Content:
- General care rules
- Major cattle diseases
- Measles
- Clostridiosis
- Endometritis
- Brucellosis
- Acidosis
- Fascioliasis
- Telyaziosis
- Actinomycosis
- Smallpox
- Babesiosis
- Rabies
- Ovarian hypofunction in cows
- Malignant catarrhal fever
- Vibriosis
- Pyroplasmosis
- Foot and mouth disease
- Nicrobacteriosis
- Anaplasmosis
- Hypodermatosis
- Dictyocaulosis
- Chlamydia
- Bursitis
- Atony
- Spongiform encephalopathy
- Vaginitis
- Listeriosis
- Mycoplasmosis
- Moraxellosis
- Aymeriosis
- Echinococcosis
- Plague
- anthrax
- Infectious rhinotracheitis
- Preventive measures
- Breeder tips
Epizootology is a link in veterinary medicine that studies the causes of the spread of animal diseases. All cattle diseases can be divided into infectious and non-infectious. The ailments of the first group are the most dangerous, since they can destroy the entire herd and even be transmitted to humans. The second group is less dangerous, but they can also lead to the death of the animal. In both cases, the farmer must be able to identify the symptoms of disease and know what first aid is needed.
General care rules
The basic rules for caring for cattle include:
- The room where the animals are kept must be dry, warm and clean. Drafts must not be allowed. Walls, floor and roof must be insulated. In winter, the temperature should be at least 10 ° C.
- The floor in the cattle room should be inclined for easy manure removal and hygiene procedures.
- Above the heads, behind or to the side of the livestock, there should be windows that can be easily opened. Window openings and doors should be on the south and east or south and west sides.
- Over the summer, the room is prepared for the winter period: disinfection is carried out, the cracks are closed.
- Before milking, the barn is cleaned. If necessary, replace the litter, which may be straw or wood shavings.
- The room must have feeders, drinkers, stalls, and tethers. Average dimensions of a stall for one animal: length 190 cm, width 140 cm, side wall height 150 cm, volume 18-20 m³. The width of the trough is 80 cm at the top and 50 cm at the bottom. Food debris is removed from the trough so that they do not rot. The harness should not prevent the animal from lying down and getting up.
- In winter, cattle are fed with hay and silage prepared in advance. Also, the animal is additionally fed with vegetables, mixed feed. There should always be water in the drinker.
- In summer, the animals are taken out to the pasture near the reservoir. In the morning and in the evening they are additionally given vegetables and compound feed.
- From the age of two months, animals begin to be vaccinated.
- Animals are regularly washed, brushed, and hooves trimmed. The water temperature during water procedures should be 16-18 ° C. The dirtiest areas are washed with soap. Cleaning is carried out in order to free the animal from pathogenic microorganisms. The brush for washing should be rigid, and each animal should be individual. If only one brush is available, it is washed and disinfected after each procedure. Cleaning is carried out 1 hour before milking. After water procedures, the skin of the animal is dried and rubbed.
Major cattle diseases
Below are the most common cattle diseases, the main symptoms and treatment options.
Measles
Cattle finnosis is also called cysticercosis. The disease begins in connection with the ingestion of bovine tapeworm larvae into the animal's body. They settle inside, turn into tapeworms, causing great harm to the animal. Other animals and humans can become infected.The main cause of the disease is non-compliance with hygiene standards.
Cattle is an intermediate link in the transfer of this disease, and a person is the main one. The causative agent of Finn's disease, which is filled with water, has a head and 4 suction cups. Infected human excrement contains eggs of the parasite, which can spread around the farmyard and end up in hay or water.
In the early stages, the disease is asymptomatic. If the following clinical signs appear, an urgent need to consult a specialist:
- a sharp increase in temperature and its jumps: it can rise sharply to 40 ° С, and then drop to 34 ° С;
- swelling of the skin;
- upset gastrointestinal tract;
- apathy;
- lack of appetite;
- muscles are weakened and flaccid;
- blindness;
- violations of coordination of movements.
Signs last for about 10 days, several days after infection. The most common result of the disease is death. Usually the diagnosis is made when the animal is slaughtered for meat. The disease is treated with the drug droncite. It is expensive and therefore rarely used by farmers. It is possible to reduce the risk of finnosis by observing preventive measures:
- compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards. This applies to both the personal hygiene of the farmer and the hygiene of the herd;
- slaughter of cattle is carried out in a separate place;
- people who are associated with livestock need to undergo a medical examination every 6 months.
Clostridiosis
Bovine clostridiosis is an infectious disease caused by the spore-forming bacillus. The infection affects the nervous system and gastrointestinal tract.
The parasite can live in soil and water. Reasons for infection:
- poor quality feed;
- contaminated water and soil;
- lack of sanitary standards.
