Content:
Chickens in every yard in rural areas are common. Often, laying hens at home are affected by diseases. However, not all owners of private farmsteads understand how to properly treat chickens.
Bird care at home
Taking good care of your poultry will help you avoid spending money on medication. In order not to have to save chickens from diseases, it is important to observe preventive measures. Adults and pullets are recommended to be kept separately. Providing vitamin food will protect you from ailments.
When a chicken is sick, it is isolated from other individuals. If the treatment of chickens does not bring the desired result, the only way out is deliverance: they are destroyed or burned. Be sure to disinfect the chicken coop. This procedure is done monthly. Insulation of the barn is mandatory in winter.
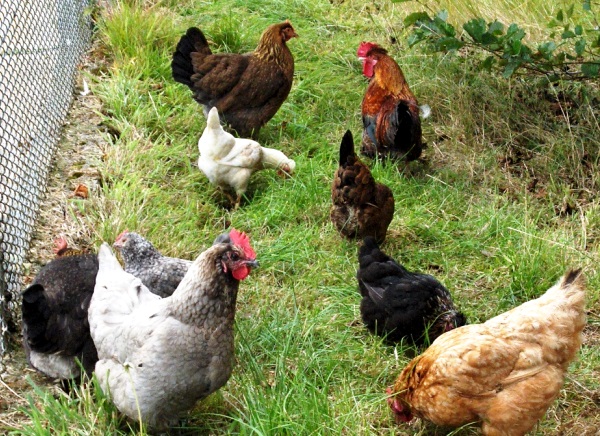
Preventive measures are taken promptly to avoid the death of the chicken population. The chickens kept on the farm are carefully examined to identify signs of illness and timely treatment.
What do the symptoms say?
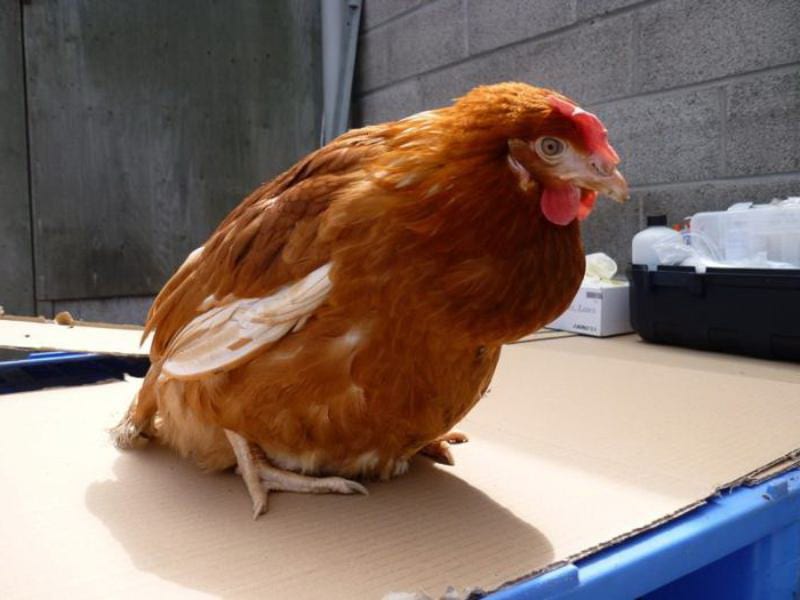
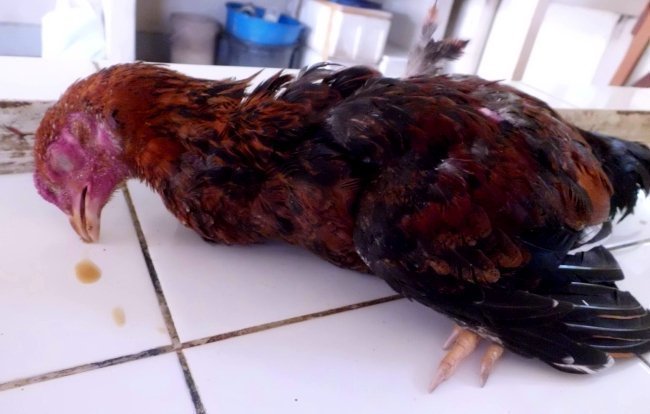
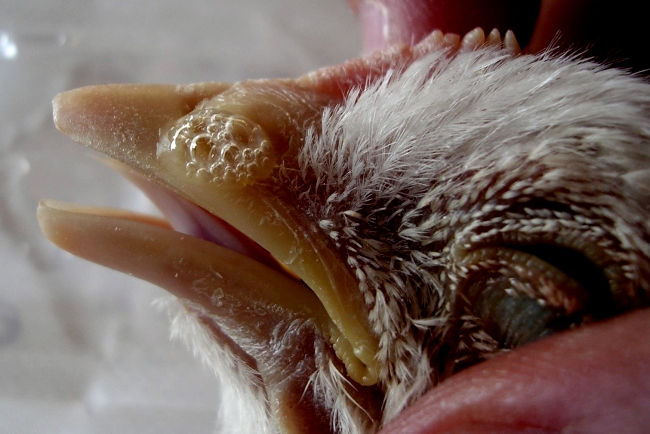
Fluid leaks from the beak or mouth
Two-month-old chickens, broilers, adult chickens are exposed to the disease - pasteurellosis. 80% of young animals die, mortality of adults is almost 100%.
