Content:
Roses are among the most popular types of home flowers. They are planted both in the garden and at home. Roses are unpretentious to care for, very beautiful and fragrant. However, sometimes diseases of roses can overtake, which will significantly jeopardize their beauty and further existence. Yet these flowers are quite delicate.
Description of signs of rose diseases and possible causes
The variety of diseases of this plant is very large, they can be caused by various reasons, therefore, they should be treated in different ways. Diseases can be of different types: fungal, parasitic, rotten, as well as viral and caused by a lack of moisture. The most popular rose diseases are discussed below.
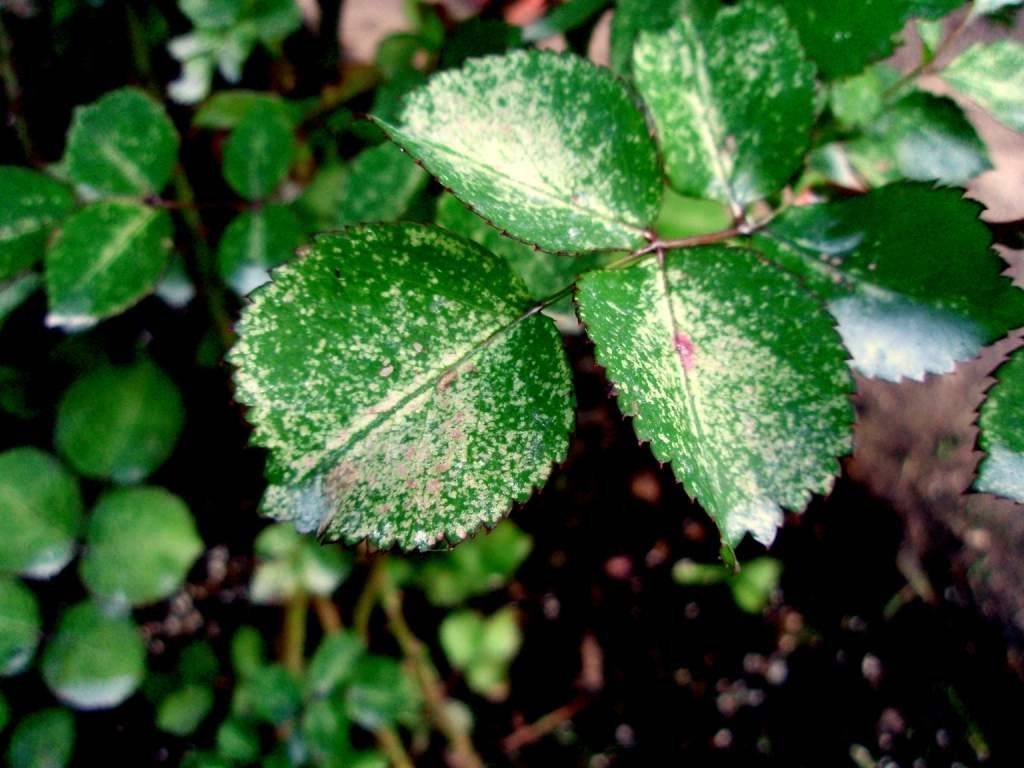
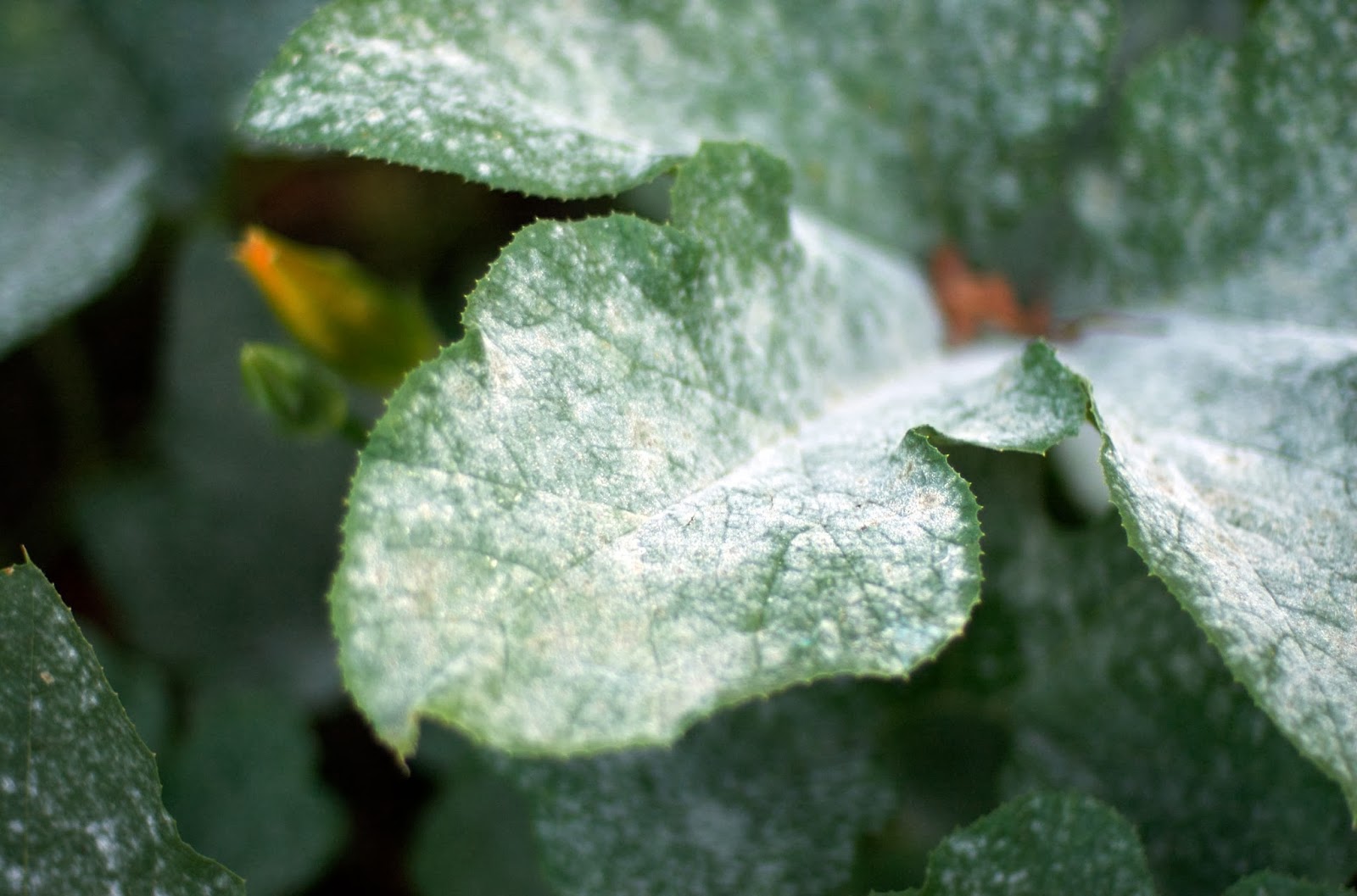
White spots on rose leaves
This is a fairly popular ailment among ornamental plants. White spots are caused by a fungus of the Sphaerotheca type. Another name for white spots is powdery mildew. First, this disease affects the leaves, but then it affects the trunk, and stems, and buds, and new shoots.
At the first stage, a plaque appears in the form of a white cobweb. Later it turns brown, covers the whole plant and gets inside, the flower begins to rot. Most often, this disease affects plants in the middle of summer, but the so-called incubation period lasts until the end of the warm season. The disease is invisible externally and at the same time affects the flower from the inside. Leaves curl on the rose and dry up. Soon the flower dies.
The most common causes of powdery mildew are:
- Excessive moisture, such as a rainy summer, groundwater, or over-watering can cause root rot, white spots, and the death of the entire plant.
- Planting density. Plants need to breathe, their leaves must be exposed to sunlight, otherwise they simply will not develop properly. The optimal distance when planting roses between plants is 20-25 cm. Then the branches will not intertwine and interfere with each other, otherwise a so-called struggle for life arises between them.
- Excess nitrogen. With an excess of nitrogen, the stems are too thick, and growth slows down. As a result, all the power does not go into the flowers, but into the stems.
- Calcium deficiency. First of all, you need to pay attention to the change in the color of the foliage. It turns yellow and becomes dry, withers, and this is a very fast process: even daily watering does not save from it.
As a preventive measure, it is better to use systemic insecticides. They will restore the water-salt balance in the plant, add calcium. This will strengthen not only the plant itself, but also the mail in which it is located.
