Content:
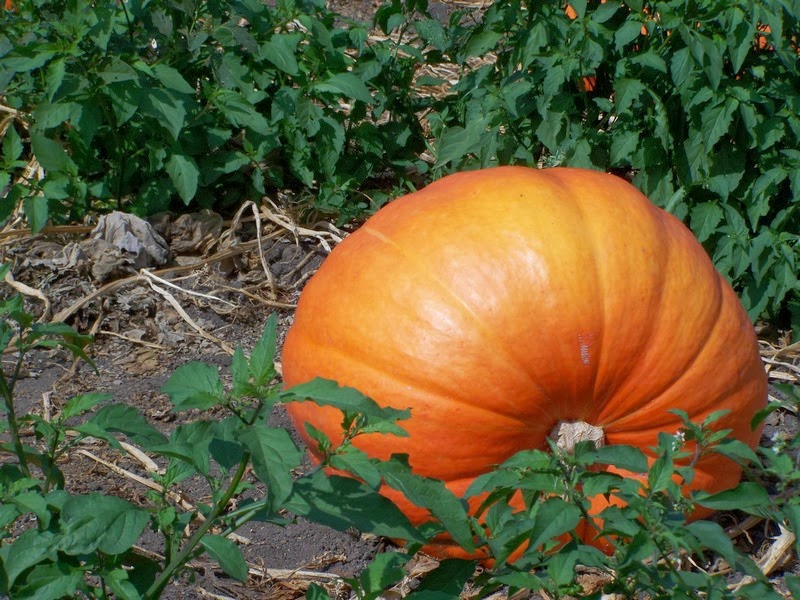
Although pumpkin is not one of the most popular crops, many gardeners who have summer cottages still plant it: the benefits and sweetness of fruits, the edibility of seeds and ease of care - these advantages contribute to the widespread distribution of pumpkin.
In order to understand how to grow a pumpkin, you first need to figure out what conditions it needs, how the pumpkin grows and what determines the quality of the fruit. She prefers fertile, loose soils, good illumination, no winds, abundant, but infrequent watering. If it is possible to satisfy all these requirements on the site, you can safely plant a pumpkin and count on a good harvest.
How to grow pumpkin
It all starts with the choice of planting material and landing method. The pumpkin is propagated by seeds. You can sow it directly into the ground or grow seedlings at home. How to plant a pumpkin correctly depends on the climatic conditions in the region: for example, in warm southern regions, even the latest varieties of it are sown in open ground. And in parts of the country with a cold climate, preliminary cultivation of seedlings is considered more rational.
Regardless of the chosen method of planting pumpkin, its seeds must be prepared before sowing.
Preparation consists of several stages:
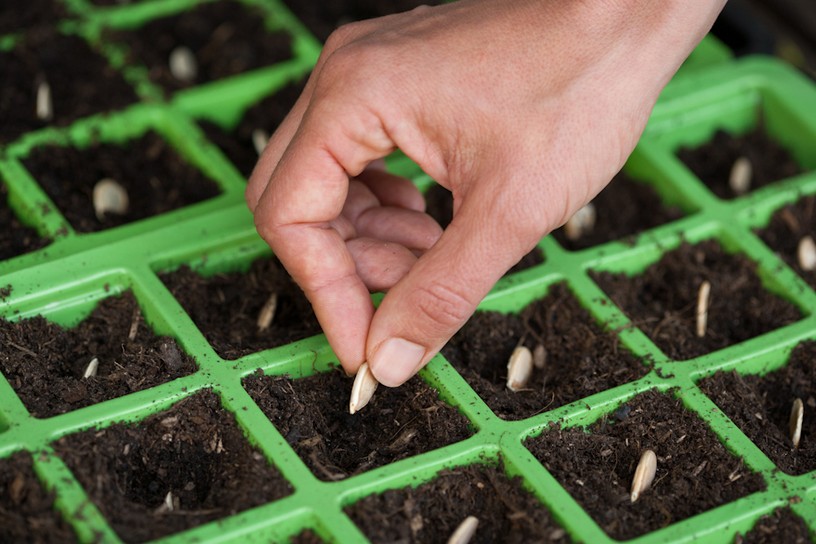
- germination. Since pumpkin seeds have a strong thick skin and will get wet for a long time in the ground, they are helped to hatch to speed up the process and increase germination. For this, the seeds are kept in water for 2 hours (temperature 500C), then placed in wet gauze or cloth and wait for the emergence of shoots;
- hardening. Already germinated pumpkin seeds need to be hardened. This is especially true when growing crops in a short and cool summer. Here you can do different things: harden with a temperature difference (for 8 hours the germinated seeds are kept at room temperature, and then it is reduced to +10C and leave for another 12 hours) or cold (just put the planting material directly in the gauze in the refrigerator for 3 ... 5 days).
