as "Oxyhom", "Rovral", "Skor". Processing can be carried out up to 5 times from early spring to the end of flowering. The last spraying will not hurt after the harvest. If this type of treatment is ineffective, they switch to more serious antimicrobial and antibacterial drugs.
- If exudate begins to appear through the cracks in the bark of the tree, then this liquid should be wiped off with a solution of copper sulfate. The affected areas are cleaned with a knife. Next, dressings moistened with an antibiotic are applied to the wounded surface. Suitable drugs: "Ofloxacin" (1 tablet per 1 liter of water), "Gentamicin" (1 ampoule per 1 liter of water).
- If a burn is detected during flowering, then this is a direct signal for the immediate use of antibiotics throughout the garden. For 5 liters of water take 1 ampoule of "Streptomycin" or 3 tablets of "Tetracycline". It is necessary to carry out antibacterial spraying three times during this period, every 4-5 days.
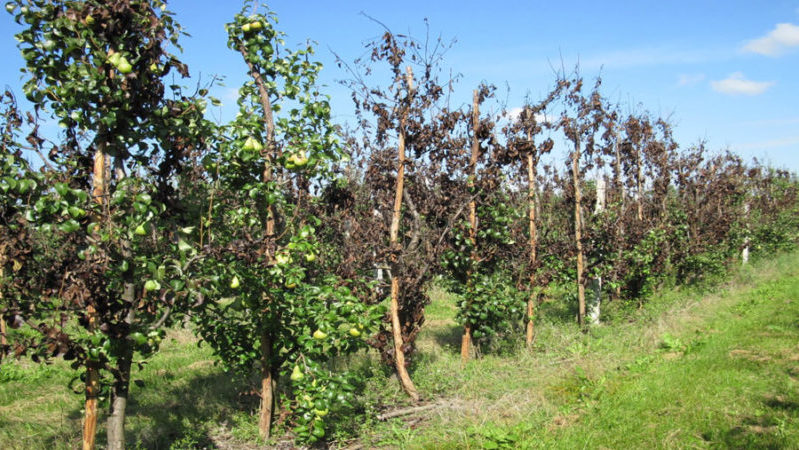
- The very last measure used to treat a bacterial burn is the destruction of a diseased tree. The plant is uprooted and burned on site. In addition, to ensure the safety of the garden, even trees located within a radius of 5 meters from the hearth are removed.
Biological stimulants deserve special attention in considering measures to combat fire blight. Because if you treat the garden with antibiotics for a long time, then the already impaired immunity of plants suffers, and the beneficial flora is erased. The market offers a large selection of stimulants (even for each type of tree) that will help crops grow stronger and cope with the disease faster.
Prevention of the development of bacterial burn
There is a set of measures that can be taken to prevent ervinia from spreading throughout the garden.
For instance:
- Conduct frequent inspections of seedlings during periods of active shoot growth, flowering and during the autumn movement of sap. It is during these time intervals that pathogenic bacteria attack most successfully and then multiply in the plant.
- Spray the garden with pest preparations, since they are the main carriers of the disease, and they themselves bring considerable harm.
- Treat plantings with biological or chemical drugs for this disease.
- Regularly carry out sanitary cleaning of the garden (eliminate the oldest plantings, free trees from unnecessary or overly stretched branches, feed the seedlings not only with stimulants, but also with natural fertilizers or minerals).
What other types of burns are there
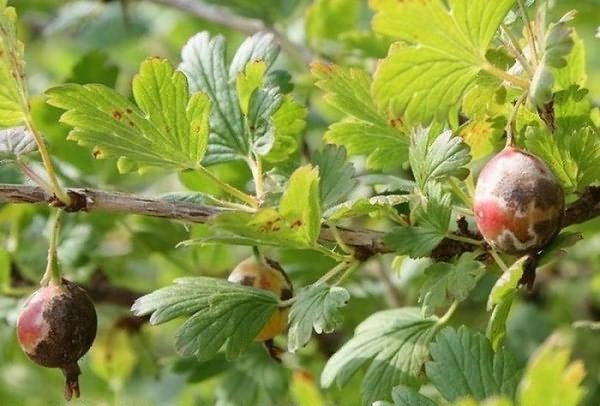
Perhaps the monilial burn of fruit trees is the most famous type of this type of plant damage. In addition, it is often confused with bacterial, especially when the exudate does not appear for a long time. However, the difference between them is great and this type of burn is provoked not by the bacterium Erwinia, but by the fungus Monilia.
It should be noted that the rate of development of moniliosis is faster. It forms whitish fungal spores on the tree, leading to the appearance of brown spots. The wind or pests pick up the spores and carry them onto healthy plants, and infection occurs. Fruit tree monilez also destroys fruit. It all comes down to the fact that the fruit pulp turns brown, becomes excessively soft and becomes covered on the surface with sporochia.The taste of such fruits gives off alcohol.
In order to infect all plant systems, the fungus will need only one and a half weeks from the beginning of development. Moniliosis is treated in a similar way as in the case of a bacterial burn.
- The paramount is pruning diseased branches.
- Then treatment with antifungal drugs (fungicides).
- In this case, Gamair, Horus, Abiga-Peak, copper sulfate, and Bordeaux liquid proved to be excellent.
When using any means, it is extremely important to follow the attached instructions.
Not only pathogens, but also the most common pesticides can "burn" trees. Moreover, this type of burn is not inferior in frequency to others. Excessive enthusiasm for gardeners with treatments, provokes a chemical burn in plants. As a result, the leaves of fruit trees are covered with brown spots, which then form holes. The number of spots and holes depends on the method of spraying and the concentration of the product in the water.
General poisoning leads to sad consequences:
- makes the ovaries fall off;
- sterilizes pollen;
- disrupts plant development (bends branches, deforms) and fruits.
If the tree was not immediately burnt, but gradually accumulated phytotoxic pesticides, then sooner or later a partial or complete loss of leaves occurs, and then drying out.
Experienced gardeners recommendations
Without some experience, it can be difficult to recognize the onset of a fire blight, especially since it spreads from top to bottom. Many people notice him only when it becomes impossible to save the fruit tree. Therefore, you should regularly inspect all the plants in the garden.
Plus a few more tips:
- Garden tools need to be decontaminated. For this, formalin is well suited. If this is not done, then when using them, you can transfer bacteria from a diseased tree to a healthy one.
- Plants such as hawthorn (however, like all wild stone fruits) provoke the appearance of the bacteria ervinium, so they must be removed from the site.
- Care should be taken when choosing drugs. Beginners have tried to treat fruit trees with fungicides more than once, in the hope that this will help the situation. However, fungicides have a therapeutic effect only on fungal diseases, and no matter how advertised, almost all of them are powerless against bacteria.
It is extremely unpleasant to find a bacterial burn on your site, since the disease is quite complex. As has been noted more than once, it is important to notice the first symptoms as early as possible and then antibiotic treatment will give the maximum effect, show the result. Gardeners who constantly monitor and care for their plantings have nothing to fear.