Content:
Rabbit breeding is a pretty lucrative business. However, these animals are demanding in terms of keeping conditions and often get sick. One sick rabbit can infect all livestock, leading to massive death. Therefore, the breeder should know about the main diseases of his wards, be able to treat and prevent them.
Causes of rabbit diseases
Rabbit diseases are one of the most common problems faced by both experienced and novice farmers. Making a diagnosis at home is difficult because many diseases have similar symptoms. Therefore, it is better not to self-medicate, but to go to a veterinary clinic.
The following are the most common causes of animal diseases:
- content in inappropriate conditions;
- malnutrition, nutritional deficiency, vitamin deficiency;
- poisoning with poisonous plants or poor quality (stale food);
- weakening of the body in pregnant and lactating rabbits;
- congenital malformations and intrauterine infections in rabbits;
- invasion of parasites that enter the body with food or water.
The most common cause is inadequate animal husbandry.
Differences between a sick rabbit and a healthy one: signs of the disease
An experienced farmer will immediately notice the disease of rabbits, since a sick animal differs from a healthy one both in appearance and behavior. Below are the main differences between a sick animal and a healthy one:
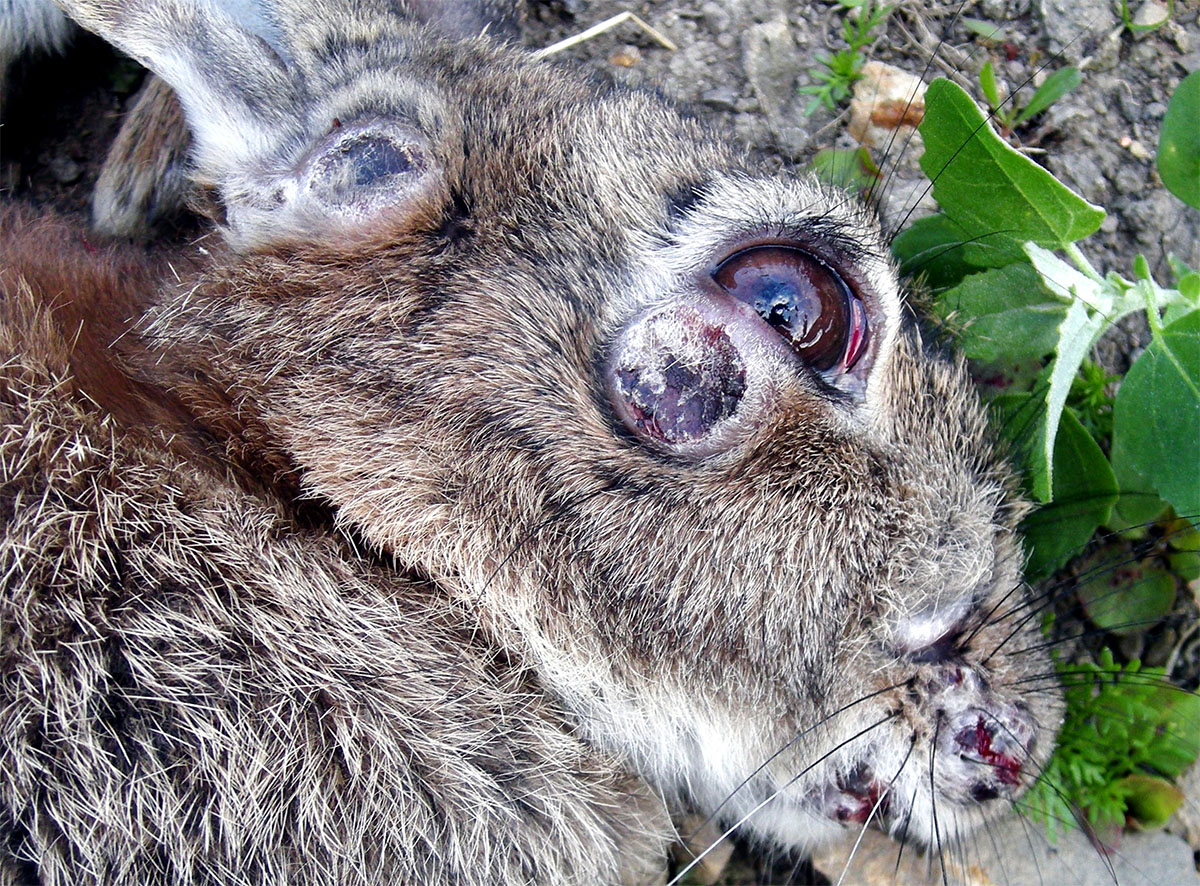
- In a healthy animal, all mucous membranes are clean, there is no discharge. Sick animals often have discharge from the eyes, the mucous membrane of the mouth and nose becomes wet.