Preparing the seat and choosing a landing pattern
There are many opinions on how to properly grow a pumpkin. The following is a standard crop planting technique.
When growing pumpkin, special requirements are imposed on the composition of the soil.
- Lend to be loose. For this, peat, sand, vermiculite and other components are introduced into heavy soils.
- Soil fertility is increased by introducing organic fertilizers - compost and humus into the planting beds. In the spring, they are added for digging the beds or covered in layers in locally dug holes, mineral fertilizers are applied.
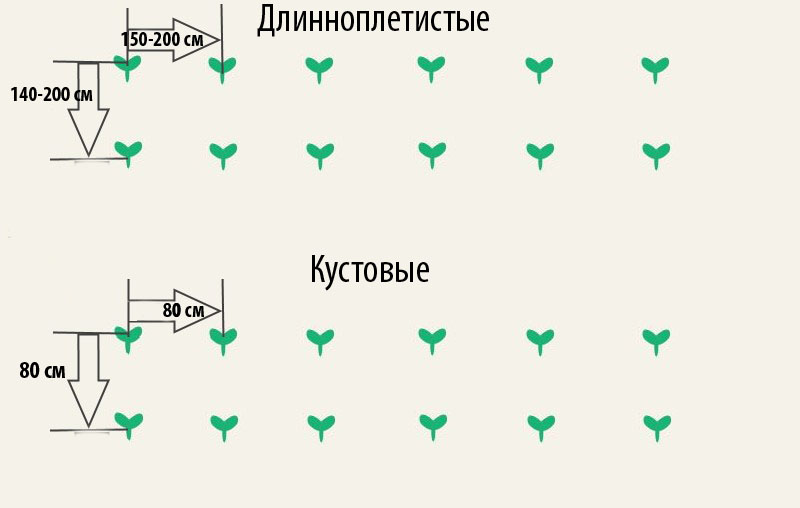
The pumpkin planting scheme depends on the growing method and the varietal parameters of the plant. The spreading scheme provides for the distances for bush - 70 × 70 cm, medium-winged - 80 × 100 cm, long-winged - 100 × 150 cm.
Growing pumpkin in spreading takes up a lot of space in the garden, which is why some gardeners practice vertical cultivation of this crop. The pumpkin is tied to a wire trellis, mesh support, strong structures. The cultivation of pumpkin in an old barrel can be attributed to the same category.In the latter case, the lashes of the plant are directed downward, so the sharp edge of the barrel must be rubberized, otherwise the stems will be damaged.
When can you plant pumpkin seeds?