The rose does not bud
Some other reasons that are characteristic of the absence of buds:
- Wrong landing site. The place should be well lit. Roses need about 8 hours of continuous sunlight a day. In general, they are quite heat-loving plants. Therefore, they need to be grown in greenhouse conditions, then the diseases of garden roses will recede.For prevention, it is enough to regularly ventilate the planting site of roses (if it is a greenhouse), as well as wipe the leaves and petals.
- Incorrect cropping. All types of roses, whether standard or climbing, require pruning. The procedure is carried out according to the type of rose. For example, shrub roses, as well as English and klaimings, should almost never be pruned, otherwise it can harm the plant's ability to branch and bloom again. It is enough to lightly trim these plants several times a year.
- Untimely removal of faded flowers. Dried flowers on houseplants must be cut off in time. This measure will avoid rotting indoor flowers.
- Illiterate care in general. Diseases and pests of roses appear mainly due to the misuse of all care methods. As a result, various underdeveloped parts of roses are often formed, for example, the petals can curl, the leaves fall off. All of this is a result of the wrong type of care being chosen.
Leaves curl up and dry up
Another type of manifestation of the disease of roses on the leaves is their folding and drying, while a red spot may appear. The most likely cause is lack of moisture. But on the other hand, the reason may be its excess. Since the leaves lose their ability to accumulate moisture, over time this negatively affects their production of oxygen, which in turn has a bad effect on the life cycle and properties of the plant.
What to do in such a situation? Protection is implied in the organization of optimal irrigation conditions. For example, water the plants 2 times a week. This is the most optimal frequency. Using this method, you can save the plant from death.
Roses got small
Sometimes the fruits of the plant can become smaller. First of all, this indicates a lack of B vitamins, as well as nitrogen. The flowers lose their original size and are no longer the same as they were at the very beginning of their growth. In this case, it is necessary to engage in feeding.
Sometimes the size of the buds decreases due to the defeat of fungal diseases. They hit the root first, and then the whole flower. In this case, a fungicide helps. This is a collection of different chemicals that help to fight not only fungus, but also various other plant diseases that are transmitted through the soil. It is recommended to treat seeds suitable for planting with a fungicide.
Black trunk
The black trunk of the rose is an unkind sign. Most likely, he says that this beautiful plant has no more than a week or two left to live. When the trunks are just beginning to turn black, they must be cut off immediately and it is even better to burn them. This method will help prevent the spread of harmful substances and microbes, and, consequently, infection of other plants. Such a disease can be a type of fungus, therefore, it is possible to destroy it only with the help of a specialist with the appropriate equipment.
Stem blackening is a must-have problem across the home. Otherwise, pets can easily begin to experience problems with the lungs and breathing. That is why, as soon as any symptoms of the plant appear, it is necessary to immediately transplant all others that are nearby, and even those that grow at a distance, in other rooms. Otherwise, you may lose all flowers.
