Content:
Stomatitis in rabbits is a common pathology that is fatal in most cases. Young animals most often suffer from an infectious form of the disease, and adult rabbits suffer from an autoimmune and traumatic type of disease. Stomatitis in a short period of time depletes the body of the animal, slows down their growth. For a long time, rabbits who have had stomatitis remain carriers of the virus, which provokes the development of repeated outbreaks of the disease. Treatment for stomatitis in rabbits should be started as soon as possible to save the lives of the animals.
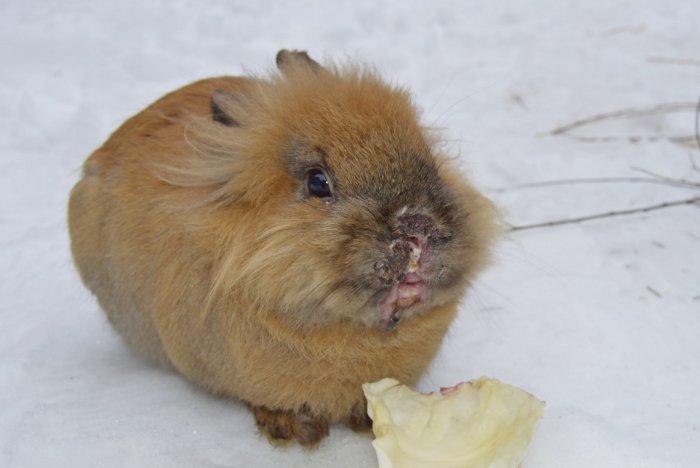
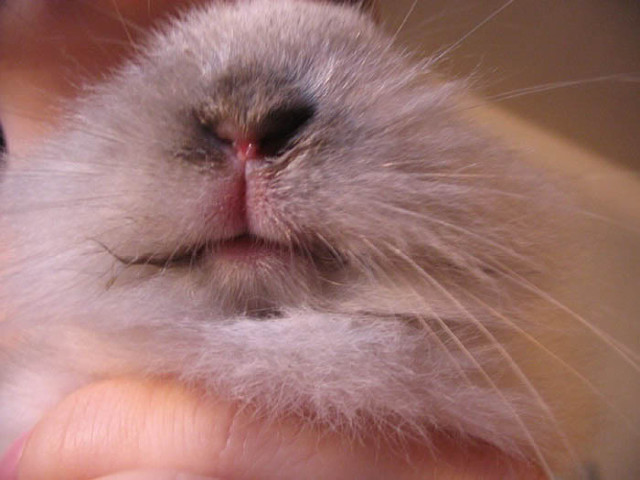
The rabbit has a wet face - the main symptoms of woodlice
The final sign of stomatitis is considered to be a wet face. The initial symptoms of the disease include:
- the appearance of a white coating on the surface of the tongue of animals;
- a change in the shade of plaque from white to grayish-red;
- increased salivation;
- redness of the nasolabial part;
- wet rabbit nose;
- the appearance of sticky sputum of the wool around the mouth in the neck, chin;
- passivity of pets, they spend a lot of time in the corner of the cage;
- itching of the tongue, as a result of which the rabbits begin to scratch their muzzle with their paws;
- decreased appetite and sudden weight loss due to painful sensations that appear while chewing food;
- the formation of purulent ulcers in the oral cavity;
- oppression;
- the occurrence of diarrhea.
As soon as the first signs of the disease were detected, it is important to immediately take measures to cure the disease. To begin with, it is worth removing sick rabbits in separate cages. Then you should start treating sick individuals and animals that were in the same room with infected rabbits. Woodlice in rabbits is a dangerous ailment that requires immediate treatment.
Causes of stomatitis
Stomatitis in rabbits can occur against the background of:
- Viruses occurring in an acute form and causing death in animals. This type of virus can be transmitted by airborne droplets. The spread of the infection is quite fast.
- Injury to the mucous membranes of the oral cavity with a sharp object or a pointed part of the teeth, which occur with malocclusion.
- Metabolic disorders and weakened immunity.
Forms of the disease
How to treat biting midsection in rabbits correctly is often asked by animal owners. The method of therapy is selected depending on the form of the disease. There are 2 forms of stomatitis:
- Mild infectious, in which rabbits recover on their own. As a rule, the owner of rabbits does not notice the development of stomatitis. The ulcers in the oral cavity are not deep, so they are not striking. Itching is insignificant, and the painful sensations practically do not bother the animals. Salivation with a mild infectious form is minimized. After a couple of days, the health of the rabbits is restored. Animals become mobile, their body weight grows rapidly due to the appearance of a good appetite. The animal's nose becomes soft and warm again. To speed up recovery, you will need to treat the oral cavity.
