Dahlias are perennial flowers, represented by a wide variety of flower caps in different colors and petal shapes. Flowers of early autumn, characterized by the peculiarities of cultivation, the need to store root tubers, as well as the susceptibility of dahlias to pests and diseases, including those that cannot be treated.
Signs of disease
Dahlia diseases can be obtained:
- when buying low-quality, infected planting material;
- transmitted from a diseased plant by insects, both pests and pollinators;
- from garden tools, when cutting or digging up diseased plants;
- from the soil;
- with improper agricultural practices;
- improper storage of tubers;
- due to weather conditions, for example, prolonged rains or sudden temperature changes.
Dahlia diseases are divided into viral, bacterial and fungal.
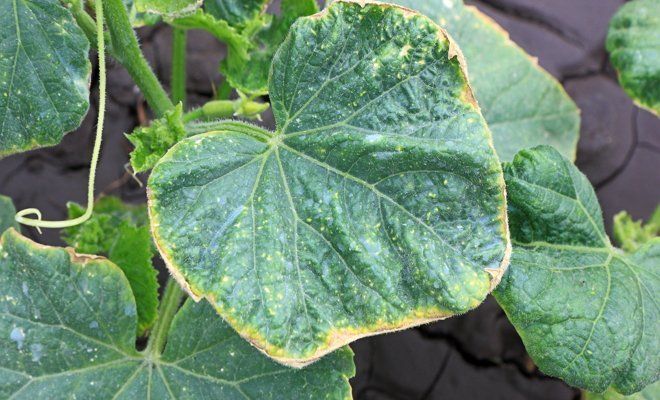
Viral diseases: viral mosaic, overgrowth virus, ring spot. The disease is expressed in brownness, yellowing or discoloration of the leaf plate, yellowing of the veins, and wrinkling of the leaves. The disease slows down the growth of the plant, it does not grow to the required height. Dahlias affected by various viruses do not bloom or develop, with low growth, unnaturally large flowers.
Viral infections in flowers are not treatable, and the plant must be removed along with the root tuber. Plant residues and plant parts cannot be used in compost pits, they must be burned because the virus is easily transmitted and infects other plants in the garden.
Fungal infections are manifested by the appearance of brown or white rot, the stems of flowers become thinner, and may break. On fallen leaves, on the stem or in its break, you can see mycelium threads, cotton-like bloom. Fusarium and verticillium wilting affects dahlia tubers. Tubers rot, become covered with white-pink bloom with fusarium, and brown with verticillosis. The fungus remains in the tuber during winter storage, exposing it to drying out. In spring, when planting, tubers are recommended to be dipped in disinfectant solutions, dried unhealthy tubers will float to the surface in this case.
When determining the condition of a plant, it is important to exclude reasons associated with the plant's requirement for growing conditions, and not with the fact that dahlia has leaf diseases.
Reasons why dahlias do not bloom:
- depleted land, dahlias were not fed, and there are not enough nutrients for flowering;
- applying a large amount of nitrogen fertilizers, forming a strong green mass, without flowering;
- recessed landing;
- late planting of non-germinated tubers;
- insufficient watering;
