Content:
Proper rearing of calves at home provides the owner with healthy cattle. Whatever breed of cows is raised (Aberdeen Angus, Holstein, Simmental, etc.), the calf needs a balanced diet and quality care from the first minutes of birth. Calves are raised at home for different purposes, therefore, the principles of care may differ, depending on them.
Calf Description
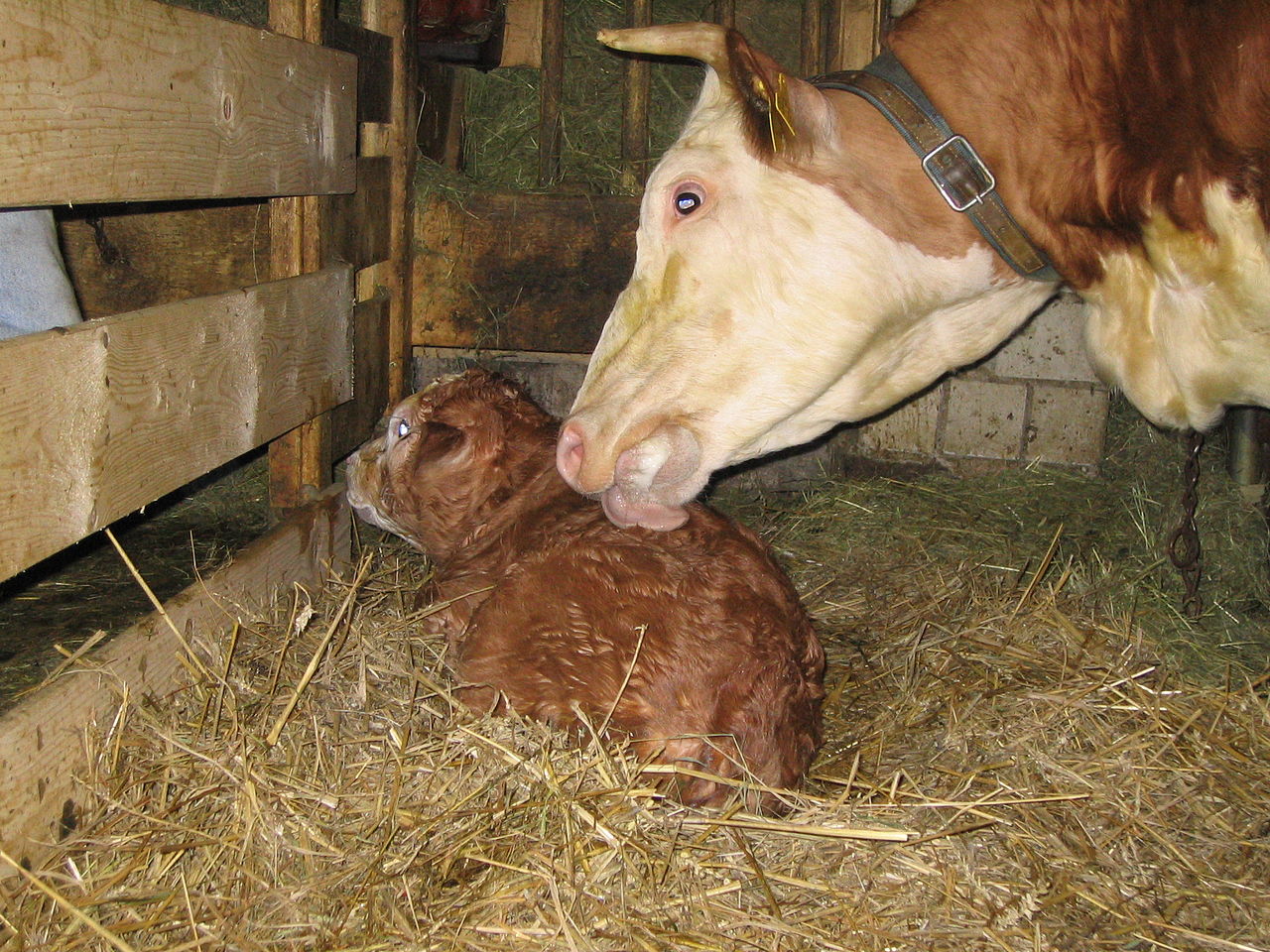
Everyone knows what the calf is called a calf. He can be born with varying degrees of physiological maturity. Not every baby can exist independently, so for some time he needs to keep in touch with his mother through milk.