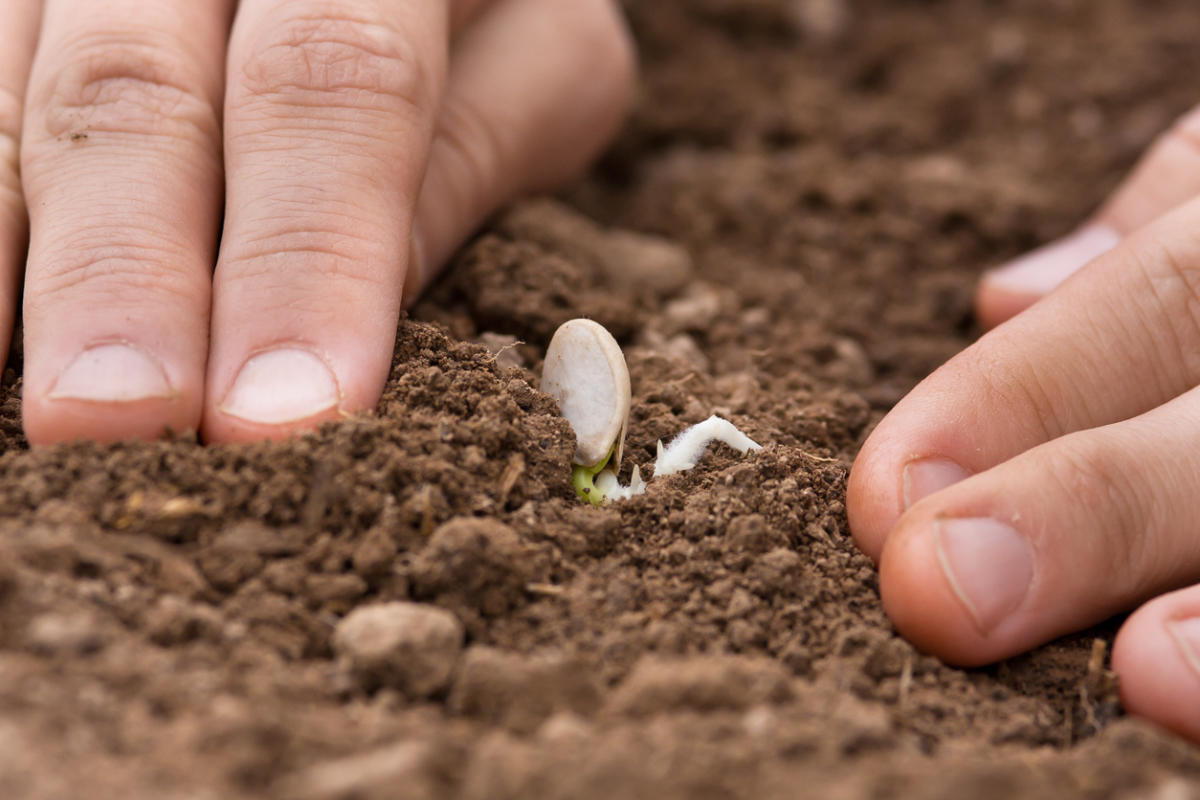
It is possible to plant seeds in the ground only when its temperature is not lower than + 10-110C. The seeding depth of pumpkin seeds should not exceed 5 cm. Several pieces (2-3) are placed in each planting hole, and after emergence they are thinned out, leaving only one, the strongest and healthiest sprout. When young shoots appear, it is important to monitor the condition of the soil - it must be moist. Be sure to loosen the soil around the sprouts.
As they grow, they are fed with fertilizers with a high nitrogen content, which contributes to an accelerated set of green mass.
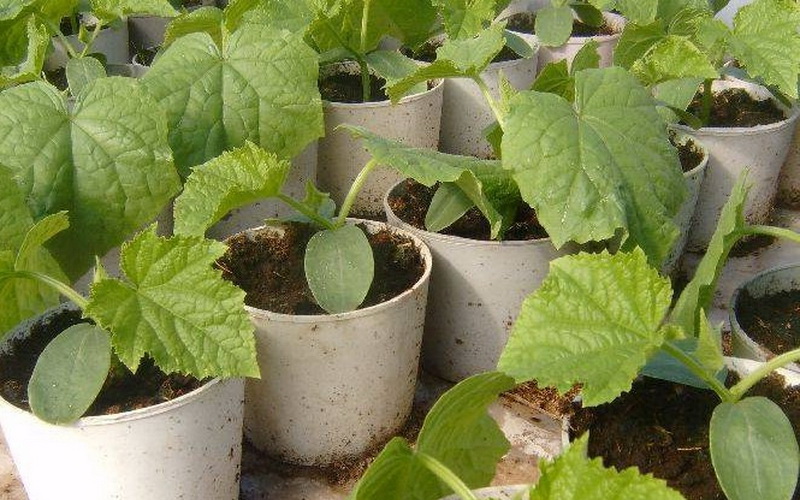
Growing pumpkin seedlings and planting dates
Pumpkin seedlings can be grown on a plot (greenhouse or greenhouse) or at home (on a balcony or windowsill). For each seed, you need to take a separate glass - the pumpkin does not tolerate transplanting to a permanent place and exposing the root system. It is enough to comply with several conditions to obtain strong seedlings.
