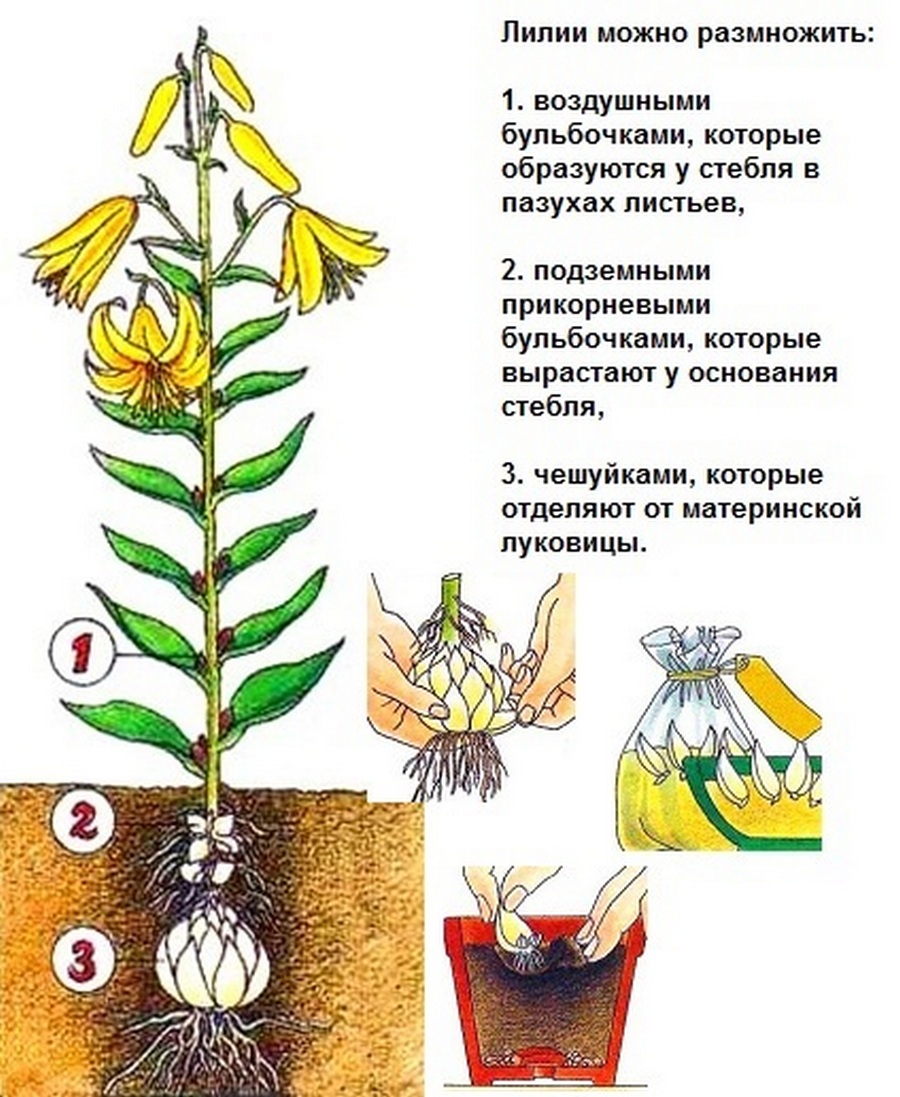
Content:
Lily has been known as a garden plant for several millennia. Rich and noble Greeks planted this magnificent flower near their home as a sign of wealth and uneasy origin. In the Middle Ages, the French gave impetus to the development and breeding of new varieties of lilies, considering this flower royal, since its image adorned the coat of arms of France during the royal dynasties of Capetian and Bourbon. At the same time, France was called the kingdom of lilies, and the king was called the king of lilies. And even then they knew about the reproduction of a flower by cuttings. How is it done today?
Lily description
The beautiful lily flower comes from the genus Liliaceae. Refers to perennial plants supplied with bulbs. Each onion consists of individual thick and fleshy lower leaves, white with a pink or yellowish tinge. It hibernates in the soil and allows the plant to begin a new life cycle with the onset of spring.
The lily stem is a continuation of the bottom of the bulb and looks simple, leafy and slightly branched at the top. This structure of the plant makes it possible to quite successfully cut it in several ways.
In general, there are 9 ways to grow a lily, each of which has the right to exist, especially when propagating expensive and rare varieties in the fall, where every opportunity to obtain planting material is used:
- division of the lily bush;
- reproduction by newly formed children;
- reproduction by bulbs that have grown at the base of the leaves;
- cuttings with stem cuttings;
- cuttings with young flower shoots;
- reproduction of lilies by leaf cuttings;
- reproduction by separating the lower leaves from the bulb;
- reproduction by sowing ripe seeds;
- spring reproduction by dissecting the bottom.