In the initial phase, females are distinguished:
- lethargy;
- blue discoloration of earrings and scallop;
- lack of appetite;
- seat in one place;
When the bird is not treated, liquid flows from the beak and nose, wheezing occurs, and breathing becomes difficult. In addition, body temperature rises, feathers ruffle, feces become greenish or yellow, blood is mixed.
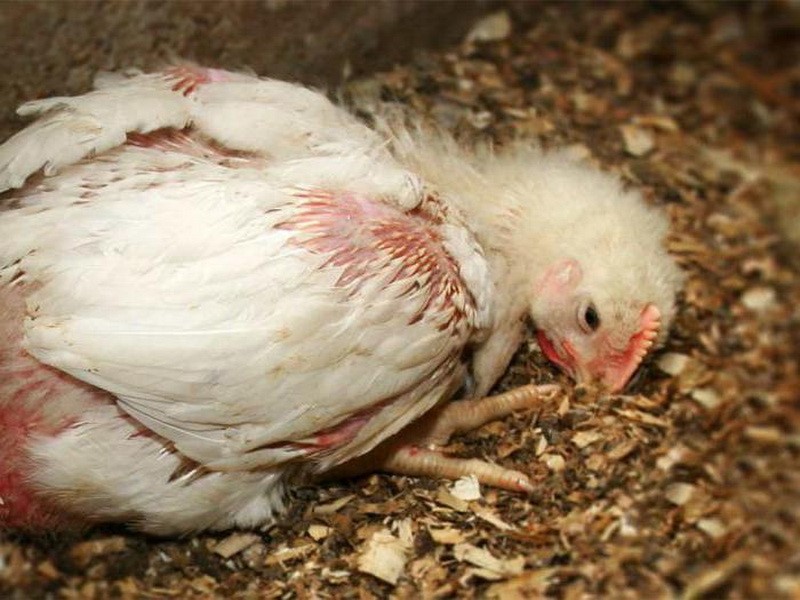
Hides his head under his wing
If the bird is lethargic, has no appetite, loses its liveliness, holds its head under its wing, then the goiter is inflamed. Observe its visual increase, the release of fluid from the larynx.
Causes of the inflammatory process:
- ingress of a foreign body;
- irrational feeding;
- vitamin A deficiency
Red dots in eggs
Tiny spots appear in a hen's egg when the yolk is separated from the ovary, when the vessel bursts. As a rule, these are single specks.
In addition, the root causes of the appearance of red dots inside the egg include:
- stress;
- lack or excess of males;
- limited space when keeping chickens;
- chicken embryo.
White spots on the liver
The source of tuberculosis is sick birds. Damage to internal organs, including the liver, is noted. Unsanitary conditions in the barn are the cause of the disease.
Lump on the neck
Inside, the formation is like a whitish fat with transverse yellow fibers and blood. Tumors are localized throughout the body. Broken specimens have a flattened shape in the center. The chicken has bluish skin and empty intestines.We are talking about Marek's disease, fibrosarcomatosis, leukemia.