The first signs of the disease are refusal to take food and water, deterioration of the general condition. Other symptoms depend on the route of infection:
- malignant edema: swelling of the subcutaneous fatty tissue, which is felt on palpation, heart rate and breathing increase;
- anaerobic enterotoxemia: the animal loses coordination and muscle spasms, the temperature rises to 41-42 ° C, breathing becomes more frequent;
- botulism: spontaneous swallowing is impaired, water can flow out through the nostrils, and rapid exhaustion occurs;
- emkar: lameness and unsteadiness appear, first dirty swellings appear, and then cold swellings come, which, upon palpation, emit a crunch, the temperature rises to 42 ° C;
- tetanus: muscle paralysis occurs, sweating increases, the digestive system is inhibited.
Treatment begins with isolating the sick animal. The drugs used are vancomycin, metronidazole, ampicillin, chlortetracycline, tetracycline. After taking antibiotics, a course of prebiotics is prescribed. Disinfection is carried out in places where livestock are kept and in adjacent territories.
Endometritis
The disease is associated with inflammation of the uterus. Endometritis in cows can occur as a result of exhaustion after childbirth, in case of violations in the provision of obstetric care, in the case of penetration of harmful bacteria into the birth canal.
Common symptoms:
- poor appetite;
- weight loss;
- lethargy;
- slight rise in temperature.
The rest of the symptoms depend on the form of the disease:
- catarrhal form: swelling of the mucous membrane, thickening of the walls of the uterus, pus is mixed into the discharge, the next fertilization does not occur;
- purulent-catarrhal appearance: the horns increase, the tone of the uterus decreases, suckers with pus and have a brown, yellow or gray tint, the uterus is swollen and soft, the canal is open by 2 fingers;
- subclinical type: there are lumps of gray-yellow in the mucus, there is pus in the discharge, spontaneous abortions up to the fifth month of pregnancy;
- gangrenous form: a rise in temperature, cessation of lactation, the uterus does not contract, the genitals are swollen, a bard or black liquid with a fetid odor is released from the uterus.
As a treatment, intravenous administration of a glucose solution, saline solution, Ringer-Lokka, calcium gluconate is used. Antibiotics with novocaine blockade are used. It is also possible to use drugs against inflammation in the form of ointments, suppositories and creams.