Lilies are perennials with a delicate fine aroma and beautiful large flowers. They are also attractive to gardeners because they do not require digging and winter storage in basements or shelter for the winter. They may well bloom in one place for several years and do not require much care and worries. Only a few species of lilies are so thermophilic and not adapted for wintering that flower growers prefer to grow them indoors.
To get an adult that can bloom, the plant he has to grow the bulb for several years. Therefore, high-quality planting material is expensive and not everyone can afford to buy it, especially if the grower wants to get a large clump of plants of the same variety.
To get more planting material from one purchased bulb, it is worth learning how to cut lilies correctly, and use different methods to get a couple of dozen new young plants from one planted lily within one summer.
Cutting lilies with a young flower shoot
Breeding lilies from young shoots is possible only at the beginning of the growing season:
- In the spring, after the emergence of shoots from the bulb, the young shoot is carefully separated when it reaches a height of 10-15 cm.
- Several longitudinal shallow cuts 2-3 cm long are made at the base of the shoot with a sharp knife and soaked for 1 hour in a solution of epin.
- The shoot is planted in the ground, deepening by 5-7 cm, watered abundantly and covered with a cut plastic bottle, from the neck of which the lid must be removed. Thus, the plant finds itself in a kind of mini-greenhouse, which maintains high humidity and heat, but the open hole on top allows the shoot to not overheat.
- After 2-3 weeks, when the roots begin to develop at the shoot, and bulbs form at the base, the bottle can be removed.
- Further care consists in regular watering and weeding. The bush will need to be spud higher so that more bulbs are formed.
- With the onset of the first frost, the shoot is dug up and the young bulbs of lilies are carefully separated from it, the children are planted in open ground for growing.
In another year, young lilies can be planted in a permanent place.
Lily propagation by cuttings from leaves
How to properly propagate lilies by cuttings without significant damage to the flowering of the plant? For this, propagation by cuttings of leaves is quite suitable. It is produced after the stem forms flower buds:
- Using a sharp knife, you need to cut off several leaves from the plant, while grabbing a small piece of the stem.
- Place the cut cuttings for 1.5-2 hours in a solution of epin or another root-forming agent.
- Plant the cut leafy cuttings in a container or box so that the leaves are half buried. The soil should be light enough.
- Pour abundantly and cover with plastic. Several times a day you need to lift the film for airing. On hot days, expose in the shade, prevent the soil from drying out or, conversely, excessive waterlogging. Soon roots, bulbs and new young leaves will develop and form at the base of the leaves.
- For the winter, the container with the newly formed lilies will need to be dug into the ground for the winter, or, being careful, plant the young plants without disturbing the earthen coma in the nursery school allocated for the young.
In such a simple way, you can get up to a dozen new lilies from a plant per season and collect planting material in the required volume for this variety.
Propagation of lilies by stem cuttings
Reproduction of lilies by stem cuttings is carried out after the end of flowering. Stem cutting consists of several leaves with a small piece of the stem. Reproduction in this way is performed as follows:
- The peduncle is cut almost at the root. A noticeable peg is stuck next to the hemp, so as not to subsequently lose the location of the plant in the garden.
- Cuttings 8-10 cm long are cut from the peduncle, on the lower half of which the leaves are removed and 2 shallow cuts are made along the cutting 2-3 cm long with a sharp knife.
- For 1-2 hours the plants are soaked in any root former and after this time they are immediately planted under a film in a mini-greenhouse. Planting is carried out at a slope of 45 ° and to a depth of two thirds of the stem. A greenhouse can be a low wire arc covered with a polymer film or covering material.
- After 2 months, the cuttings will root in the greenhouse and give small onions, which at the very end of summer can be carefully transplanted to a permanent place. But the best option would be to leave them in this place until next spring.
- It must be remembered that watering in the greenhouse should be regular and at the same time moderate, so as not to dry out and not cause water stagnation and waterlogging.
Growing lilies from cuttings does not require special skills and abilities from the gardener and even a novice amateur gardener can perform these simple operations. You only need diligence and attention when performing these agrotechnical techniques.
Reproduction of lilies in other ways is less productive in terms of the number of new plants per season, but it is simply impossible to cut some varieties of lilies, for example, with leaves. The most successfully propagated in this way are varieties such as Regale, Tigrovaya, White, which have a slow growth of bulbs. Therefore, grafting is the best way for them to get fast offspring.
Also, the propagation of lilies by layering has a conditional relationship to cuttings. If the peduncle falls to the ground due to gusts of wind or rain, you can take advantage of this and get several new plants. Several notches are made on the fallen peduncle with a knife and, without separating it from the bulb, they are sprinkled with a low mound of earth, watered with epin and kept in this position until next spring. A peduncle under the ground will give roots and grow young bulbs.
Thus, there are several ways to cut lilies at home. Which one is better to choose is decided by the florist himself. You can use several at once, then to stop the choice on the fastest and most effective.