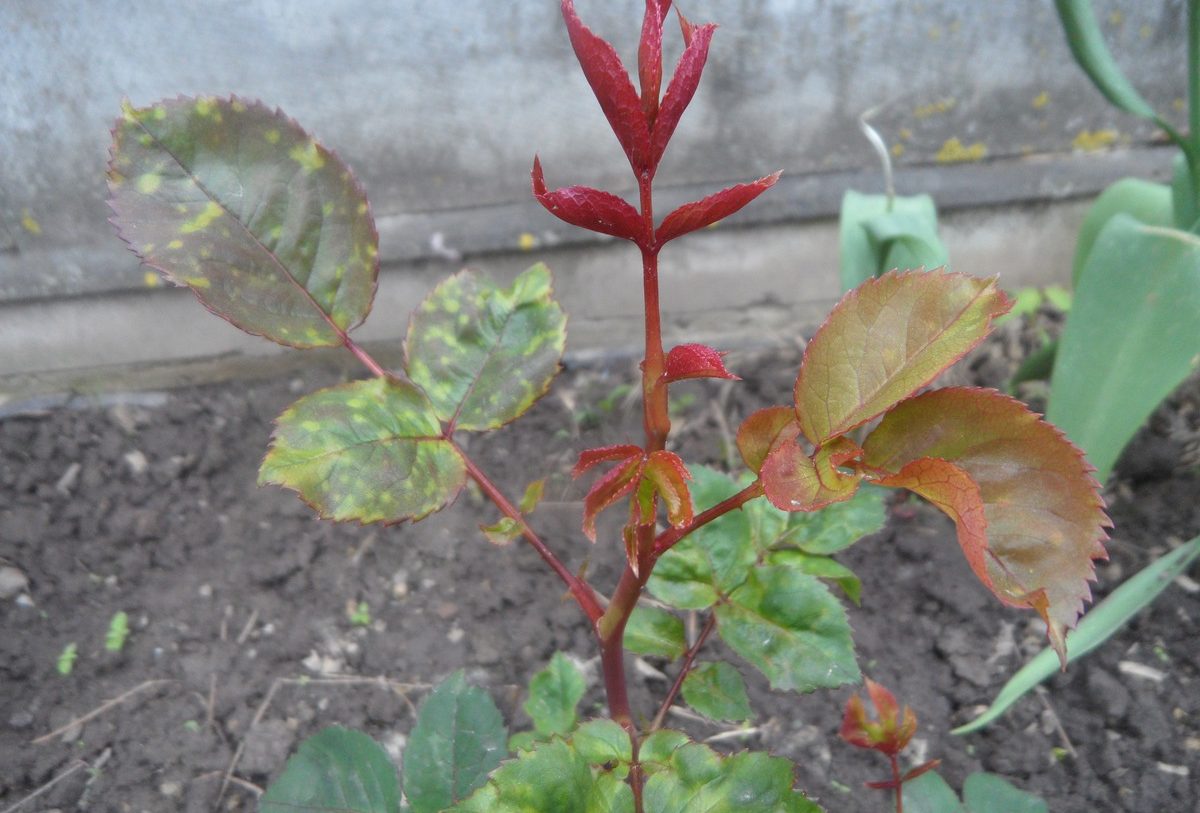
Red spots appeared on the flowers of roses
After red growths have appeared on the inner side of the rose, it is necessary, firstly, to understand why the rose does not give buds (most likely, it does not have enough vitamins and trace elements in the soil for this), and to start fertilizing, and secondly, check existing flowers and buds for the presence of certain diseases.
Mold on roses
Mold is usually caused by powdery mildew. This is such a fungal formation that most often appears on the inner side of the plant, damages it, and then spreads tightly throughout the flower. Due to the high level of humidity (or, for example, it is always cold in the apartment), mold spreads very quickly. The incubation period lasts several weeks, therefore, dozens of others can infect such roses.
Symptoms are white or green spots that suddenly appear on the inside of the roses, which, in fact, can be wiped off with a regular damp cloth, but even after using it, they appear again. To get rid of mold, you have to use "serious treatment". However, the question of how to treat roses for diseases should be considered from the point of view of an individual approach to each flower.
Speckled rose flowers
Specks on roses appear due to high humidity and air temperature. The grower needs to take control of these parameters and track changes in plant growth.
Diseases of roses
Diseases of roses and their treatment are often associated with climatic conditions, but can also be caused by external viruses.
The most common ones are:
- Septoria. Blackening of the plant, softening of leaves and stems. To combat it, it is necessary to keep all other plants away from the diseased flower so that in no case do irreparable damage to the roses (and not only) that are located nearby. For prevention, it is important to organize feeding with new soil in time, which contains all the necessary trace elements.
- Another disease that roses suffer from is bacterial cancer. Perhaps the first sign is why the rose is not budding. First of all, the reason for this may be the presence of cancer cells. Unusual bumps appear on the rose, the growth darkens and hardens, which leads to decay.
- Viral wilting. This is a causative virus, spreading as quickly as possible. Viral wilting is very dangerous, as it can affect all roses at once.
- Infectious burn. The causative agent of this disease is a marsupial mushroom. The main feature is a black stem with a seemingly rusty outgrowth. Soon the leaves begin to fall off, as well as the root rot.
- Cytosporosis. This is an infectious disease that causes the entire flower to dry out. The disease is very common.
- Fungal diseases. These include powdery mildew on roses. Arises from very high humidity.
Not all diseases are amenable to quick treatment, so you need to approach the process thoroughly.
How to treat rose diseases
How to treat roses for diseases is perhaps the most important question. For starters, get the right rose remedy. The most effective are:
- Fungicides. These are substances that prevent the spread of fungal infections. They are biological and chemical in composition. Dilute 50 g / 10 l in water and water the plants.
- Pure color. Instructions for use for roses, dosage implies 2 ml of the product diluted in 5 liters of water. Pure flowers for roses are applied once a month.
- Fitosporin for roses. Before planting, add 20 ml of the product diluted in water to the soil.