- A severe form in which the rabbits die in 5-7 days if treatment was not started in a timely manner.The general condition of the animal begins to change with an increase in salivation. The rabbit becomes motionless and spends almost all the time in the corner of the cage. The sick individual constantly moves its lips, from the side it seems that the animal is chewing food. Rabbits experience unpleasant painful sensations while eating. As a result, animals stop eating, and dramatically lose body weight. Foamy saliva appears on the edges of the lips, under the lower lip and in the neck area, the coat becomes sticky, slobbering and moist. The rabbit is itchy and constantly scratches its muzzle with its paws. Its coat loses its luster and becomes unattractive. A few days after the onset of severe stomatitis, the animal begins uncontrolled diarrhea. If you start therapy in a timely manner, you can achieve recovery of rabbits after 10-14 days. The coat of a sick individual retains its stickiness for a long period of time. In some cases, hair loss may occur in the neck area. In place of sores, traces may remain for a long time, after which scars form.
Consequences of stomatitis
The consequences of mild and severe stomatitis have a number of differences. With an easy stage of the disease, the intervention of veterinarians is not required. The immunity of rabbits is able to overcome the disease on its own, therefore, it is not recommended to give medication to sick individuals. As a rule, self-recovery occurs on the 6-7th day. No negative consequences are observed.
With severe stomatitis, rabbits die in most cases. To prevent the occurrence of a severe form of the disease, it is important to systematically disinfect:
- cells;
- inventory;
- premises;
- drinkers.
Treatment of the disease
What to do if a rabbit has a wet nose if sores are also found in the oral cavity. After diagnosing an infectious type of stomatitis or the appearance of a wet face in animals, therapy should be directed to:
- Elimination of inflammation that develops in the oral mucosa. For this purpose, veterinarians use a weak solution of potassium permanganate for washing and a solution of "Lugol with glycerin" to lubricate the ulcers. You can buy drugs in any pharmacy chain. The procedures should be done 4 times a day for 10 days. Lugol helps to disinfect, dry the skin and eliminate the inflammatory process. Glycerin at the same time prevents burns and accelerates the healing process.
- Rabbits have a wet face with what to treat to help the animal. When saliva flows strongly and ulcers are visible in the oral cavity of sick individuals, you can pour powders like "Biomycin" or "Streptomycin".
- If a wet face is observed in rabbits, treatment should be aimed primarily at increasing immunity. To do this, veterinarians advise using immunostimulating drugs like Fosprenil and Roncoleukin.
- How to treat wood lice in rabbits. In order to enhance the anti-inflammatory effect in infectious stomatitis, drugs such as Traumeel, Travmatin, Liarsin and Echinacea compositum are used.
- For the treatment of severe forms of the disease, veterinarians use antibiotics like Baytril and Biomycin.
- Treat the oral cavity with Tetracycline.