- lack of mulching and hilling;
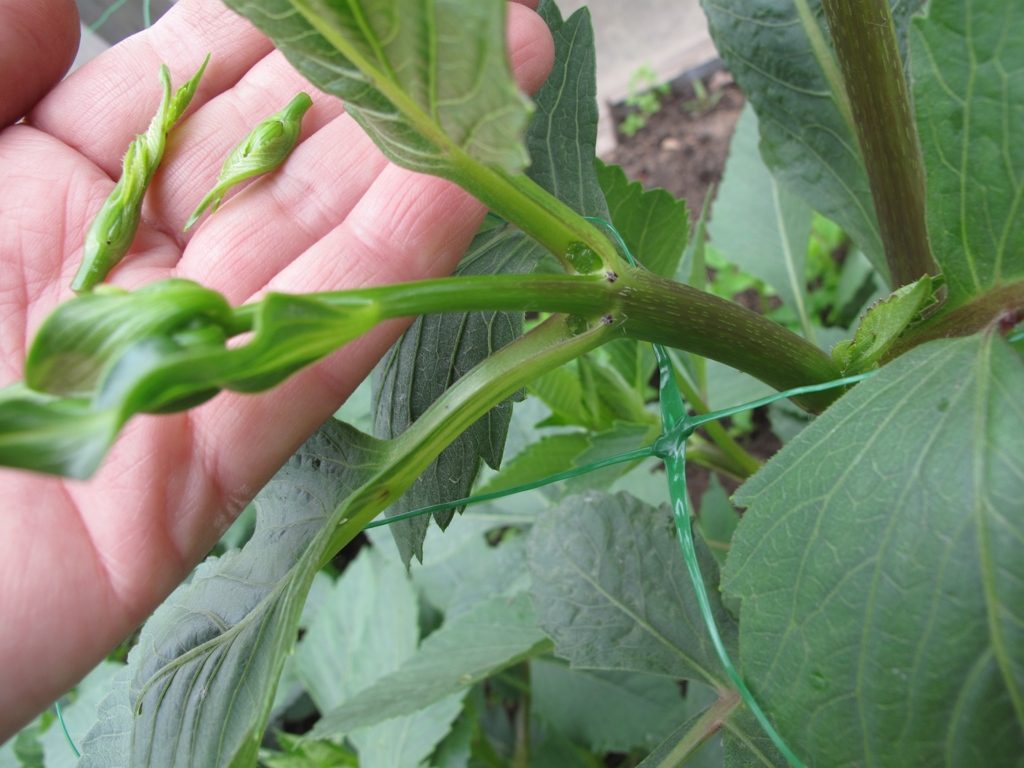
- pinching of the growth point, pinching and shaping of the bush were not carried out, except for low-growing varieties;
- aging of the tuber;
- landing in an insufficiently sunny place;
- lack of crop rotation.
If the dahlia is short, this may be due to the peculiarity of the variety.
The leaves of flowers can curl due to the attack of aphids or the appearance of a spider mite. The leaves also curl up due to the defeat of the flower by causative agents of fungal diseases.
When infected with bacterial cancer, tubers are affected, which is found during the autumn digging of dahlias.On the roots, at the base of the stems, white growths are formed, which later darken and rot. Such a plant should be destroyed. Bacteria remain in the soil for 5 years, so planting is not repeated in the same place during this time.
Overgrowth cancer manifests itself in the formation of a large number of thin roots on the root collar, which prevent the tubers from developing. Deformed tubers do not respond to treatment.
Dahlia disease treatment
There are no cures for viral, bacterial and most fungal diseases. Infected plants should be discarded and destroyed. It is important not to feel sorry for the infected specimen and remove it from the flower garden in a timely manner so that the disease is not transmitted to other plants.
During winter storage of tubers, condensation on the planting material and excessive humidity in the room should not be allowed.
Thickened plantings, without the possibility of good ventilation of plants, especially after rains, lead to the appearance of major fungal diseases and the reasons why dahlias begin to grow poorly.
Flowers or branches that begin to wither become sources of infection, so be sure to cut them off.
You can try to get rid of fungal diseases such as leaf spot, gray rot and powdery mildew by removing the affected areas of the plant and applying fungicides, Bordeaux liquid or copper-soap solution.
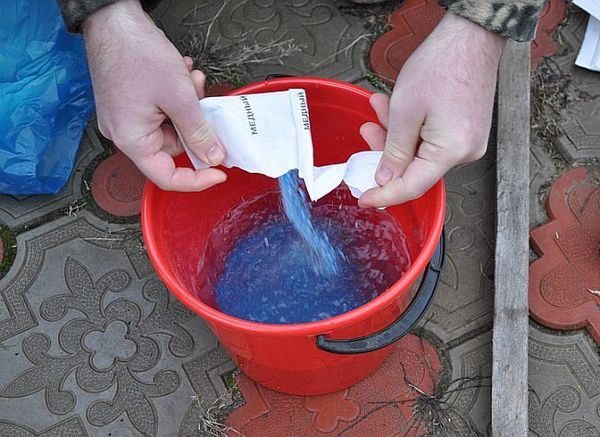
For a copper-soap solution, 100 g of laundry soap is dissolved in 9 liters of hot water. 10 g of copper sulfate is diluted in 1 liter of water. Then, carefully, constantly stirring, pour a solution of copper sulfate into soapy water. The resulting hot mixture, blue in color, is used immediately, without waiting for it to cool. When using hard water, 10 g of soda ash can be added to the solution.
If the spread of the fungus continues and after therapeutic spraying, the plant should be destroyed, along with the root tuber. Disinfect the well.