- Home for roses. This is a preparation with a low copper content. The addition of Homa removes rust and stains on plants. Add to water and spray on plants every day.
- Oxyhom. This substance is also added during planting. It prevents the development of fungi. For 1 liter of water - 3 ml of Oxychom.
- Profit Gold. Used for pest control.Approved for use up to 4 times a season as a top dressing.
- Ordan. A drug that fights against various pathogens that arise in high humidity conditions, for example, in greenhouses. Carry out processing during the growing season.
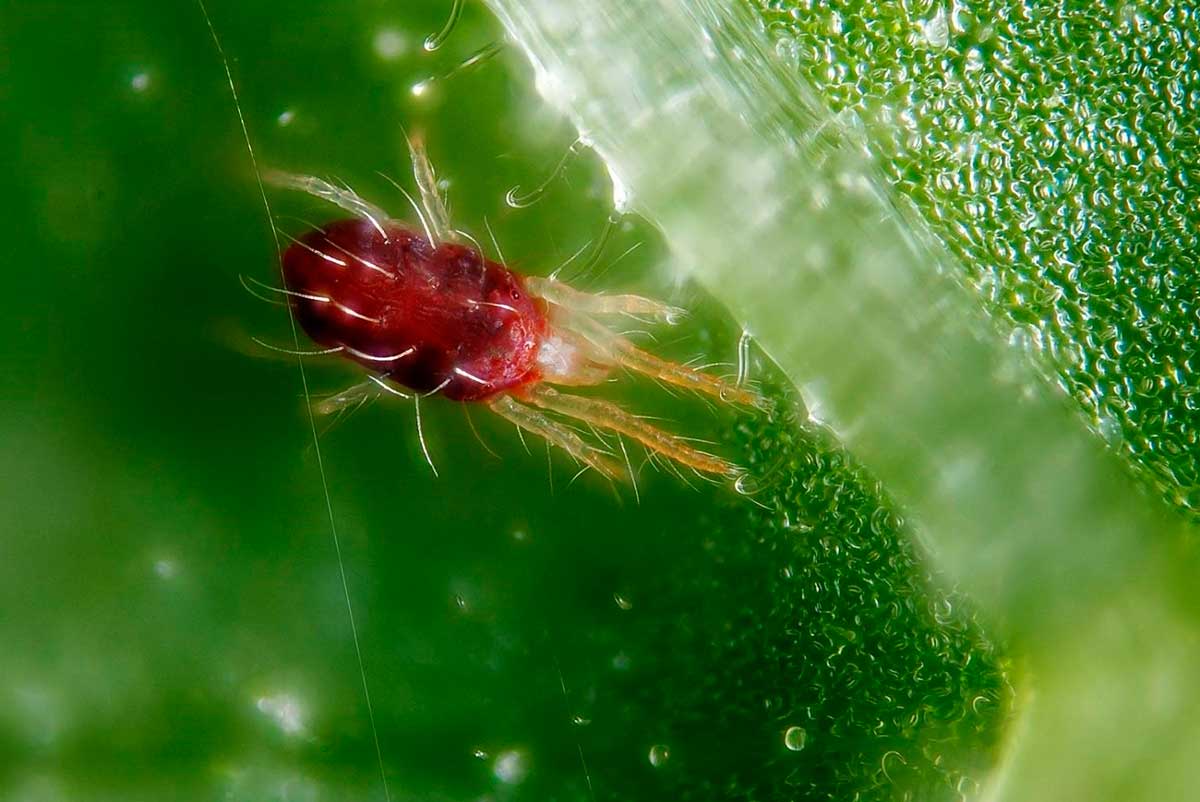
Pest control methods
The most common rose pests are:
- pink aphid;
- spider mite;
- slobbering penny;
- furry deer.
The methods of dealing with all are approximately identical. With a small amount - press, with a large amount - poison. It is recommended to poison with insecticidal plants and other chemicals.
Preventive measures
Basically, all preventive measures are to treat the soil and leaves several times a year with appropriate preparations. It is also important to plant roses in areas that are well ventilated and have a soil rich in trace elements. Timely and correctly carried out pruning will also help prevent a number of diseases.
Despite their beauty and showiness, roses can be quite demanding to care for, especially during their illness. But in today's world, there are also plenty of options for providing proper care. In addition, if you are afraid of possible difficulties, you can always choose varieties that are resistant to diseases.