- Usually rabbits are quite active, but a sick animal may lose interest in the world around it and lie for a long time without moving.
- If the animal is not upset in the stomach and intestines, the stool will be hard in the form of characteristic dry "peas". If the rabbit has problems with the digestive system, the stool can be thin, offensive with a lot of mucus, often irritation of the anus and severe itching in this area join such stool.
- There is often no discharge from the ears. But, if a dangerous infection has made its way into the rabbitry, mucous or purulent discharge, weeping wounds or sores can be noted inside the auricles, which cause great discomfort to the animals.
- The heart of a strong, sturdy animal beats evenly and calmly. In animals weakened by the disease, there may be a too frequent or, conversely, too rare pulse.
However, one should not assume that in the absence of the above signs of diseases, rabbits are absolutely healthy. The main difficulty in the treatment and diagnosis of diseases in these animals lies precisely in the fact that many dangerous infections at the very beginning are asymptomatic or have a long incubation period. Therefore, if in appearance everything is in order with the animal, but it seems to the farmer that the rabbit behaves unusually (refuses food, has become lethargic), the veterinarian may prescribe tests.
Rabbit disease symptoms
Rabbit diseases, symptoms and their treatment are things any farmer should know about. Many ailments develop rapidly.It is necessary to treat in a timely manner, because, having lost time, you can lose all livestock overnight.
Below are the main symptoms of the most common diseases:
- An upset stomach or poisoning is manifested by frequent stools, itching in the anal area, vomiting with a foul smelling vomiting, and severe bloating.
- Skin diseases can be diagnosed by the presence of sores on the skin and mucous membranes, as well as in connection with complete or partial loss of hair (this is most often the case with ringworm and other forms of lichen).
- With helminthic invasions, animals become lethargic, their appetite decreases, they look weakened.
- Respiratory diseases are manifested by rapid breathing, profuse nasal discharge, general weakness and fever.
Each of these symptoms can be observed with a whole group of diseases, so you should not engage in self-diagnosis based on 1-2 signs of the disease. After the onset of alarming symptoms, you should immediately consult a specialist.
Types of rabbit diseases: invasive, infectious and non-infectious
Treatment of rabbits should only be started after diagnosis. Even if the disease in itself is not contagious and not dangerous to other animals, the sick individual should first of all be isolated from healthy ones. But this should only be done if the veterinarian has diagnosed an infectious disease. Noncommunicable diseases are not transmitted from one individual to another.
Experts identify 3 large groups of diseases that rabbits of different breeds are susceptible to:
- Infectious diseases are caused by a virus or bacterium, spread rapidly and can cause the sudden death of an entire livestock.
- Non-infectious are not contagious. This group includes, for example, allergic reactions to a certain type of food, poisoning, disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system, vitamin deficiency.
- Invasive - diseases caused by the ingestion of dangerous parasites. The most common disease is the so-called "helminthic invasion". However, what farmers call "worms" in everyday life, in professional language can mean a wide variety of parasites. The exact type of invasion can only be determined by a doctor based on blood tests, feces, and mucous secretions. A specialist examines biological material under a microscope and identifies a parasite that lives in the animal's body.
Most common diseases
The most common diseases of these animals are:
- rabbit pasteurellosis (an infection that causes hemorrhagic inflammation);
- eimeriosis of rabbits (a disease caused by the vital activity of an intestinal parasite, similar to helminths);
- rabbit psoroptosis (an invasive disease in which the ears of animals itch, wounds and ulcers appear on them).