Brucellosis
Bovine brucellosis is an infectious invasive disease that can be transmitted to humans. The disease is caused by the bacteria Brucells abortus, which affects all organs. They enter the body through water, food or insect bites.
Symptoms of the disease include:
- the external genitals and the udder are swollen;
- brown or transparent discharge from the genitals;
- spontaneous abortions occur at 5-8 months;
- the calf is born dead or lethargic;
- from the moment of delivery, the afterbirth is delayed in the uterus for 8 hours;
- after an abortion or childbirth, the udder swells, mastitis appears, and the milk yield decreases.
For treatment, antibiotics and immunomodulators are prescribed:
- tetracyclines;
- streptomycin;
- rifampicin;
- chloramphenicol.
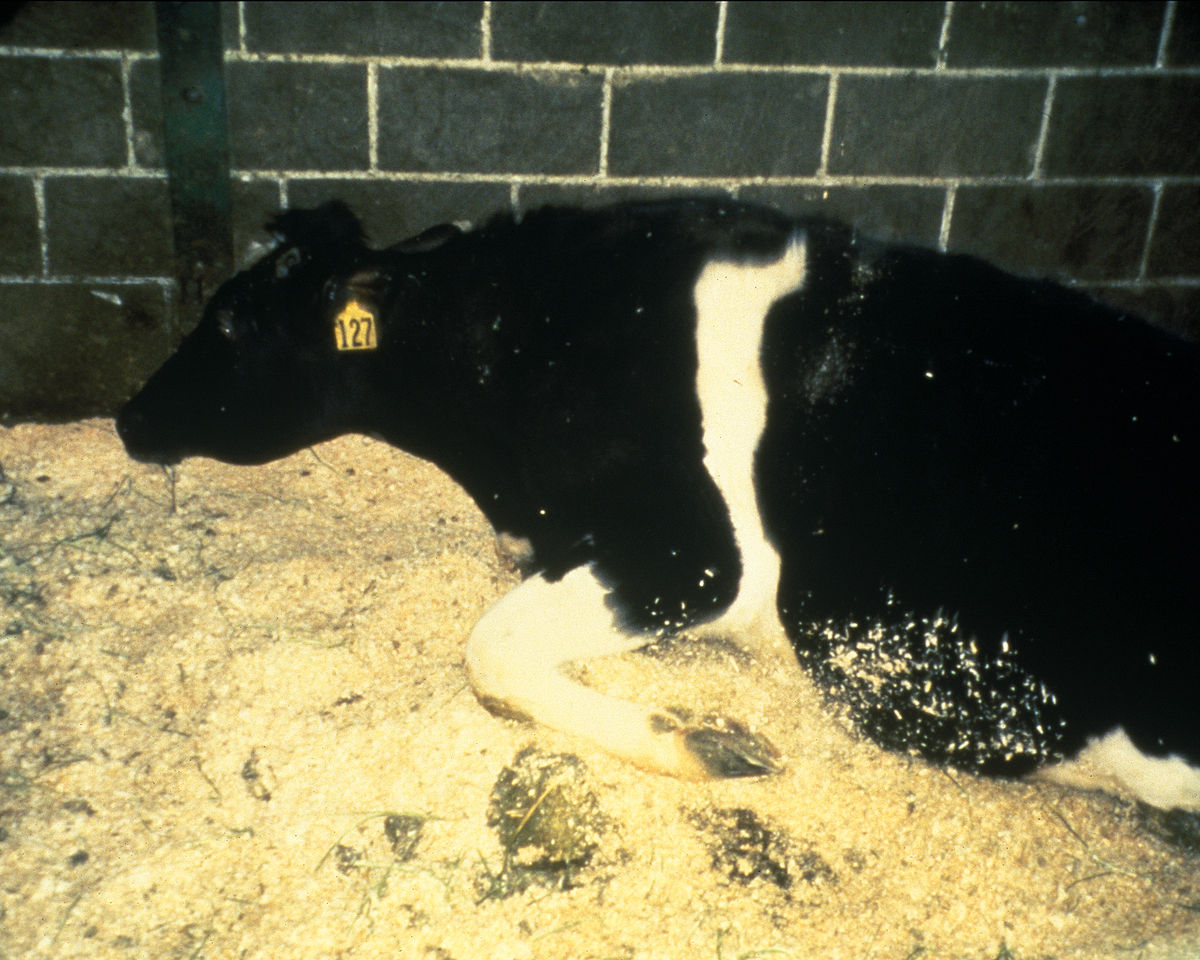
Acidosis
Cow acidosis is a disease associated with rumen acidification. The reasons for its appearance:
- the use of easily digestible carbohydrates in excessive quantities;
- eating spoiled cattle feed containing butyric acid;
- finely chopped feed.
Symptoms of acidosis in cattle:
- loss of activity in the animal, it lies and breathes heavily;
- the scar is dense, the belly is swollen;
- development of diarrhea;
- development of tachycardia;
- the animal falls into a coma.
The disease is associated with improper feeding. The livestock breeder needs to take a responsible approach to the preparation of voluminous feed.
Fascioliasis
Fascioliasis is a disease associated with exposure to the liver of parasites. Symptoms of the disease:
- decreased appetite up to complete refusal of food;
- temperature rise to 41 ° С;
- weakness and decreased activity;
- the amount of milk decreases, up to its complete absence;
- an enlarged liver;
- acute reaction to touch.
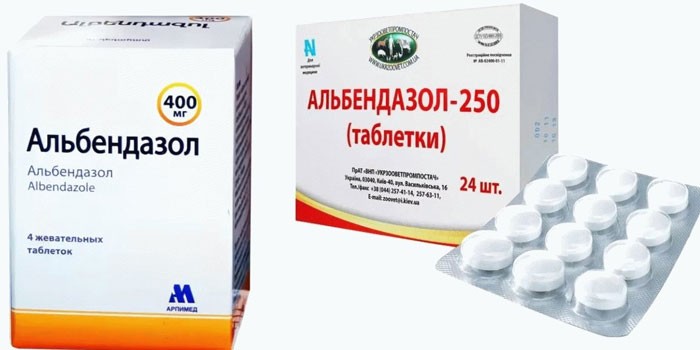
For treatment, albendazole, polytrem is used. Medicines are given according to the instructions. For 1 kg of weight, 10 mg of the drug is taken. A suspension of fazinex is also used at the rate of 8-12 mg per 1 kg of weight.
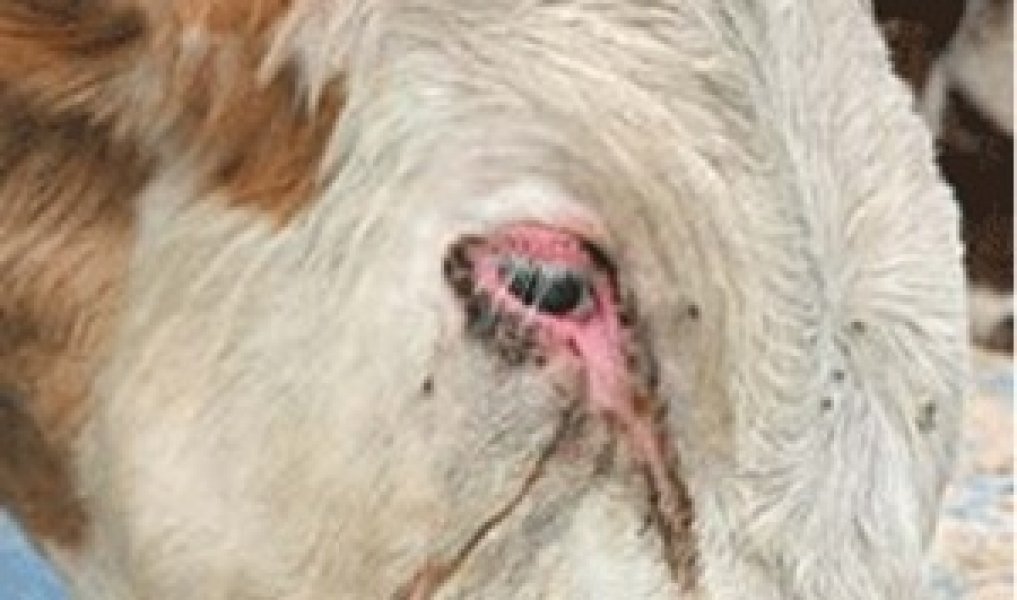
Telyaziosis
Thelaziosis in cattle is one of the types of helminthiasis. It is caused by nematodes, which provoke eye pathologies. Stage one symptoms:
- tearing;
- photophobia;
- the eyes become inflamed.