A newborn animal has a number of biological and physiological characteristics:
- many enzyme systems are practically absent;
- the mechanism of thermal and water regulation is poorly developed;
- the blood has a slightly acidic or neutral reaction;
- the immune system is weakened or practically absent.
How much a newborn calf weighs is difficult to answer, since there are no clear values. The weight of a newborn calf should be at least 6-8% of the mother's weight (or the average weight typical for this breed), a healthy calf rises to its feet within 0.5-2 hours. The sucking reflex and appetite should already be clearly manifested. Healthy babies frolic after feeding, look well-groomed, the skin is shiny and shiny.
Depending on the breed of the cow and the bull, the calf is born in unpredictable colors:
- white;
- redhead;
- black speckled and so on.
Raising calves at home
The conditions of keeping affect the efficiency and productivity of raising young cattle. There are a huge number of methods, but most often two are used:
- Cold growing method.
- Traditional method.
It is important to know how to care for the calves with each method.
Cold growing method
This method of existence is equally suitable for raising cows of meat and dairy breeds. Young calves are kept in separate huts, which are located in an open area. From the name it is clear that in this case heating is not provided.
They begin to raise calves using this technology from the first days of life.
Advantages:
- Since the baby is exposed to harsh conditions of detention, all internal reserves are mobilized in him. The calf is gaining weight quickly.
- In such conditions, small animals are provided with vitamin D naturally.
- The body works with maximum efficiency, as it undergoes good hardening. As a result, calves rarely get sick.
A significant disadvantage of this method is the high cost of keeping, since animals in a cold climate require more feed, and the equipment of the territory for their maintenance requires decent investments.
Traditional method
This option for raising calves has been used for a very long time, but does not lose its relevance.The bottom line is very simple: until a certain time, the calves are kept with the cow. When the young have reached a certain age, they are separated from the cow.
Positive sides:
- Calves should be given less attention. Even with a sharp cold snap, babies remain protected.
- This method does not require any costs, therefore it is economically beneficial.
Negative points:
- With this content, digestive problems are often encountered.
- When a disease occurs, the infection is transmitted to other calves and cows;
- Calves are susceptible to problems such as weak immunity and rickets, as young animals do not receive enough UV rays.
Young cattle weight
Determining the weight of a calf is an important task for every cattle owner, but it is not always possible to weigh a bull calf. Knowledge of mass is often required for calculating the rate of a drug or for selling.
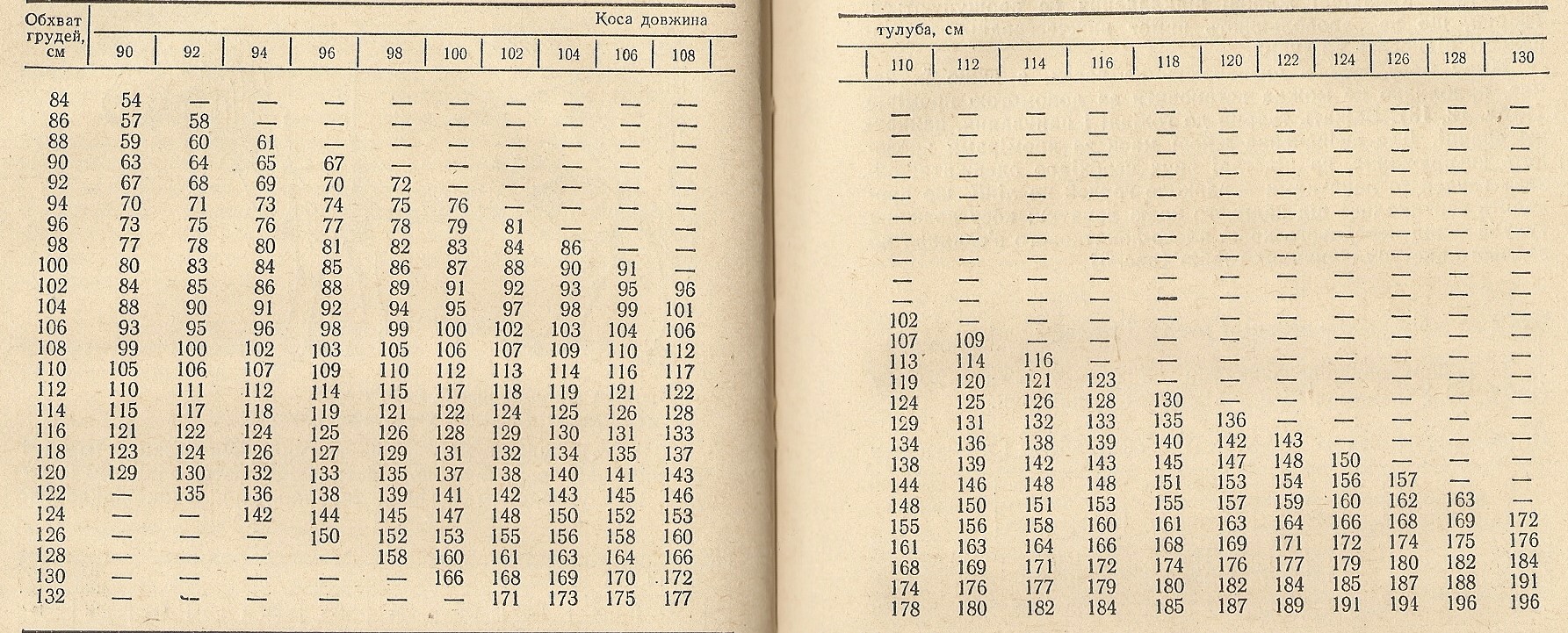
It is easier and more reliable to find out the calf's weight on the scales, but they are not always available on the farm, but you need to weigh them regularly. In such cases, a special weight table is used, which helps to find out the weight of the calf at different periods of life by measurements.
For this it is necessary to measure the following parameters:
- The girth of the animal's chest. The measurement is taken along a line behind the shoulder blades and around the chest (parallel to the shoulder blades).
- Oblique body length. The definition is carried out from the edge of the shoulder of the scapular joint to the posterior projections of the ischial tuberosities.
The table is easy to use: first you need to find the line with the desired chest girth, then the length of the oblique line. There will be an approximate weight at the intersection.
Calf care principles
The entire period of rearing calves can be divided into three main stages:
- Dairy, or prophylactic.
- A period of intense growth, or transitional.
- Final feeding period.
Milk period
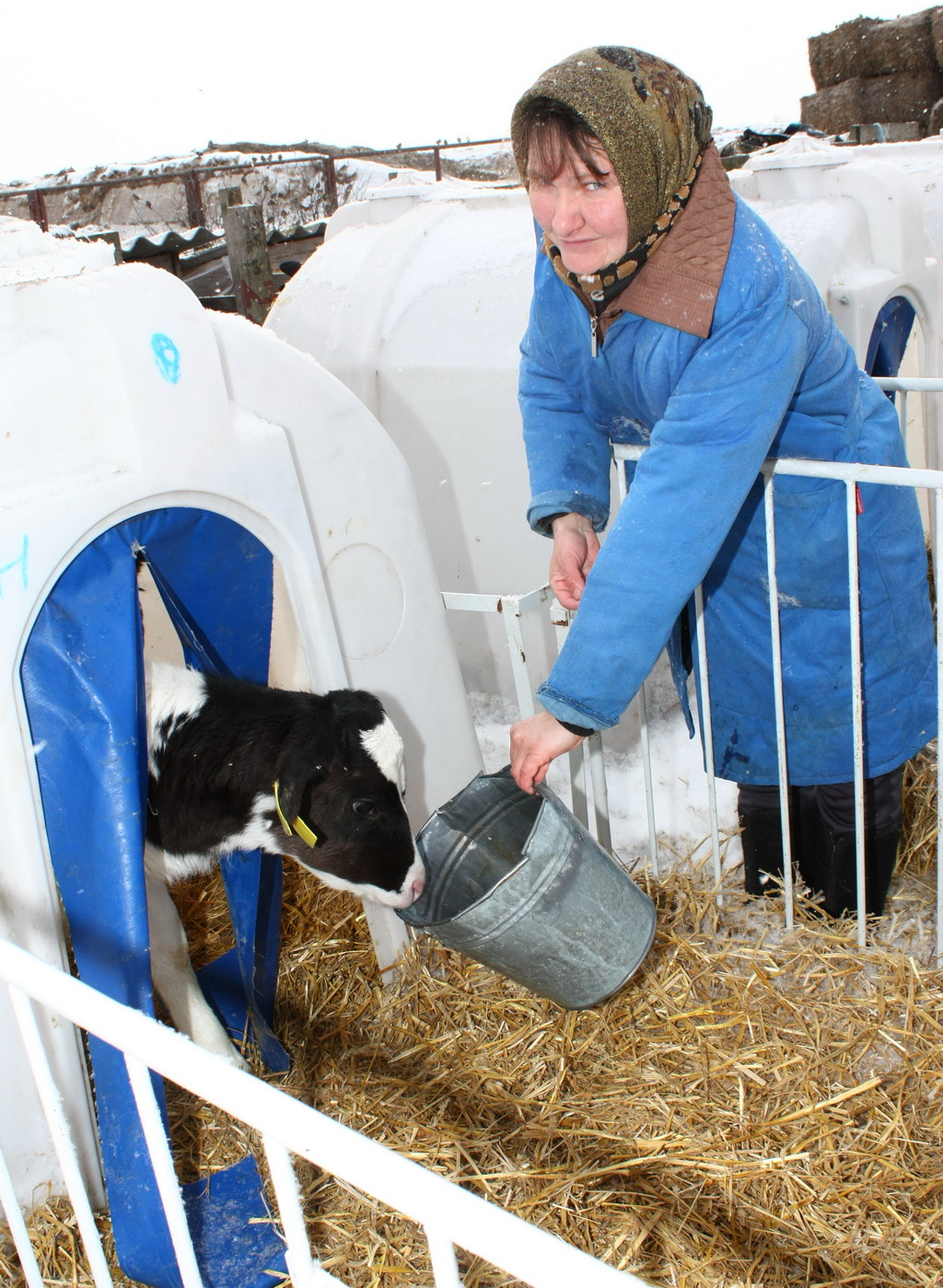
Feeding calves begins with 1.5-2 liters of colostrum, which is given to a calf in the first two hours of life. The second feeding is repeated 6-7 hours after birth.
The first 2-3 days, the calves are watered 4-5 times a day. For one feeding, the calves drink about 1.5-2 liters. But you should not overfeed, as this will lead to indigestion, and sometimes death.
Breastfeeding utensils should be thoroughly washed and disinfected after each meal. It is also important to clean all areas in the room that get dirty.