Yellow swelling
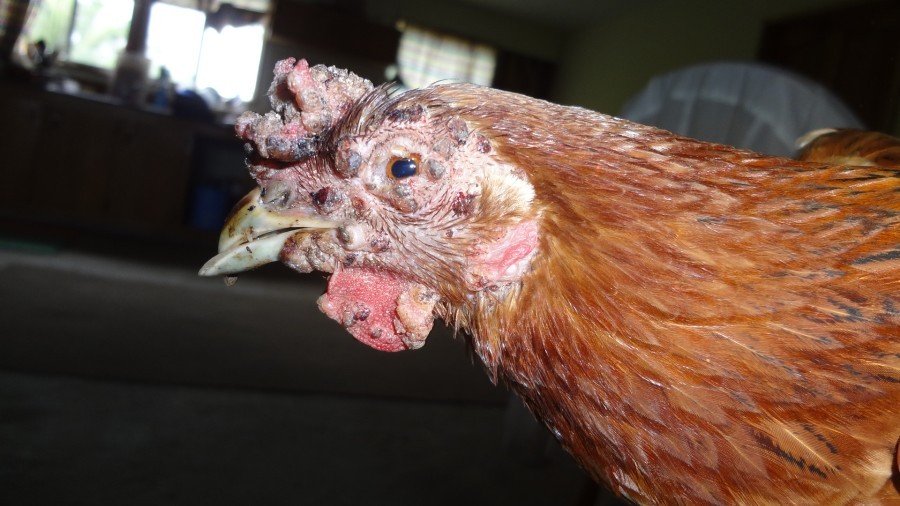
If yellow outgrowths form on the hen's crest, eyes, and catkins, smallpox attacks the chickens. Chickens have difficulty breathing, the swallowing reflex is weakened. This is the symptomatology of smallpox at the initial stage, Marek's disease.
Chickens are infected through unhealthy birds, rodents, parasites, food and water. With Marek's disease, tumors form on the skin, skeleton, and organs. Birds have impaired motor functions.
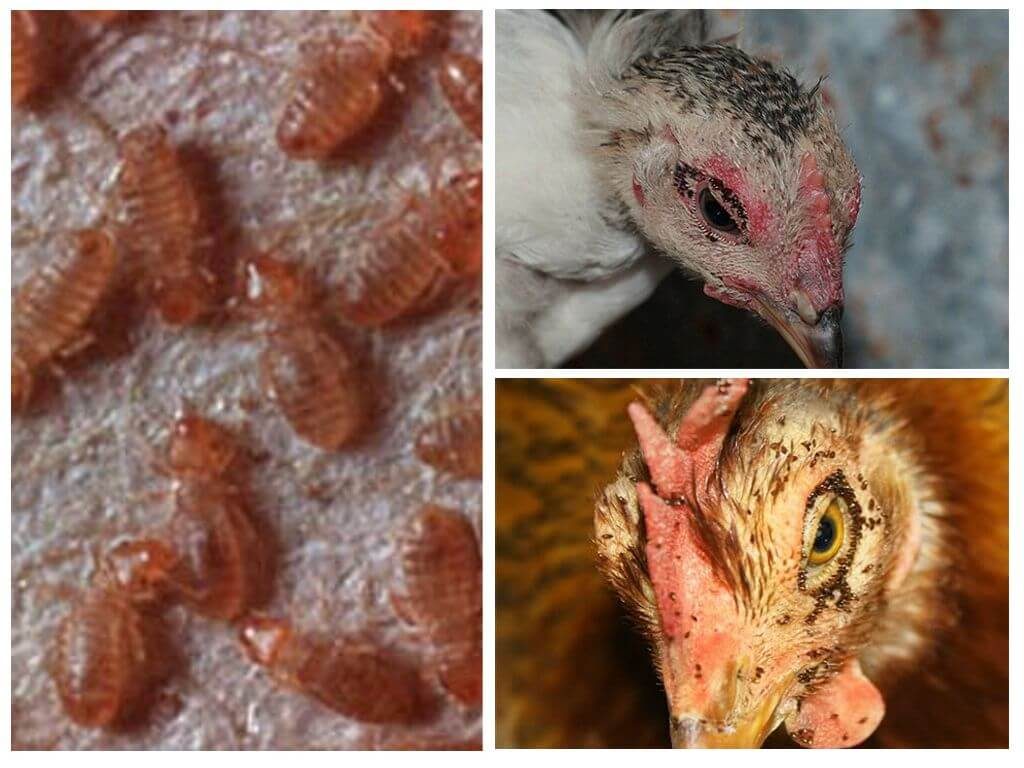
Itching
Microscopic insects can be seen if the bird's plumage is examined carefully. Manifestation of anxiety: birds itch all the time - pests have started. The blood-sucking parasites that live on the skin of chickens are chicken lice and bed bugs. They are also found on perches, in nests.