Deprive in rabbits is also not uncommon, and it can be caused by two factors: the penetration of infection into the body or metabolic disorders associated with poor nutrition and lack of vitamins. In young animals, an inflammatory disease of bumblebees is often found, in which ulcers appear on the oral mucosa. If left untreated, this disease, which at first goes unnoticed, can turn the ulcers into an abscess.
Animals often suffer from passalurosis. This is a disease in which rabbits develop diarrhea and severe itching in the anus. It is often found in decorative rabbits with an improperly organized diet.
Animals can also get sick with neurological diseases.In these cases, their front or hind limbs often fail. Paresis of the paws is quite common, especially in weakened animals. It also happens in pregnant rabbits. It is easy to diagnose paresis: first, the sick animal begins to fall slightly on its hind legs, and then drag them along with it while moving.
The fungal disease mycoplasmosis is manifested by a severe runny nose and inflammation of the eyes. Rabbit fur in sick animals becomes dull, the color of the skin changes. The incidence of fungal infections increases if animals are kept in a room with high air humidity. The fungus is dangerous because it often affects the bronchi and lungs, and causes acute and chronic respiratory infections.
Medicines
Ditrim is commonly used to treat the most common diseases. If a farmer bought ditrim from a veterinary pharmacy, the instructions for use for rabbits must be strictly followed. Ditrim for rabbits is inexpensive, it can always be found on the free market under the trade name Ditrim. For 1 liter of water, 1 ml of medicine is used.
- Novocain is often used to relieve pain and severe itching. The dosage is calculated by the veterinarian depending on the weight of the animal.
- Lactic acid is used to normalize metabolism in animals. If a veterinarian has prescribed a remedy such as lactic acid for rabbits, read the instructions for how to give it. Usually, a 5% solution of the substance is used to treat and prevent infections.
- Eimeterm for rabbits is actively used in veterinary practice. The medicine is produced in the form of a suspension, which is applied to the root of the tongue, opening the mouth of the animal.
- Enroflon is used to fight infections. For 1 liter of water, 0.5 ml of medicine is used. The drug is given to animals together with water.
If animals are abruptly, rather than gradually transferred to a new premix or any other type of food, they may have stomach problems. Chiktonik, a drug that contains bifidobacteria, helps well with indigestion. The drug is effective for diarrhea, constipation and bloating in both adults and young animals.
For lesions of the skin, anus and genitals, metronidazole is used. The drug is diluted in water: 0.5 ml per 1 kg of live weight. The course of treatment is several days.
For the expulsion of parasites, the drug ivermectin (trade name ivermec) is used. Take 0.1 ml of solution per 5 kg of weight. The drug is administered intramuscularly. Also amprolium has proven its effectiveness in the fight against parasites. For 1 ml of suspension, 0.5 l of water. The resulting solution is fed to sick animals for 2-3 days.
Disease prevention
Diseases in domestic rabbits are much easier to prevent than to cure. To prevent animals from getting sick, you need:
- do not lead strangers into the rabbitry, as they can introduce dangerous bacteria and viruses on the soles of shoes;
- daily observe the appearance and well-being of animals;
- make sure that the animals always have enough fresh and clean water;
- promptly remove the remnants of uneaten feed, as it is a potential source of infection.
It is better to make the floor in the rabbitry mesh to make it easier to clean the room of droppings.Also, at the entrance to the room, you need to lay a rubber sponge mat and moisten it daily with any disinfectant from a veterinary pharmacy.
Rabbits should not be kept in close proximity to other rodents (nutria, chinchillas), because some of their diseases can be transmitted to rabbits.
It is also worth regularly disinfecting the cells and premises, giving the animals antiparasitic drugs. Before you bring an animal bought in the market or from a private owner to the rabbitry, you need to keep it in quarantine for some time - in isolation from others.
If the rabbits are sick, don't panic. The main thing is to contact a specialist in time to make a diagnosis and take all the necessary measures. Then the disease will not have time to spread to other animals.