As a treatment, eye rinsing is done using:
- potassium iodide solution: dissolve 1 g of crystalline iodine in 100 ml of boiled water, add 1.5 g of potassium iodide. Dilute the solution with water to give a total volume of 2 liters. They wash their eyes several times;
- boric acid solution: 3 ml of the concentrate is dissolved in 100 ml of boiled water. The eyelids, conjunctiva and corners of the eyes are washed.
Actinomycosis
Bovine actinomycosis is a disease that is infectious and chronic. It is provoked by a radiant fungus. As a result, granulomatous foci are formed in various organs and tissues, abscesses and fistulas are formed.
Symptoms:
- actinomycoma: the appearance of a tumor on the head, lower jaw;
- the neoplasm extends to the udder, lymph nodes, bone tissue;
- abscesses open outward or down the throat;
- teeth fall out;
- the bones of the skull are deformed.
Treatment can be:
- conservative. It is carried out at the initial stages of the development of the disease. Iodine preparations are injected inside the actinomycoma. Oxytetracycline and polymyxin are also used. Sometimes used intravenous infusion from a mixture of iodine with potassium salt;
- operational - produce excision of the neoplasm with a capsule.
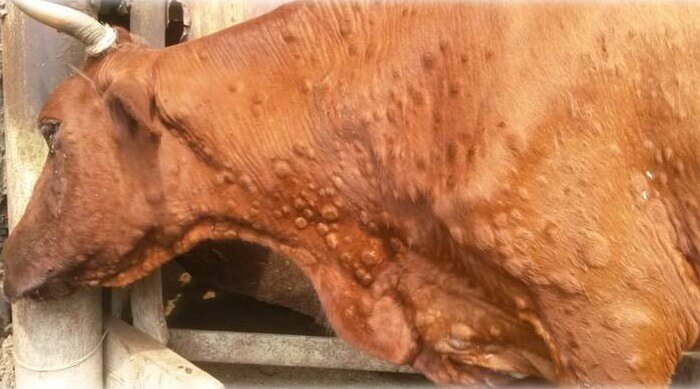
Smallpox
Smallpox in a cow is a disease caused by viruses. The disease affects the mucous membranes of the mouth and nose, as well as the skin of the udder and lips. Symptoms:
- decreased appetite;
- temperature up to 40 ° С;
- anxiety and aggression;
- difficulty in lactation;
- swelling of the udder and nipples;
- while walking, the animal spreads its legs wide;
- the inflammatory process begins with the appearance of small reddish spots, which then turn into a state of papules.
Treatment:
- the use of drugs, mainly antibiotics are prescribed;
- cauterization of ulcers with potassium iodide, brown, chloramine;
- for wound healing, petroleum jelly and ichthyol ointment are used;
- ointments with vegetable oils and glycerin are used to soften the skin.
Babesiosis
This disease is associated with the development of parasitic babesia in organs and tissues. Symptoms of babesiosis in cattle include:
- the temperature rises to 41 ° C;
- mucous membranes are pale, have a yellowish tint;
- fever and fever;
- the body is depleted;
- rapid breathing;
- spotted spotting is present on the mucous membranes;
- frequent heartbeat;
- bloody discharge with urine;
- blood density decreases sharply;
- erythrocytes decrease in the blood.