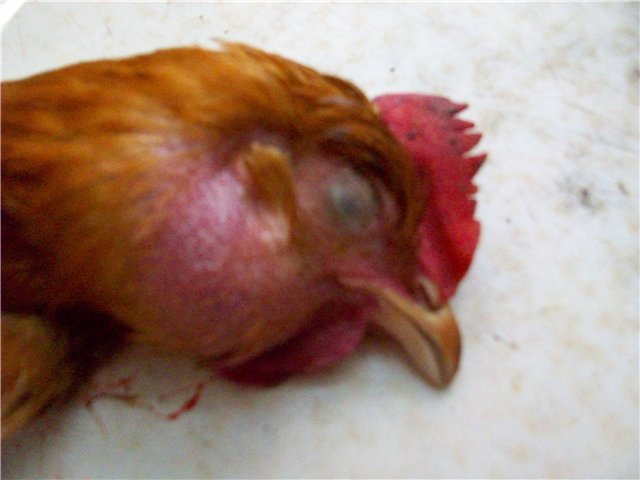
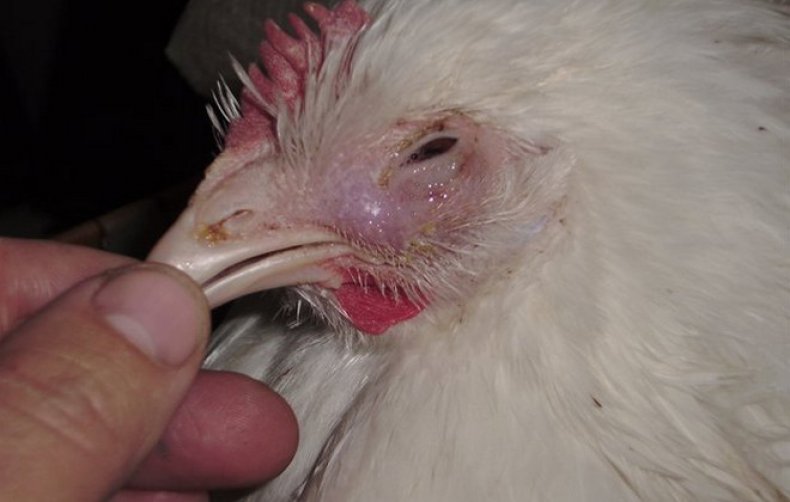
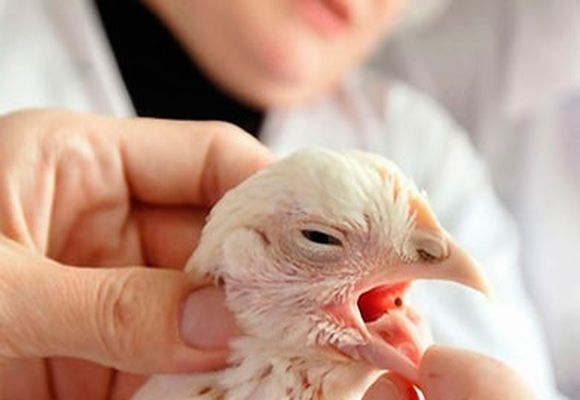
Wet beak
It is a manifestation of psittacosis, which affects the nervous system, respiratory and digestive organs of the chicken.
Symptoms:
- wheezing when breathing;
- appetite disappears;
- is rapidly losing weight;
- fluidly defecates.
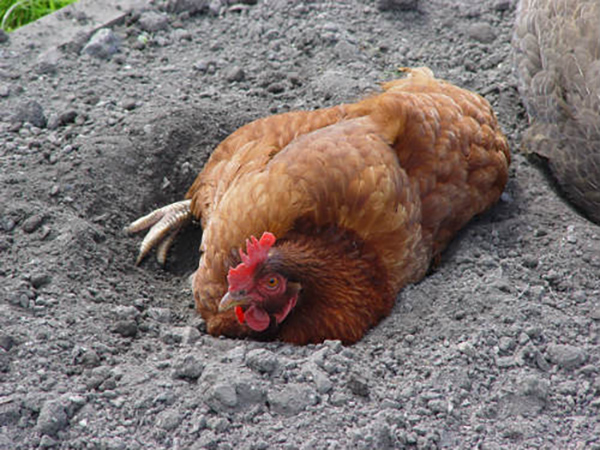
Bathing in the ground
Females have parasites. Down-eaters feed on feathers and down of chickens. Pests live on the skin of birds. The chicken is constantly itching. Harmful insects are visible to the naked eye. Bathing in wood ash is a reliable protection of chickens from pests.