After the calves reach the age of 2-3 weeks, they organize regular walks. Their duration directly depends on weather conditions and the state of health of the young. The first walks should not exceed 10-15 minutes. Then they are gradually increased to 1-1.5 hours.
From the 5th day of life, after feeding with colostrum, the calves are given boiled water (temperature - within 20-25 degrees).
Gradually, other feeds are added to milk for month-old calves:
- Vegetables in the form of carrots, potatoes and beets are introduced into the feed from 2-3 weeks;
- A liquid solution with the addition of oatmeal and barley flour is administered from 3-4 weeks.
Difficult to digest feed in the form of compound feed, rye and pea flour should not be introduced earlier than six months, since only by this age the digestive system is formed in the young.
A period of intense growth
The second period of rearing calves (after half a year) is characterized by an intensive set of muscle mass. It is important to provide feeding in such a way that the weight by the year increases 7-8 times, compared to the original at birth, by 1.5 years - 11-12 times. Gobies are growing rapidly.
Fattening
During this period, animals are offered a large amount of plant food in their diet, which will help in the final formation of the skeleton and muscle tissue. You can already give such a delicacy as bread. By 18 months, the live weight of the calf should be about 450 kg, while the yield of pure meat is about 55%.
Calf house
A small calf needs a good housing, as does a complete feed. Under poor conditions, calves grow up sluggish, with weak immunity.
The room should be bright, warm and well ventilated. It is important that good ventilation and ventilation is organized. The room temperature is maintained at 15-18 degrees.
The humidity in the room must be sure, otherwise there is a high probability of developing viral pneumonia. The maximum value is 70%.
Barn or group house
Most often, group houses are used for keeping calves, which are made of metal-plastic or plastic with a hemisphere shape. They are durable and built to last. Often such structures are called manger or calf shed. In most cases, a plastic calf house has a capacity of about 15 calves, its height reaches 2.2 m.
In the group house, babies are kept on a straw mat. It is changed every 2-3 weeks.