As a treatment:
- isolate the animal, ensuring complete rest;
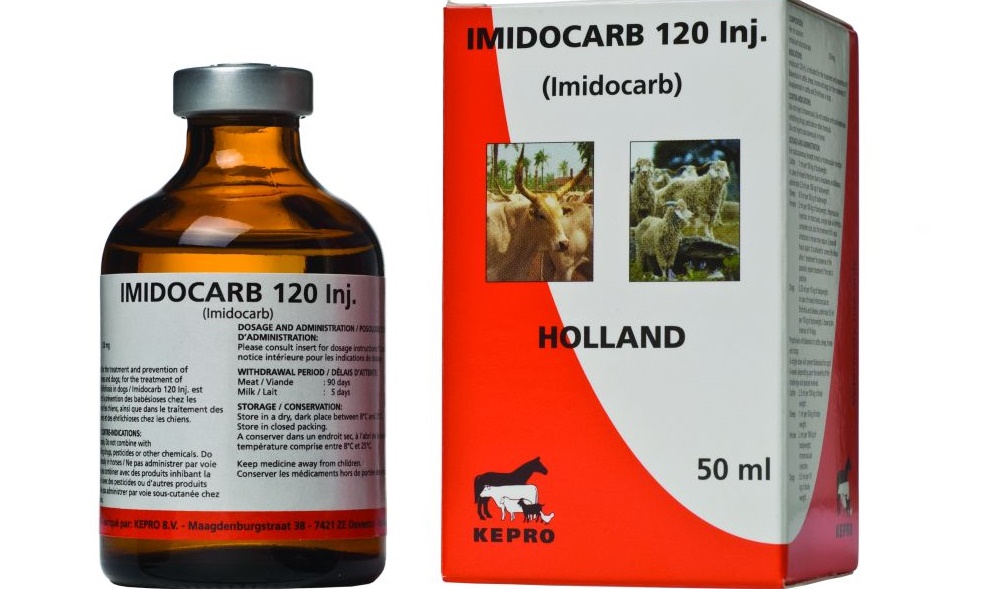
- use drugs acaprin, imidocarb, hemosporidin, tripoflovin;
- control the cattle nutrition.
Rabies
Rabies in cows is a disease that can be transmitted to other animals and humans. In this disease, viruses infect the central nervous system. Symptoms can be violent and calm. When violent, there are:
- behavior change: irritability, manifested by aggression towards other animals;
- salivation;
- frequent urination;
- heavy sweating.
In a calm form, the animal is lethargic, depressed, he has no appetite.
If an infected animal is identified, it is urgently isolated.
Ovarian hypofunction in cows
With this pathology, hormonal activity decreases, which causes a weakening of the manifestation of signs of the sexual cycle. Symptoms of ovarian hypofunction in cows:
- mild sexual arousal;
- violation of the rhythms of the sexual cycle;
- perhaps a strong weight loss of the animal or its obesity;
- the appearance of a persistent corpus luteum;
- reduced ovaries.
Treatment:
- introduction of nutrients, macro- and microelements into the diet of feed;
- introduction of gravohormone;
- the appointment of drugs containing gonadotropic hormones.
Malignant catarrhal fever
The disease causes inflammation of the mucous membranes of the respiratory and digestive tract, as well as the conjunctiva of the eye. In the acute form, the following symptoms appear:
- the mucous membranes of the nose, throat and mouth become inflamed;
- when a virus enters the eyes, the conjunctiva becomes inflamed, the eyes turn red, watery, photophobia appears;
- eyes become cloudy, ulcers appear in them. If untreated, blindness may occur;
- ulcers appear on the nasal mucosa;
- temperature rise up to 42 ° С;
- breathing becomes more frequent, bronchitis appears, pneumonia is possible;
- strong salivation;
- cystitis develops;
- ulcers appear on the genitals;
- lymph nodes enlarge;
- strong excitement or, conversely, depression;
- impaired coordination;
- epileptic seizures or coma may appear.
In the hyperacute form, the animal dies in 3-4 days. In addition to the above signs, cattle have:
- reduction in milk yield;
- violation of appetite;
- diarrhea, there is blood in the stool;
- dry and hot nose.
In the subacute form, the symptoms are the same as in the acute form, only less pronounced.
The infected cow is transferred to a separate room. There are no specific medicines for the treatment of catarrhal fever. Of the symptomatic remedies used:
- caffeine, which is injected for the proper functioning of the heart 2 times a day under the skin;
- 1% boric acid solution is instilled into the eyes;
- a weak solution of potassium permanganate or chamomile is used to disinfect ulcers on the membranes;
- Ichthyol, tannin are used to combat diarrhea;
- 10% calcium chloride solution to reduce edema;
- for the central nervous system alcohol with a strength of 40%.
Vibriosis
Vibriosis is a sexually transmitted disease of an infectious nature. Symptoms of vibriosis in cattle:
- the vagina swells;
- bloody white discharge appears, which is replaced by purulent;
- abortion in the first half of pregnancy;
- delayed afterbirth;
- purulent endometritis;
- vaginitis.
Treatment:
- after an abortion, introduction into the uterine cavity of 50 ml of vegetable oil or fish oil with 1 g of penicillin. Enter 3-4 times with an interval of 2-3 days;
- intramuscular injection of penicillin 3 times a day, 4 thousand units per 1 kg of body weight.
Pyroplasmosis
The source of infection is ticks. Piroplasms enter the animal's body, which infect erythrocytes and lymphocytes.
Symptoms:
- refusal to eat;
- intense thirst;
- temperature rise up to 42 ° С;
- it is difficult for the animal to move;
- milk yield decreases;
- pulse quickens;
- blood vessels increase on the mucous membranes;
- increased lacrimation.