Overview of chicken diseases
Histomoniasis
In another way, typhlohepatitis is called. Considered to be parasitic infectious diseases. With the development of histomonosis, changes in the liver and anomalies of the cecum are established.
Manifestations, as with helminthiasis infection:
- no appetite;
- weight loss;
- weakness;
- cramping.
Affected hens do not lay eggs. For treatment, Furazolidone is appropriate. Vitamins are introduced into poultry feed for prophylactic purposes. Detection of symptoms and timely treatment of histomonosis in chickens will allow you to quickly cope with the disease.
Yolk peritonitis
To the reasons that give rise in chickens, the development of yolk peritonitis includes:
- excess phosphorus;
- overfeeding with proteins;
- crowded content;
- dampness in the room;
- lack of choline, vitamins E, B6, A, B1, D, calcium.
Symptoms:
- decreased ability to lay eggs;
- loss of appetite;
- oppression.
The acute course of the disease is characterized by dropsy and bloating, which lacks feathers.
Chickens are treated with both streptomycin and gentamicin.
Infectious bronchitis
Infectious bronchitis of chickens is distinguished by damage to the respiratory system. For adult living creatures, damage to the reproductive system and a decline or cessation of egg production are typical.
The causative agent of the disease is virion. The virus is found in chicken eggs and internal tissues. They fight the virion with ultraviolet light and disinfectants.
Infection of livestock occurs:
- by airborne droplets;
- through the bedding;
- through working tools.
When the hens are sick, quarantine is introduced for 12 months on the farm. The disease threatens nearby poultry farms and causes up to 70% of the death of livestock.
Symptoms:
- the chicken coughs up;
- mucus, rhinitis is released from the nose;
- sometimes conjunctivitis occurs;
- young animals do not eat;
- nestles against heat sources;
- problems with the urinary system begin;
- diarrhea opens.
Making a correct diagnosis means quarantine - the disease cannot be cured. It is prohibited to sell poultry meat. The hen house is systematically sanitized using aerosols with chlorine-turpentine, aluminum iodide, Lugol's solution.
Preventive measures include:
- quarantine period for chickens within 10 days;
- vaccination before oviposition.
Hemophilia
Another name is contagious rhinitis.
Root causes in chickens hemophilia are:
- vitamin deficiency;
- drafts;
- hypothermia;
- the accumulation of gases in the chicken coop.
Symptoms:
- emaciation of birds;
- mucous discharge from the beak;
- loss of appetite;
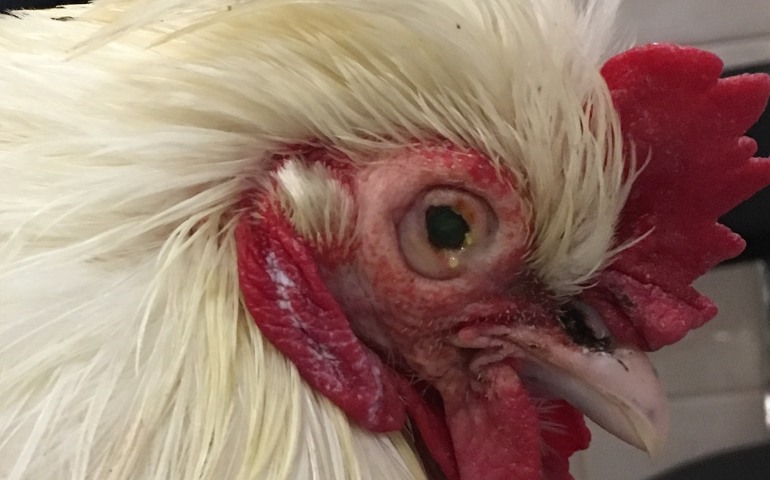
- inflammation of the conjunctiva of the eye;
- blindness;
- difficulty breathing and coughing;
- bonding to the eyelid;
- shaking your head.
In the treatment of hemophilia:
- peel the crusts with cotton pads moistened with furacilin or tetracycline;
- additive to drinking phthalazole or Spofadazineetazole, soluble Norsulfazole or Sulfadimezin.