Pest control
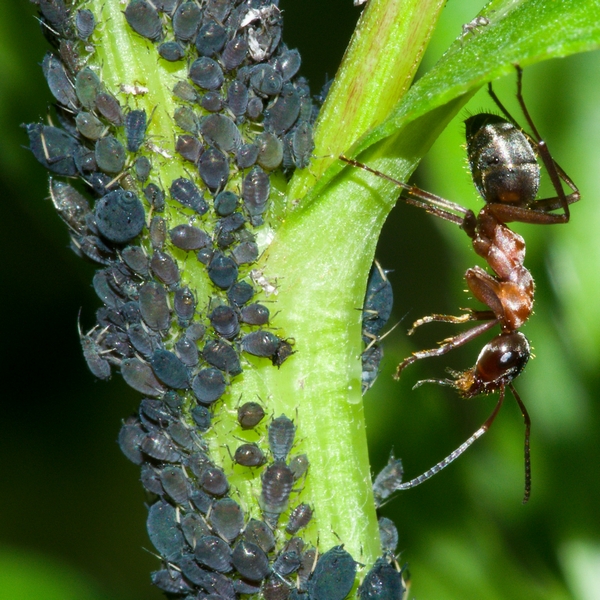
Aphids are a pest that feeds on dahlia sap; they are also the cause of various plant diseases. Aphid infestation is detected visually when black insects are visible on the dahlia. When aphids are affected, yellowing and curling of the leaves will become noticeable, as well as the formation of "honeydew" - sticky mucus.
Aphids on dahlias how to fight: if found in small quantities, insects are removed along with the green part of the plant. The sticky mucus secreted by aphids feeds on ants, which move the aphids through the plants. Therefore, when aphids appear, you should pay attention to whether ants have appeared nearby, and take control measures against them.
Insecticides, a solution of green or laundry soap - what can be used to treat aphids on dahlias with large areas of damage. Also, a one percent solution of karbofos and other insecticides for flowers are used for spraying.
To improve the garden and fight aphids, beneficial insects, for example, ladybirds, are attracted or brought to the site.
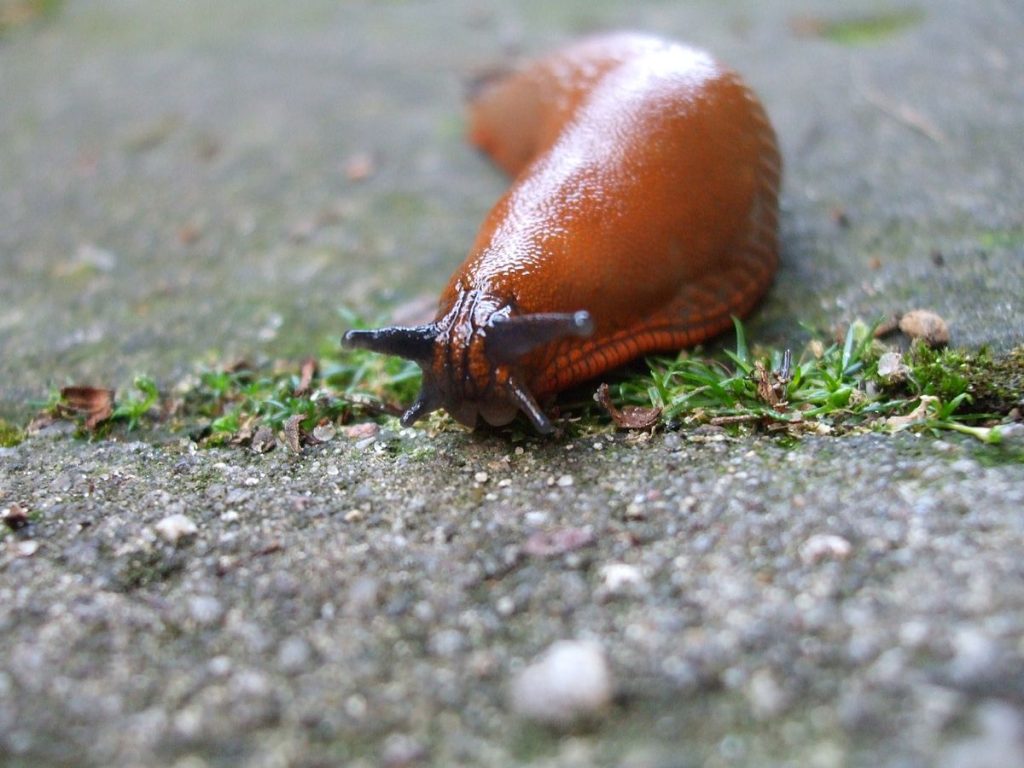
Slugs are plant-damaging gastropods that are often invisible because they are active at night. Slugs also appear after precipitation has fallen and high humidity persists; they like to be in shaded areas. Therefore, it is important to choose the right growing place and not thicken the planting of dahlias. Slugs can destroy leaves completely, first gnawing grooves and holes in the leaf plates.