The temperature regime during the day is about + 18-200С, at night - + 13-50C, then the seedlings will not be frail and elongated.
The soil in the pots should be damp, but not wet.
A week after the emergence of seedlings, young shoots are fed with a nitrogen-containing fertilizer.
The optimal age for planting pumpkin seedlings is 20-30 days. Younger plants do not take root well, and overgrown seedlings often break and damage when planting. The pumpkin is planted after the threat of return frosts has passed, in a warmed up to +120 From the soil. The air temperature should not fall below +130C. In the Leningrad region, and in the Moscow region, low temperatures can prevail at night. Then the seedlings need to be provided with temporary shelters (plastic bottles, paper caps, etc.).
Planting of seedlings takes place in accordance with the selected scheme in pre-prepared and spilled holes. The seedlings must be carefully removed from the containers (so that the root of the plants is not exposed) and placed in the planting holes, without burying the earthen lump: it must be at the same level with the ground. Each plant needs to be huddled a little, creating a slide no more than 2 cm in height. Such hilling will not allow the roots to be exposed during watering.
Pumpkin care
Growing and caring for a pumpkin is not difficult - this culture is unpretentious, competent planting, taking into account all requirements, is already half the success. But in order to obtain a harvest of varietal size and high quality, some manipulations will have to be performed. How to care for pumpkin during the season?
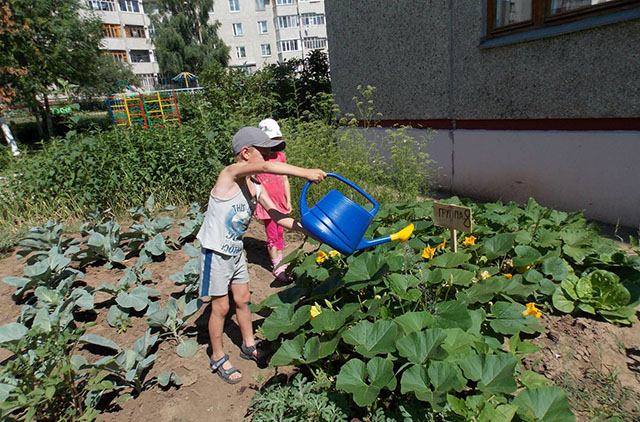
Watering mode
The first time after planting in a permanent place, pumpkin seedlings need frequent, but moderate watering. As the plants grow, the frequency of watering is reduced to once or twice a week, depending on weather conditions. At the same time, it becomes more abundant - the soil should get wet to a depth of 40 cm, since it is there that the bulk of the sucking roots lies.
Watering is carried out exclusively at the root, trying not to get on the leaves and especially on the pumpkin flowers. To keep moisture in the soil as long as possible, it is recommended to mulch the soil immediately after planting seedlings (or emergence of seedlings when sowing seeds). Watering is completely stopped after the growth of pumpkins stops.
Pollination
The pumpkin produces male and female flowers on the same bush, so there are no problems with pollination. Growing pumpkin for seeds is another matter. To maintain the purity of the variety, they resort to artificial pollination: the flowers that have not yet opened are tied with threads or rubber bands. At about noon, the flowers, if they were not tied, would like to open. It is at this time that they begin to pollinate: they cut off the male flower, remove the thread from it, expose the stamen, untie the female flower and process the pistil with the stamen with pollen. After pollination, the female specimen is again tied with a thread (elastic band).