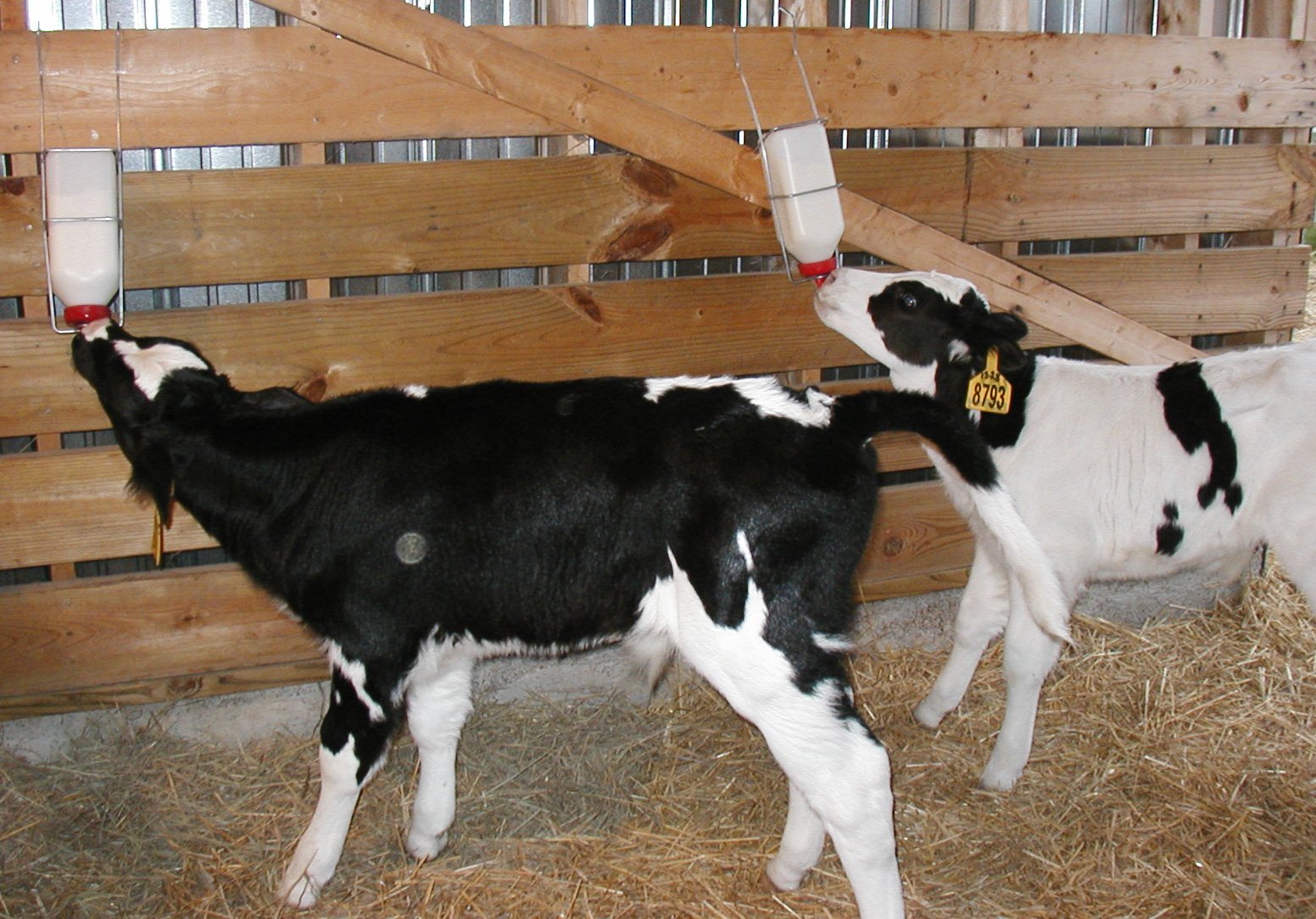
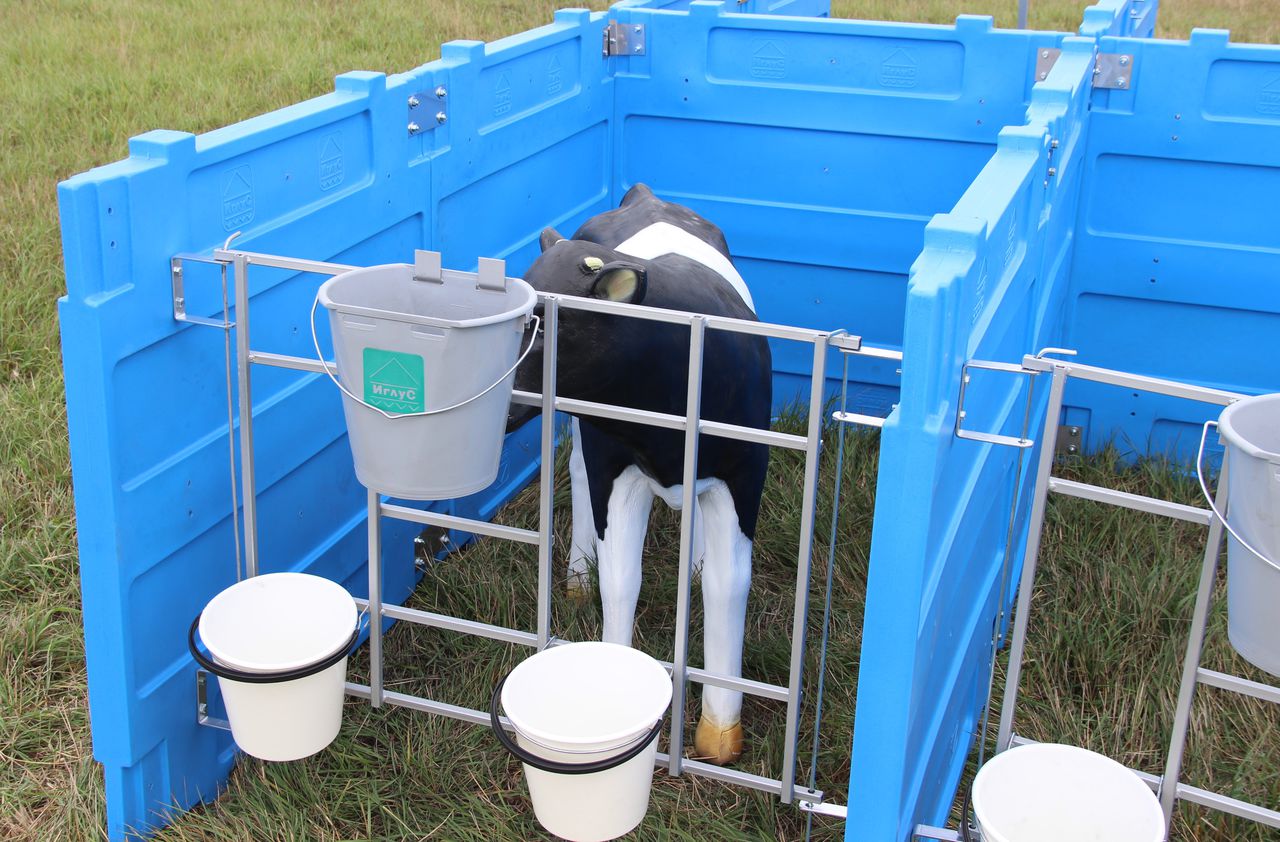
Individual cage
Many farms use individual calf cages. This helps to avoid many problems, as they do not have the opportunity to suck each other or find and swallow wool.
To keep the litter dry at all times, you can make a slightly sloped floor. When replacing straw, baking soda and disinfection should be carried out.
The cage with dimensions 1.2x1.5 m, which has 3 steel walls and a door made of steel tubes, received the most positive reviews.
If you are not gaining weight
If for some time a small calf does not gain weight, you need to panic, why this happens, there can be many reasons. First of all, it is a digestive disorder. In this case, weight loss is accompanied by diarrhea.
Also, worms can affect the weight of young calves. You will need to drink young animals against parasites.
Often, weight gain is disturbed due to improper care. Therefore, with a similar problem, it is recommended:
- Contact your veterinarian for advice on what to do if the calf is not growing;
- Revise the cow diet;
- Improve the quality of care.
As you can see, calf breeding is a very complex and laborious process that should be approached with all responsibility. After all, the future health and productivity of cattle, as well as the duration of the vital productivity of the animal, depend on the peculiarities of keeping young animals.