Prevention:
- adhere to poultry keeping standards;
- disinfect the barn and appliances;
- insulate the poultry house;
- adding vitamin A to food.
Laryngotracheitis
Refers to infectious pathologies that are detected in chickens. With laryngotracheitis, inflammation of the trachea and larynx is noted, sometimes conjunctivitis occurs. In recovered animals, the appearance of immunity is noted for a long period.
Manifestations:
- labored breathing;
- inflammatory process of the mucous membranes;
- decrease in egg production.
Therapy is not effective in advanced cases. Thromexin is used to alleviate the condition of sick birds. Watered with an aqueous solution of the drug: the first day - 2 g per 1 liter, then - 1 g per 1 liter. The course of treatment is at least 5 days until recovery.
Preventive measures include:
- sanitation support;
- vaccination;
- quarantine for livestock.
Ascariasis
The development of the disease is observed if ascaris eggs enter the chicken body. The eggs hatch worms - intestinal parasites. Infection of chickens with ascariasis is carried out by the fecal-oral method. A sick bird quickly loses weight and loses its appetite. Ascariasis is characterized by lethargy and suspension of egg production. When there is no stool, parasites clog the intestines. In chickens, the simultaneous course of ascariasis along with heterocytosis is sometimes noted.
Treat with carbon tetrachloride or phenothiazine.
Gout
Belongs to non-infectious diseases, the cause of which is a violation of metabolic processes. Uric acid accumulates in excess in the blood and tissues. Adults are affected by gout, or uric acid diathesis.
With gout, the joints, serous membranes, and internal organs are affected.
Tracked in the acute phase:
- refusal to eat;
- weak legs;
- decrease in egg production;
- worsening of the condition;
- whitish feces;
- intestinal irritation.
Smallpox
Chickens sometimes become infected with a viral infection. The main symptom of smallpox is ulcers. Chickens get sick on contact.
Sources of infection:
- water;
- food;
- unhealthy layers.
Timeliness of therapy is appreciated. Treatment of the affected foci from the outside with antiseptics: furacilin, as well as boric acid. Tetracycline is mixed into the feed for 7 days. When the cause of the disease is not determined in time, sick chickens are disposed of.
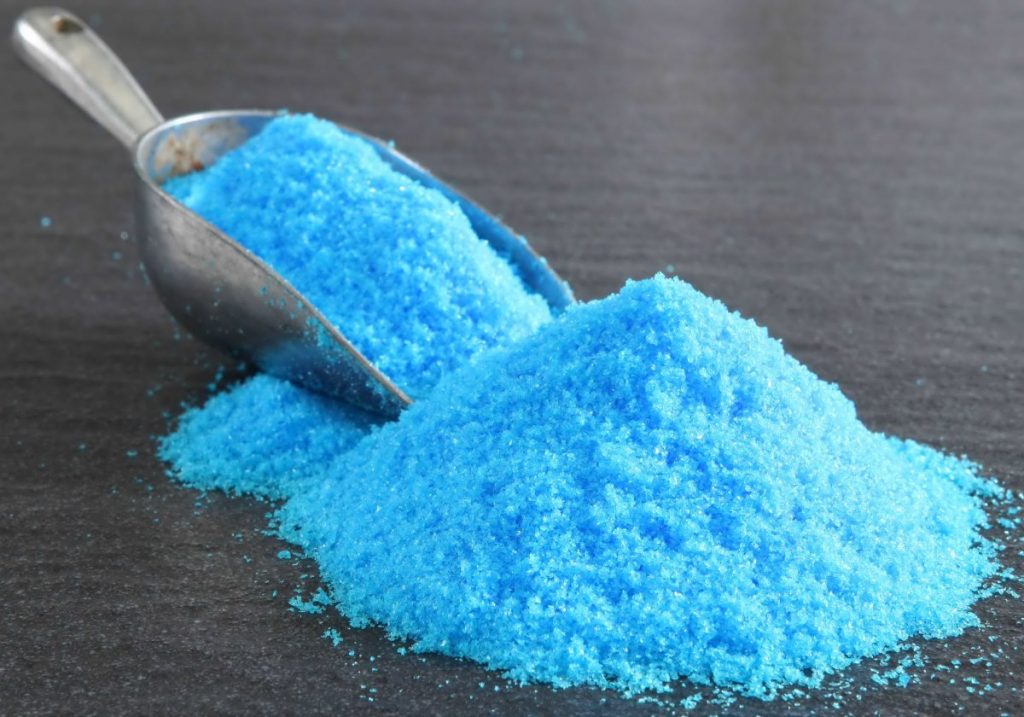
Aspergillosis
The disease is caused by a fungus and affects the respiratory system.