A few days later, when the fruit is tied, the thread is removed and tied around the stem of the pumpkin, so you can mark the fruit with the same purity of the variety. After harvesting, this specimen will be used for harvesting planting material.
Formation
In order for the fruits of a decent size to ripen on the pumpkin, you need to form it correctly. In the general case, formation includes several stages.
- Determination of the number of main stems. The number of lashes directly depends on the large-fruited variety - for a pumpkin with a portioned fruit size, it is typical to grow 2-3 stems, for plants with large pumpkins - in 1 stem. All other side shoots must be cut off in time.
- Plucking the whips. In bush forms, the tip is pinched to stimulate the formation of lateral shoots (since it is on them that female flowers appear). In climbing species, to limit the growth of stems, a pinch is made, counting 5-6 leaves from the extreme ovary.
- Control of the number of ovaries. If the fruits are small (weighing up to 3 kg), 3-5 ovaries are left on the bush, the rest are removed. To grow a large pumpkin, you need to leave as few pumpkins as possible on the lashes - most often one.
- Removing leaves. All diseased and pest-affected leaves must be removed. In bush forms, foliage thinning is carried out to improve the illumination of the fruits.
The question of how to grow a very large pumpkin loses its relevance over the years. Recently, gardeners are giving preference to varieties with portioned fruits and refuse to grow giant pumpkins. Small pumpkins can be consumed at one time without refrigeration.
Top dressing
Since pumpkin consumes a huge amount of nutrients from the soil throughout the season, it needs periodic fertilization. She is responsive to liquid fertilizing with organic matter: infusion of mullein or slurry diluted in water (4: 1, respectively) is introduced under the root. During periods of flowering and fruiting, it is especially important to provide sufficient potassium nutrition - potassium sulfate, ammophos, ash are added. You can also fertilize pumpkin with complex universal dressings.
For the whole season, on average, 3-4 pumpkin feeding is carried out:
- 10 days after planting (3 weeks after sowing the seeds);
- before flowering;
- during flowering;
- during fruiting.
Protection from pests and diseases
The most malicious pests of pumpkin are spider mites and melon aphids. Both feed on juices, sucking them out of the integuments of the plant, and live mainly on the undersides of the leaves. The leaves affected by the tick are entangled with a thin cobweb, yellow dots subsequently appear, the leaf turns completely yellow and dries up. When aphids are affected, the leaves curl and also die off. In the fight against these pests, depending on the area of the lesion, repelling infusions or chemical preparations are used.
Pumpkin can get sick with various types of rot that cause fungi, or bacterial diseases (bacteriosis).For fungal diseases, fungicides are used, in general, when fighting pumpkin diseases, preparations containing copper and sulfur have proven themselves well.
Harvesting
The timing of the pumpkin harvest is planned based on the varietal ripening dates and the appearance of the bushes. The ripening period or another variety is usually indicated on the package and can be: early (90-100 days from the moment of germination), medium (about 115 days) or late (200 days). To assess the readiness for harvesting by external signs of the fruit, pay attention to:
- leaves, they should already turn yellow or dry out altogether;
- the peduncle, which should become woody and tough and dry;
- the color of the fruit rind, it must be varietal and pronounced;
- crust hardness.
Large-fruited pumpkin is harvested immediately after the first frost, so in many regions it does not always have time to ripen. Incompletely ripe pumpkins are sent for ripening - storage at a temperature of about +200C (in cooler conditions, they rot). You need to pick the fruits very carefully, trying not to cause mechanical damage. It is recommended to cut the pumpkin together with a stem 3-4 cm long. In general, the pumpkin is well stored at room temperatures. Some varieties are able to lay until the next harvest.
Butternut pumpkin must be harvested before frost, and varieties of hard-barked pumpkin are harvested before anyone else - most of them are early ripening, and the fruits are not stored for a long time.
Knowing when to plant and how to grow pumpkin, observing the rules of agricultural technology, you can count on a good harvest.