A sick animal should be given clean water, sour milk and vitamin supplements. For cattle, flavacridine or trypaphoavine is prescribed, which are given intravenously. Berenil is injected intramuscularly to calves. Glauber's salt restore the work of the heart. To reduce thirst, the animal is given sodium chloride, and to increase immunity - vitamin B12.
Foot and mouth disease
Foot and mouth disease is a viral disease that causes excessive salivation. A person can become infected with this ailment.
Symptoms:
- fever;
- the membranes of the nose and mouth become inflamed;
- foam appears at the mouth, and saliva flows strongly;
- damage to the mammary glands;
- with normal feeding, weight is reduced.
The animal is isolated. The mucous membranes are treated with a solution of acetic acid or potassium permanganate. The hooves are regularly washed and smeared with tar. There are no drugs that treat this disease, so drugs are used to eliminate the symptoms.
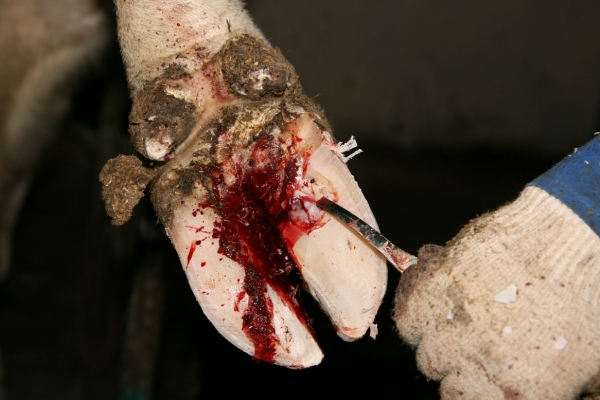
Nicrobacteriosis
This disease is contagious. The disease first affects the skin and tissues, and then the mucous membranes and internal organs. The causative agent is anaerobic stick. Only a specialist can determine the disease.
General signs of the disease:
- refusal to eat;
- lethargy;
- general malaise;
- decreased productivity;
- the animal limps and tightens its hooves;
- intense purulent discharge;
- when feeling the limbs, the animal has pain;
- ulcers appear on the skin and mucous membranes.
The sick animal is isolated. The hooves are treated surgically (pus and deformities are removed). The affected cavities are sanitized using antimicrobial agents. They are also treated with antiseptics in the form of powders and powders. The drug dibiomycin is injected intramuscularly.
Anaplasmosis
Anaplasmosis is caused by anaplasma, which affects the function of the mammary glands. It is a blood-parasitic disease that occurs with anemia, exhaustion and fever.
Symptoms:
- metabolic disease;
- the animal experiences oxygen starvation due to damage to erythrocytes;
- iron deficiency occurs;
- temperature rise to 41 ° С;
- mucous membranes acquire a yellowish tint.
Parasites are killed with antibiotics terramycin, oxytetracycline. The drugs are served once a day at the rate of 6-10 thousand units per 1 kg of weight. They also suppress the activity of parasites with the help of oxshel, tetradur, oxytetra-200. Take 1 time in 3-4 days.
Hypodermatosis
This disease is parasitic, which is caused by gadflies of the genus hypodermis. In another way, the disease is called a subcutaneous gadfly. The affected areas become inflamed, fertility decreases, and general poisoning of the body occurs. Symptoms:
- swelling of the esophagus;
- belching;
- refusal to feed;
- paralysis of the hind legs;
- improper swallowing;
- staggering gait;
- the neck protrudes.
After a gadfly injury, a painful seal forms under the skin. One animal can have up to 200 such balls.
Dictyocaulosis
With dictyaculosis, parasites (helminths) affect the respiratory organs of herbivores, more often young animals. Among the symptoms of the disease are:
- rapid breathing;
- diarrhea;
- violation of appetite;
- mucus is secreted from the nasal cavity;
- temperature rise to 41 ° С;
- wheezing is heard in the chest when listening;
- the first fortnight there is a slight cough, which gets worse over time.
In especially severe cases, the animal is constantly lying, coughs heavily, foam comes out of the mouth, breathing is heavy with wheezing.
To eliminate the parasite, a solution of crystalline iodine is used. To prepare it, take a container with dark walls. A solution of crystalline iodine is diluted in it in 1.5 volumes of potassium iodide. Distilled water is poured in in a ratio of 1500: 1. The mixture is heated to 30 ° C. Immediately after preparation, the drug is injected into the trachea with a syringe. For an animal up to a year, the dosage is 80 ml, over 130 ml. Also used drugs such as 40% solution of loxuran, divezid, ditrazine citrate.
Chlamydia
This disease is infectious. It is manifested by frequent rhinitis, polyarthritis, gastroenteritis, conjunctiva, bronchitis.
The symptoms of the disease depend on its form:
- respiratory: temperature 40-41 ° C, serous discharge, cough, swelling of the nasal mucosa, rapid breathing, swelling of the eyelids;
- intestinal: temperature 40 ° C, diarrhea, refusal to eat, depression, ulcers appear on the mucous membrane;
- genital: delayed afterbirth, abortion;
- encephalitis: damage to the central nervous system, the animal has uncoordinated movement, convulsions in the body, trembling of the head;
- conjunctivitis: ordinary conjunctivitis with lacrimation.