Development aspergillosis inbirds accompanied by:
- coughing and sneezing;
- intermittent breathing;
- blood excrement;
- nasal discharge.
The disease is cured with copper sulfate, which is poured into chicken food and drink for several days in a row.
Sinusitis
In another way, the disease is called flu. Respiratory tract damage occurs.
The main symptoms include:
- wheezing;
- swelling of the eyelids;
- convulsions;
- lacrimation;
- oozing discharge from the beak.
Prevention:
- mixing greens with food;
- rejection of defective products.
Spirochetosis
Dangerous infection.
Signs:
- diarrhea;
- high temperature (42 ° C);
- no appetite;
- thirst;
- indifference;
- drowsiness;
- low egg production;
- decrease in body weight;
- anemia of the mucous membranes.
In treatment, Atoxil and Novarsenol are used, which are administered intramuscularly.
Prevention consists in getting rid of ticks in chicken coops. Kerosene, creolin just right for room disinfection.
Tuberculosis
The bacterial infection is transmitted by airborne droplets. It is caused by avian-type mycobacteria. Unsanitary conditions contribute to the development of the disease. The sick chicken is lethargic, apathetic, with a pale comb. The main signs are weight loss, lack of eggs.
Prevention of tuberculosis requires:
- keep the barn clean;
- disinfect twice using caustic alkali and formaldehyde (3%), 20% chlorine suspension and 5% freshly slaked lime. Consumption of the drug per 1 m2 of area - 1 liter;
- layers are reacquired one month after measures are taken.
Avitaminosis
The content in the cage is one of the causes of chicken disease, then ready-made mixtures are replaced in the diet with natural feed.
Birds are characterized by:
- weight loss;
- weakness;
- loss of feathers;
- conjunctivitis.
Help will be provided by rational nutrition and the addition of fresh vitamin herbs to the feed.
Ornithobacteriosis
Infection. Infections are promoted by unfavorable conditions of detention, non-observance of sanitary rules, various ailments that are accompanied by damage to the respiratory tract.
Symptoms:
- runny nose;
- moisture in the eyes;
- sneezing;
- inhibition of the development of young individuals;
- reduction in egg production in adult chickens.
Ornithobacteriosis is treated with antibiotics.
Monocytosis
Another name is blue comb. Young animals are affected.
Symptoms:
- cyanosis of the head;
- diarrhea;
- liver necrosis;
- depression;
- kidney gout;
- no appetite;
- wrinkled earrings and scallop;
- bluish shade of the comb.
Sulfanilamide drugs, antibiotics of the tetracycline group are effective.
Syngamoz
The trachea and lungs are affected.
Symptoms:
- lack of appetite;
- emaciation;
- apathy.
In the treatment of the disease of chickens are used:
- introduction of 2 drops of iodine solution with a needle through the larynx;
- an addition to food of Liperazine, Phenothiazine at the rate of 50 mg per 1 kg of body weight.
Prevention:
- compliance with the rules of feeding and keeping poultry;
- sanitizing the chicken coop and appliances with carbolic acid;
- separation of young stock from old chickens.
Aymeriosis
A parasitic infection that is caused by the simplest microorganisms is chicken eimeriosis, or coccidiosis. Chicks are often infected at the age of 2-8 weeks. The death of two-month-old chickens is a defeat by the Eimeria.
The incubation period ranges from 3-5 days.
In the acute course of the disease, they monitor:
- depressed state;
- thirst;
- rejection of food;
- lowered wings;
- ruffled feathers;
- bunching up to warm up.
Treatment of the disease is reduced to giving the bird coccidiostatics. Eimeria remedies have different dosages and duration of the course of therapy, it is useful to adhere to the instructions and recommendations of the veterinarian.
For prevention, it is advisable to follow the rules for keeping poultry. Prevent chicken manure from entering food. It is advisable to keep birds in cages with mesh floors, which are easy to disinfect. Due to the resistance of eimeria to negative factors, annealing with a blowtorch of equipment is ideal for disinfection.
Experienced poultry farmers advise
If a chicken broke a leg
With injuries, open (bone sticking out) and closed fractures are distinguished.