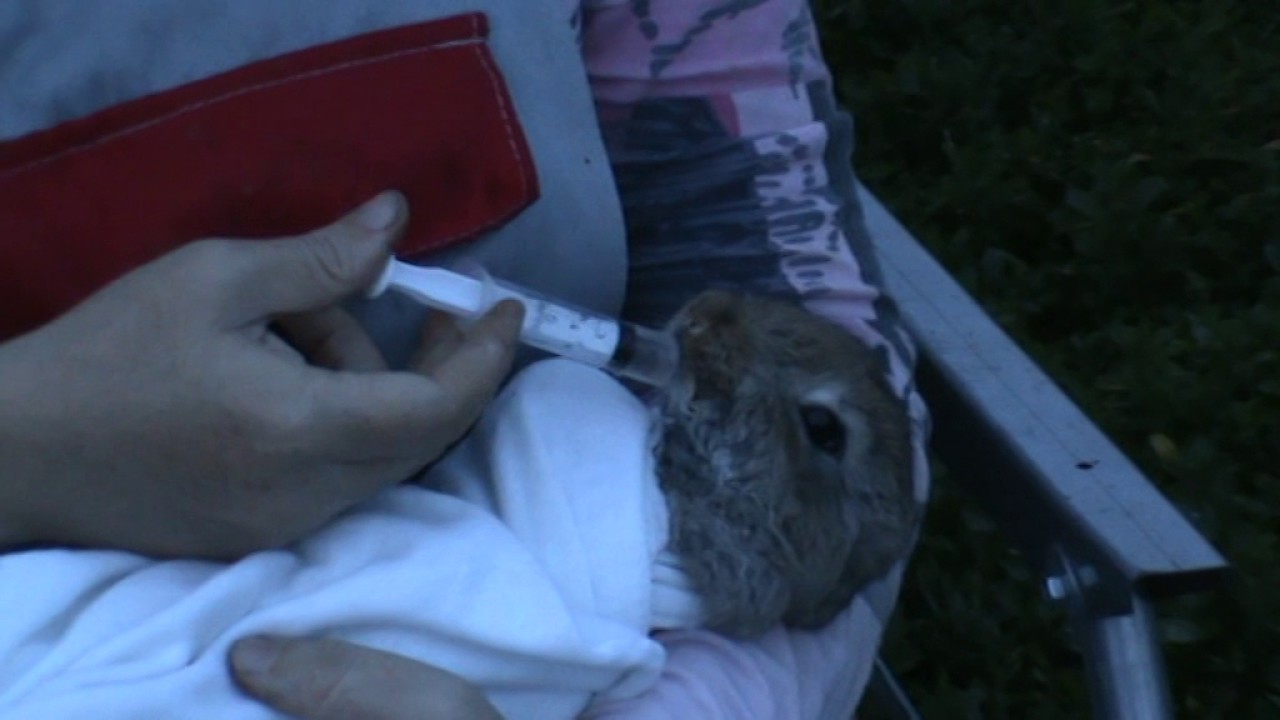
- If a sick individual is emaciated, a biting midge is found in rabbits, experts recommend subcutaneously or intravenously to inject a drip injection of saline and glucose (5%). In order to accelerate recovery, metabolic stimulants can be used, which include Catosal, Mikrovitam and Gamavit.
- Wet muzzle in rabbits treatment in this case should be immediate. After undergoing antibiotic treatment, it is important to use drugs that help restore the intestinal microflora (Lactoferon and Vetom).
- Woodlice in rabbits than to treat to eliminate soreness. Sprinkle sores with Nystatin several times a day, why not use such an effective remedy in treatment.
How to treat a wet face in rabbits correctly so as not to harm the animal's body. If there is a protracted course of the disease in order to eliminate the inflammatory process of the skin, you can use furacilin or potassium permanganate for rinsing and lubricating the inflamed skin with Levomekol, Kremgen or Levosin.
Folk remedies for treatment
Often, in the treatment of rabbits for stomatitis, owners use folk methods. The most popular folk remedies include:
- Apidermine, a remedy made on the basis of bee products, which effectively copes with the treatment of ulcers, burns and suppuration, will help cure woodlice. Apidermine helps to eliminate spasms and inflammation. With the help of the drug, you can increase immunity and speed up the healing process.
- Daily treatment of the oral mucosa with propolis-based ointment, a folk method that will help you quickly heal.
- To speed up the healing process of ulcers, it is worth using decoctions based on medicinal chamomile, sage, calendula and oak bark. The broth should be systematically poured into the rabbits with a syringe (without a needle) instead of water.
- Drinking rabbits with broths based on stellate will help cure animals of a dangerous infectious disease.
- When a wet face appears in animals, we carry out treatment using copper sulfate (2%) and potassium permanganate.
- Cages and rabbit equipment should be systematically treated with a solution of slaked lime or a special disinfectant. The main condition for breeding any animals is cleanliness in their premises.
- Streptocides can be used to treat stomatitis in rabbits. Half a tablet is crushed to a powdery state and poured into the mouth of a sick individual. The treatment procedure is repeated after 9-10 hours.
Prevention
To prevent the onset and development of stomatitis in rabbits, it is important to use preventive rules:
- Systematically clean and disinfect cages, premises, equipment and drinkers. The bedding should be replaced in a timely manner, and the inventory should be cleaned daily.
- Disinfection of walls, floor surfaces and feeders 3-4 times a week.
- Every 3 days, conduct a detailed examination of the animals for deviations.
- Every 7 days, water the rabbits with a weak solution of potassium permanganate.
- As soon as the young are removed from the rabbit, it is important to urgently vaccinate.
- Eliminate contact of recovered individuals with healthy rabbits.
Observing the listed preventive measures, you can avoid such a dangerous ailment for rabbits as stomatitis.