Treatment is carried out with oxytetracycline, convalescent serum is administered. In case of bronchial damage, aerosol preparations are used.
Bursitis
The onset of the disease occurs after injury. The symptoms of the disease depend on the form:
- purulent: tendons swell, limbs tremble, lameness and severe pain;
- aseptic: an inflammatory process begins in the damaged joint;
- ossifying: swelling in the joint area begins to acquire a spherical shape, the ratio of calcium and phosphorus changes sharply in the animal;
- serous: a yellow liquid forms in the damaged area, severe pain, lameness, an increase in the size of the limb.
In aseptic form, alcohol dressings are used, antibiotics are injected into the sore spot. Hydrocortisone is used to correct the symptoms. Warming compresses will help the regeneration process. It is also recommended to massage the sore spot. When treating a purulent form, dead tissue is removed. To relieve pain, a solution of novocaine is administered.
Atony
With this disease, the work of the stomach is disrupted. Symptoms:
- refusal to eat;
- lack of activity;
- reduction in milk yield;
- weight loss;
- temperature 40 ° C.
The animal is transferred to a fasting diet for a day. Water is served without restrictions. To restore the alkaline balance, salt is added to the liquid in the amount of 10 g per 1 bucket. Walking 2 hours a day is obligatory. The cow is given a remedy based on Glauber's salt. For 1 liter of boiled water, take 200 g of Glauber's salt. Then 400 g of vegetable oil is added to the solution.
Spongiform encephalopathy
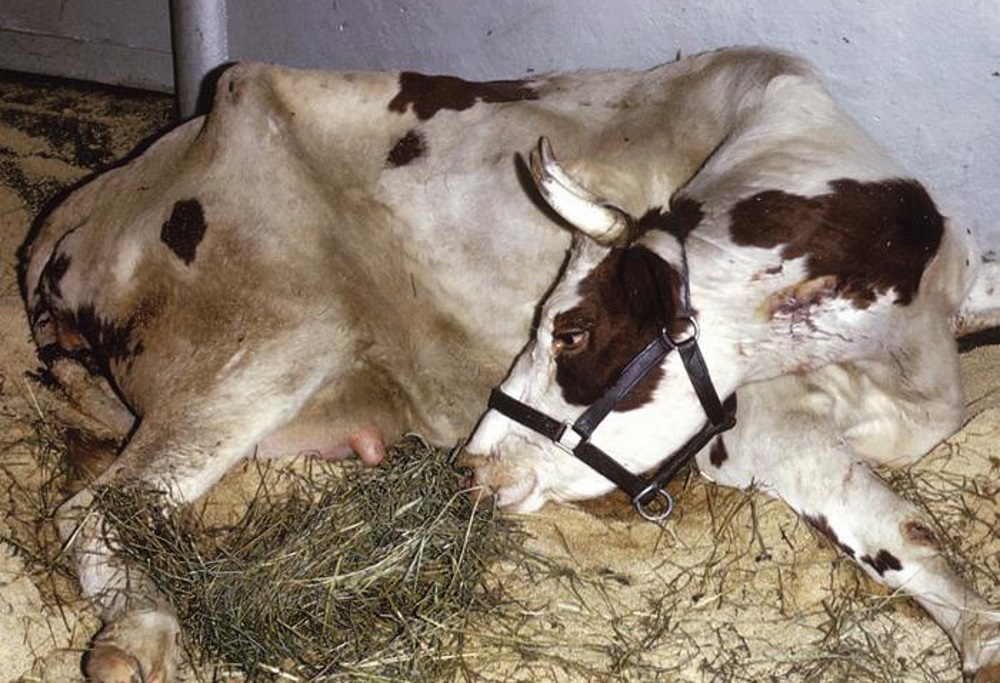
This disease is infectious, develops slowly, damage to the central nervous system occurs, one hundred percent death. The incubation period can last up to 8 years.The course of the disease passes without an increase in temperature, and a normal appetite is maintained. Despite this, milk yield is declining. There are 3 types of nervous manifestations:
- first: the appearance of fear, nervousness, aggressiveness, teeth grinding;
- second: trotting movements, bowing of the hind limbs;
- third: violation of sensitivity.
Treatment for this disease is ineffective.
Vaginitis
With vaginitis in cattle, the vagina becomes inflamed due to infection. Symptoms:
- anxiety;
- frequent urination;
- itching in the vagina;
- swelling of the genitals;
- the vulva has a deep red color;
- mucous, purulent, sometimes bloody vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor.
Treatment is carried out locally. In advanced cases, antibiotics are used. For irrigation of the mucous membrane, disinfectants are used. For douching, a weak solution of potassium permanganate is used (2 crystals are taken for 1 liter of water), furacilin (4 tablets per 1 liter of water), vagotil (15 ml per 1 liter of water). The solutions are injected into the vagina using a pear.