Required:
- Straighten the bones.
- Disinfect the wound.
- Apply a splint.
- Re-bandage.
- Cut off the feather.
If the wing is broken
In case of dislocation (the injured area is swollen and reddish) and incomplete fracture of the wing, the injury area is tightly bandaged. When a chicken has a broken wing, you will need to bandage it to the body.The chicken will not be able to move it, while causing itself pain and making it difficult to recover.
Restrain the bird from moving until it recovers. It is advisable to organize separate content. Similar injuries will heal within 2 or 3 weeks.
If the skin of the neck is injured
At times, wounds appear when injured by other animals.
It is necessary:
- Cleansing the wound.
- Cleaning of feathers near the injured area.
- Washing with potassium permanganate.
- Lubrication with iodine.
- Stitching.
- Bandaging.
- Chicken deposition.
- Re-processing and bandaging.
- Removing stitches when the wound is overgrown.
From answers to common questions
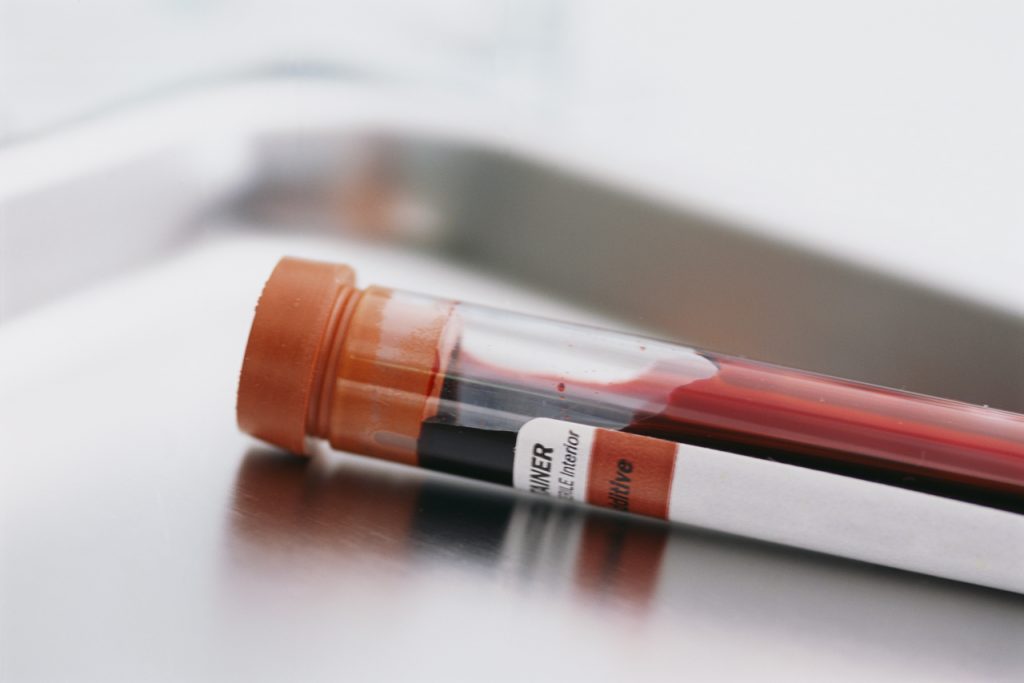
Normal blood counts in laying hens
Chicken blood is taken from a vein on the wing, leg, claw. On the jugular vein, it is easier to take blood from the claw, which flows slowly. If the chicken weighs 0.5 kg, the sampling volume is 5 ml. CBC is a count of white and red blood cells. Counting the number of red blood cells - hematocrit. For most chickens, the normal hematocrit is 37-50%. A parameter less than 37% indicates anemia. Less than 15% - a hen needs a blood transfusion. Dehydration is indicated by the abundance of red blood cells. The platelet count ranges from 20,000 to 30,000 per ml of blood.
Why does a chicken lay eggs in the blood?
Why does chicken liver decompose?
A chicken's liver is destroyed if the bird suffers:
- Tuberculosis (presence of white spots on an enlarged liver).
- Marek's syndrome.
- Leukemia.
- Coccidosis.
Diseases of chickens can cause inconvenience and grief to the owner of the chicken backyard. The pathologies that threaten to reduce the number of poultry are different. Having an understanding of the symptoms and methods of therapy and prevention of ailments, it is possible to help the inhabitants of the poultry house, avoiding the death of laying hens.