Insects are collected by hand from plants or caught with bait.As bait-traps, soaked boards, cloth or cut raw potatoes spread out in the aisles of dahlias are used. Slugs are irritated by scattered dry wood ash, red pepper, but such methods lose their effectiveness after watering or rain.
Granular chemicals, which contain the name of the substance - metaldehyde or potassium salt, effectively destroy slugs. The preparations are scattered over the soil between flowers.
Preventive measures
With diseases of dahlias and the fight against them, preventive measures, proper planting and flower care are effective. Agrotechnical methods of growing:
- Landing site. Dahlias are planted in a warm, sunny place, without cold air blowing. To eliminate drafts, planting flowers near any fences or buildings would be a good way. In the shade, dahlias will grow weak, they will be affected by slugs. From the wind, tall species of flowers are able to break, they build supports.
- Watering. Dahlia is a moisture-loving plant. Improper watering can lead to the reason why the dahlia leaf turns yellow. Flowers require abundant, but not frequent watering, without stagnation of water in the soil, in order to avoid rotting of root tubers, including during storage.
- Soil and dressing. A dahlia growing on soil that is not suitable for acidity will wither and turn yellow. The plant is responsive to fertilizing and weak soil acidity. Flowers on impoverished lands are fed up to four times during the growing season. Nitrogen-containing fertilizers are used to a lesser extent, because they are able to inhibit the development of buds, and lead to the spread of fungal spores. With a lack of nutrients in the soil, the plant is exposed to various diseases due to the fact that its immunity decreases, the leaves acquire an unnatural appearance - chlorous or purple, the processes of photosynthesis are disrupted. It is most favorable to use complex mineral fertilizers. When planting in a planting hole, it is necessary to fill up fertile soil, humus. Top dressing is stopped at the end of summer in order to form a good root tuber.
- Healthy tubers. Dahlia's diseases that appear during the growing season remain in its root tubers during the storage period. Affected tubers planted in the new season will not develop into strong bushes with healthy buds. Such plants will have to be removed from the flower bed. Harvesting healthy tubers should be done in sunny, dry weather. Tubers are inspected before harvesting, disinfected with fungicides, dried in a well-ventilated shaded place.
- Landing. Each tuber is planted separately, observing the distance, depending on the variety of dahlias, from 50 to 100 cm. For a favorable growth, a dahlia requires a large feeding area and a sufficient earthen lump. Thickened plantings contribute to the development of pathogens of fungal diseases. For planting in an annual way, it is recommended to choose low varieties. In one season, a tall dahlia will not have time to fully develop, raising questions about why the dahlia does not grow.
- Bush formation. The lack of the formation of a tall species of dahlias can slow down the growth of buds and weaken the development of roots. In this case, the main nutrition and strength of the plant is spent on the formation of green mass. Therefore, dahlias are formed, leaving only a few central stems, the rest of the stepsons are removed. For the formation of large caps of flowers in the future, it is recommended to cut the first blooming flower.
- Tool. Flowers can become infected with viral diseases through a garden tool when cutting, propagating or digging up plants. Therefore, to work with healthy dahlias, pruners, scissors and shovels should be disinfected with alcohol or burned with fire each time.
If signs of disease or pest damage are found on flowers, the condition of the dahlia should be carefully evaluated, excluding its vegetative features and requirements for growing conditions. The land where the infected dahlias grew is deeply dug up, disinfected with lime, calcium salts, solutions of fungicides or copper sulfate. In the future, crop rotation is observed and dahlias are not planted in their original place.
Pests and diseases of dahlias can often appear in different numbers, depending on the weather conditions of the current year, even among experienced gardeners. But the general improvement of the garden and the correct planting of beautiful dahlias will help reduce the risks of damage to the flower garden.