Listeriosis
The disease affects the nervous system. Listeriosis has several forms:
- septic: a sharp rise in temperature, depression and apathy, refusal to eat, diarrhea, convulsions;
- genital develops in pregnant cows. Against its background, secondary diseases arise, among which the most common are metritis and mastitis;
- nervous listeriosis: fever, loss of appetite, depression, lacrimation, mucous membranes have a bluish tint, body trembling, impaired coordination.
There is no special medicine to fight this disease. The drug is selected based on the age and form of the disease. Among the antibiotics used are terramycin, biomycin, tetracycline.
Mycoplasmosis
The disease is provoked by mycoplasmas - microorganisms that do not fit the description of either bacteria or viruses. The disease affects the respiratory system, pneumonia, arthritis, mastitis, endometritis develop.
Symptoms:
- oppression:
- refusal to eat;
- temperature rise;
- dry cough;
- wheezing;
- sneezing;
- rapid breathing.
With inflammation of the cornea of the eye, fear of light, tearing, reddening of the cornea is manifested.
Moraxellosis
Moraxellosis, or infectious keratoconjunctivitis, is manifested by karatal conjunctivitis, purulent ulcerative keratitis. In animals, the conjunctiva turns red and swells. The cornea is cloudy and rough.
As a treatment, ointments with broad-spectrum antibiotics (tetracycline, erythromycin, tylosin) are used.
Aymeriosis
This is a parasitic disease that affects the digestive system. In acute form:
- the animal is oppressed and weakened;
- there is mucus and blood in the feces;
- temperature 40 ° C;
- increased frequency of bowel movements;
- the mucous membranes of the mouth and nose have a bluish tint.
In the chronic form:
- refusal of water and feed;
- exhaustion;
- mucous membranes are bluish in color;
- slight increase in temperature.
The animal is isolated. A special diet including vitamins is applied. Phthalazole or sulfadimezine, norsulfazole are used for 5 days.
Echinococcosis
The disease is chronic, parasitic in nature, which is caused by cestodes that settle in various organs. There are no pronounced signs. If the bladder in the lungs is damaged, the animal begins to have shortness of breath and a prolonged cough. With liver damage, its increase and soreness are noted. The animal is losing weight. It is impossible to cure the disease.
Plague
A disease with a long history. It is viral in nature. The disease affects the intestines, digestive system, respiratory tract and skin. In places of lesion, necrotic processes appear and ulcers appear, which are covered with a layer of dead epithelium. The plague has several stages:
- the first: a rise in temperature up to 41 ° C, agitation, rapid breathing and palpitations, refusal to eat, dry skin on the nose, red throat and mucous eyes;
- second: the appearance of ulcers on the conjunctiva, on the vulva, in the nose and mouth, frequent sneezing, profuse salivation;
- the third: normalization of temperature, severe diarrhea, there is blood in the feces, mucus, during bowel movements, the animal feels pain, breathing is frequent and heavy.
Plague treatment is regulated by international veterinary legislation.
anthrax
Infection. In the transient form, the animal dies in a few minutes. Signs:
- temperature 41 ° C;
- sharp excitement turning into apathy;
- increased heart rate;
- mucous membranes have a blue tint.
In acute form:
- rapid breathing and heartbeat;
- decreased appetite;
- temperature rise up to 42 ° С;
- swelling of the throat or abdomen;
- cessation of milk production.
Infectious rhinotracheitis
The disease often develops on dysfunctional farms. It affects the respiratory tract, genitals, and the central nervous system. The animal's temperature rises to 42 ° C. The animal is depressed, he has a severe cough, heavy breathing, serous nasal flow.
As a treatment, a hyperimmune serum is used, which is injected under the skin in an amount of 2 ml per 1 kg of body weight. It is also possible to introduce into the nasal cavity at the rate of 2-4 ml per 1 kg of weight. To combat pathogens of secondary diseases, antibiotics and sulfa drugs are used.
Preventive measures
As a prevention of cattle diseases:
- keeping the room clean;
- conducting a sanitary assessment;
- every six months the room is disinfected;
- checking milk for brucellosis, tuberculosis;
- 2 times a year, cattle are fed with anthelmetics;
- conducting veterinary examinations;
- in the summer, the animal is treated with repellents to protect it from insects;
- administration of vaccines.
Breeder tips
In addition to the above:
- timely vaccination is required;
- the animal should not be given a lot of bran and other milk-producing feed;
- with traumatic bruises, a compress of vinegar diluted with water helps well;
- to replenish the lack of vitamins, carrots, yellow pumpkin varieties, oats, wheat are introduced into the diet;
- cereals are given milled, and hay - milled.
Diseases in cows and their symptoms are very diverse. Some of them are incurable and cause great damage to the household. Therefore, compliance with the basic rules of care and preventive measures is simply necessary to preserve the health of animals.